Shaohui Peng
Segmental Advantage Estimation: Enhancing PPO for Long-Context LLM Training
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Training Large Language Models (LLMs) for reasoning tasks is increasingly driven by Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), where Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) provides a principled framework for stable policy updates. However, the practical application of PPO is hindered by unreliable advantage estimation in the sparse-reward RLVR regime. This issue arises because the sparse rewards in RLVR lead to inaccurate intermediate value predictions, which in turn introduce significant bias when aggregated at every token by Generalized Advantage Estimation (GAE). To address this, we introduce Segmental Advantage Estimation (SAE), which mitigates the bias that GAE can incur in RLVR. Our key insight is that aggregating $n$-step advantages at every token(as in GAE) is unnecessary and often introduces excessive bias, since individual tokens carry minimal information. Instead, SAE first partitions the generated sequence into coherent sub-segments using low-probability tokens as heuristic boundaries. It then selectively computes variance-reduced advantage estimates only from these information-rich segment transitions, effectively filtering out noise from intermediate tokens. Our experiments demonstrate that SAE achieves superior performance, with marked improvements in final scores, training stability, and sample efficiency. These gains are shown to be consistent across multiple model sizes, and a correlation analysis confirms that our proposed advantage estimator achieves a higher correlation with an approximate ground-truth advantage, justifying its superior performance.
Run, Ruminate, and Regulate: A Dual-process Thinking System for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) requires an agent to dynamically explore complex 3D environments following human instructions. Recent research underscores the potential of harnessing large language models (LLMs) for VLN, given their commonsense knowledge and general reasoning capabilities. Despite their strengths, a substantial gap in task completion performance persists between LLM-based approaches and domain experts, as LLMs inherently struggle to comprehend real-world spatial correlations precisely. Additionally, introducing LLMs is accompanied with substantial computational cost and inference latency. To address these issues, we propose a novel dual-process thinking framework dubbed R3, integrating LLMs' generalization capabilities with VLN-specific expertise in a zero-shot manner. The framework comprises three core modules: Runner, Ruminator, and Regulator. The Runner is a lightweight transformer-based expert model that ensures efficient and accurate navigation under regular circumstances. The Ruminator employs a powerful multimodal LLM as the backbone and adopts chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting to elicit structured reasoning. The Regulator monitors the navigation progress and controls the appropriate thinking mode according to three criteria, integrating Runner and Ruminator harmoniously. Experimental results illustrate that R3 significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art methods, exceeding 3.28% and 3.30% in SPL and RGSPL respectively on the REVERIE benchmark. This pronounced enhancement highlights the effectiveness of our method in handling challenging VLN tasks.
QiMeng-Attention: SOTA Attention Operator is generated by SOTA Attention Algorithm
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:The attention operator remains a critical performance bottleneck in large language models (LLMs), particularly for long-context scenarios. While FlashAttention is the most widely used and effective GPU-aware acceleration algorithm, it must require time-consuming and hardware-specific manual implementation, limiting adaptability across GPU architectures. Existing LLMs have shown a lot of promise in code generation tasks, but struggle to generate high-performance attention code. The key challenge is it cannot comprehend the complex data flow and computation process of the attention operator and utilize low-level primitive to exploit GPU performance. To address the above challenge, we propose an LLM-friendly Thinking Language (LLM-TL) to help LLMs decouple the generation of high-level optimization logic and low-level implementation on GPU, and enhance LLMs' understanding of attention operator. Along with a 2-stage reasoning workflow, TL-Code generation and translation, the LLMs can automatically generate FlashAttention implementation on diverse GPUs, establishing a self-optimizing paradigm for generating high-performance attention operators in attention-centric algorithms. Verified on A100, RTX8000, and T4 GPUs, the performance of our methods significantly outshines that of vanilla LLMs, achieving a speed-up of up to 35.16x. Besides, our method not only surpasses human-optimized libraries (cuDNN and official library) in most scenarios but also extends support to unsupported hardware and data types, reducing development time from months to minutes compared with human experts.
QiMeng: Fully Automated Hardware and Software Design for Processor Chip
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:Processor chip design technology serves as a key frontier driving breakthroughs in computer science and related fields. With the rapid advancement of information technology, conventional design paradigms face three major challenges: the physical constraints of fabrication technologies, the escalating demands for design resources, and the increasing diversity of ecosystems. Automated processor chip design has emerged as a transformative solution to address these challenges. While recent breakthroughs in Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly Large Language Models (LLMs) techniques, have opened new possibilities for fully automated processor chip design, substantial challenges remain in establishing domain-specific LLMs for processor chip design. In this paper, we propose QiMeng, a novel system for fully automated hardware and software design of processor chips. QiMeng comprises three hierarchical layers. In the bottom-layer, we construct a domain-specific Large Processor Chip Model (LPCM) that introduces novel designs in architecture, training, and inference, to address key challenges such as knowledge representation gap, data scarcity, correctness assurance, and enormous solution space. In the middle-layer, leveraging the LPCM's knowledge representation and inference capabilities, we develop the Hardware Design Agent and the Software Design Agent to automate the design of hardware and software for processor chips. Currently, several components of QiMeng have been completed and successfully applied in various top-layer applications, demonstrating significant advantages and providing a feasible solution for efficient, fully automated hardware/software design of processor chips. Future research will focus on integrating all components and performing iterative top-down and bottom-up design processes to establish a comprehensive QiMeng system.
QiMeng-TensorOp: Automatically Generating High-Performance Tensor Operators with Hardware Primitives
May 08, 2025Abstract:Computation-intensive tensor operators constitute over 90\% of the computations in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Deep Neural Networks.Automatically and efficiently generating high-performance tensor operators with hardware primitives is crucial for diverse and ever-evolving hardware architectures like RISC-V, ARM, and GPUs, as manually optimized implementation takes at least months and lacks portability.LLMs excel at generating high-level language codes, but they struggle to fully comprehend hardware characteristics and produce high-performance tensor operators. We introduce a tensor-operator auto-generation framework with a one-line user prompt (QiMeng-TensorOp), which enables LLMs to automatically exploit hardware characteristics to generate tensor operators with hardware primitives, and tune parameters for optimal performance across diverse hardware. Experimental results on various hardware platforms, SOTA LLMs, and typical tensor operators demonstrate that QiMeng-TensorOp effectively unleashes the computing capability of various hardware platforms, and automatically generates tensor operators of superior performance. Compared with vanilla LLMs, QiMeng-TensorOp achieves up to $1291 \times$ performance improvement. Even compared with human experts, QiMeng-TensorOp could reach $251 \%$ of OpenBLAS on RISC-V CPUs, and $124 \%$ of cuBLAS on NVIDIA GPUs. Additionally, QiMeng-TensorOp also significantly reduces development costs by $200 \times$ compared with human experts.
World-Consistent Data Generation for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) is a challenging task that requires an agent to navigate through photorealistic environments following natural-language instructions. One main obstacle existing in VLN is data scarcity, leading to poor generalization performance over unseen environments. Tough data argumentation is a promising way for scaling up the dataset, how to generate VLN data both diverse and world-consistent remains problematic. To cope with this issue, we propose the world-consistent data generation (WCGEN), an efficacious data-augmentation framework satisfying both diversity and world-consistency, targeting at enhancing the generalizations of agents to novel environments. Roughly, our framework consists of two stages, the trajectory stage which leverages a point-cloud based technique to ensure spatial coherency among viewpoints, and the viewpoint stage which adopts a novel angle synthesis method to guarantee spatial and wraparound consistency within the entire observation. By accurately predicting viewpoint changes with 3D knowledge, our approach maintains the world-consistency during the generation procedure. Experiments on a wide range of datasets verify the effectiveness of our method, demonstrating that our data augmentation strategy enables agents to achieve new state-of-the-art results on all navigation tasks, and is capable of enhancing the VLN agents' generalization ability to unseen environments.
Ex3: Automatic Novel Writing by Extracting, Excelsior and Expanding
Aug 16, 2024



Abstract:Generating long-term texts such as novels using artificial intelligence has always been a challenge. A common approach is to use large language models (LLMs) to construct a hierarchical framework that first plans and then writes. Despite the fact that the generated novels reach a sufficient length, they exhibit poor logical coherence and appeal in their plots and deficiencies in character and event depiction, ultimately compromising the overall narrative quality. In this paper, we propose a method named Extracting Excelsior and Expanding. Ex3 initially extracts structure information from raw novel data. By combining this structure information with the novel data, an instruction-following dataset is meticulously crafted. This dataset is then utilized to fine-tune the LLM, aiming for excelsior generation performance. In the final stage, a tree-like expansion method is deployed to facilitate the generation of arbitrarily long novels. Evaluation against previous methods showcases Ex3's ability to produce higher-quality long-form novels.
Prompt-based Visual Alignment for Zero-shot Policy Transfer
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Overfitting in RL has become one of the main obstacles to applications in reinforcement learning(RL). Existing methods do not provide explicit semantic constrain for the feature extractor, hindering the agent from learning a unified cross-domain representation and resulting in performance degradation on unseen domains. Besides, abundant data from multiple domains are needed. To address these issues, in this work, we propose prompt-based visual alignment (PVA), a robust framework to mitigate the detrimental domain bias in the image for zero-shot policy transfer. Inspired that Visual-Language Model (VLM) can serve as a bridge to connect both text space and image space, we leverage the semantic information contained in a text sequence as an explicit constraint to train a visual aligner. Thus, the visual aligner can map images from multiple domains to a unified domain and achieve good generalization performance. To better depict semantic information, prompt tuning is applied to learn a sequence of learnable tokens. With explicit constraints of semantic information, PVA can learn unified cross-domain representation under limited access to cross-domain data and achieves great zero-shot generalization ability in unseen domains. We verify PVA on a vision-based autonomous driving task with CARLA simulator. Experiments show that the agent generalizes well on unseen domains under limited access to multi-domain data.
Luban: Building Open-Ended Creative Agents via Autonomous Embodied Verification
May 24, 2024Abstract:Building open agents has always been the ultimate goal in AI research, and creative agents are the more enticing. Existing LLM agents excel at long-horizon tasks with well-defined goals (e.g., `mine diamonds' in Minecraft). However, they encounter difficulties on creative tasks with open goals and abstract criteria due to the inability to bridge the gap between them, thus lacking feedback for self-improvement in solving the task. In this work, we introduce autonomous embodied verification techniques for agents to fill the gap, laying the groundwork for creative tasks. Specifically, we propose the Luban agent target creative building tasks in Minecraft, which equips with two-level autonomous embodied verification inspired by human design practices: (1) visual verification of 3D structural speculates, which comes from agent synthesized CAD modeling programs; (2) pragmatic verification of the creation by generating and verifying environment-relevant functionality programs based on the abstract criteria. Extensive multi-dimensional human studies and Elo ratings show that the Luban completes diverse creative building tasks in our proposed benchmark and outperforms other baselines ($33\%$ to $100\%$) in both visualization and pragmatism. Additional demos on the real-world robotic arm show the creation potential of the Luban in the physical world.
Assessing and Understanding Creativity in Large Language Models
Jan 23, 2024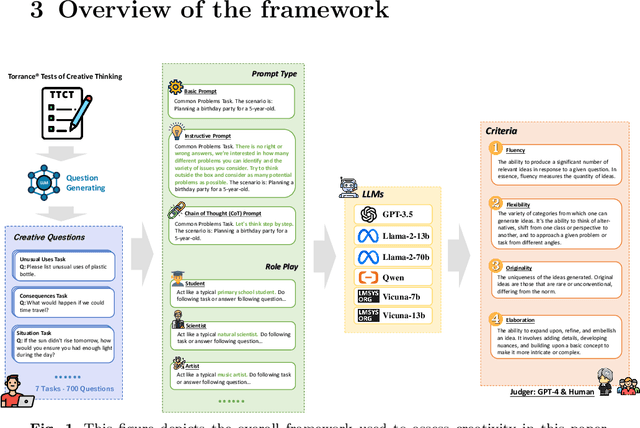
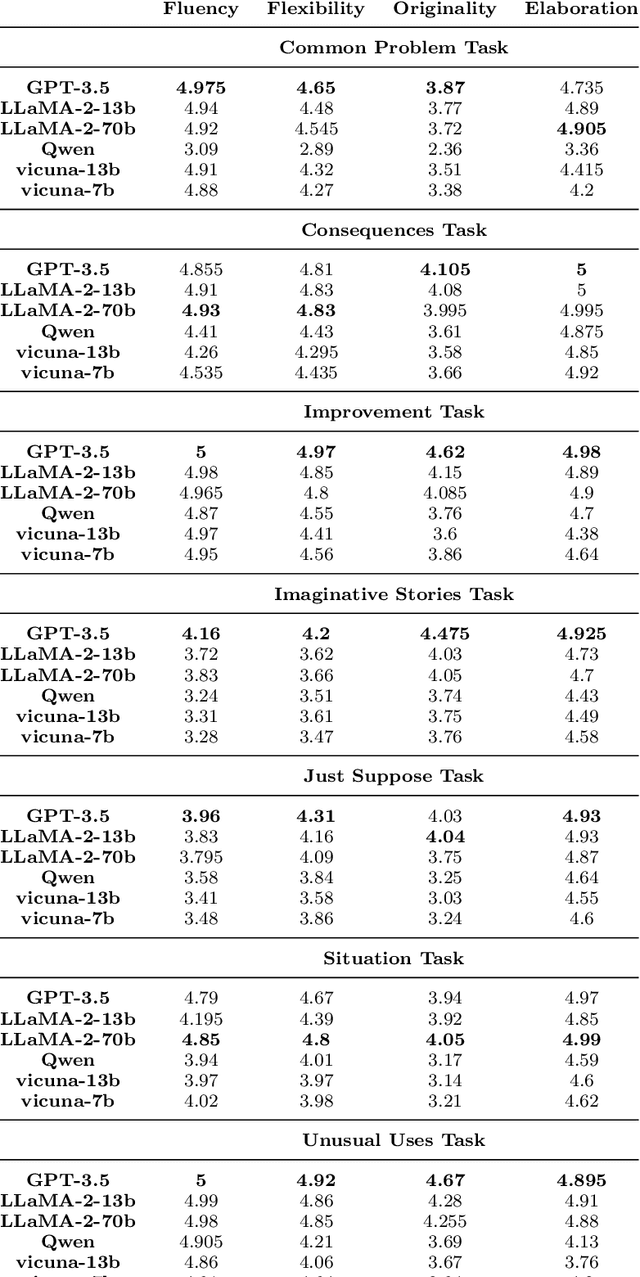
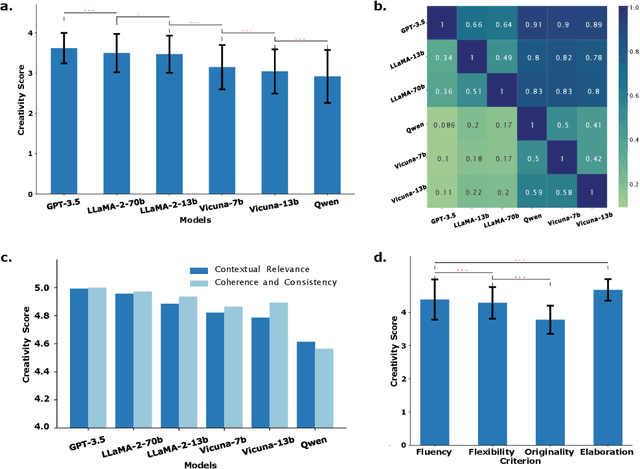
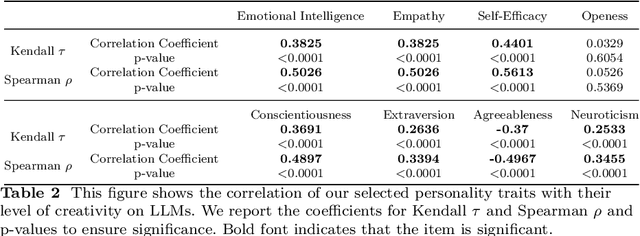
Abstract:In the field of natural language processing, the rapid development of large language model (LLM) has attracted more and more attention. LLMs have shown a high level of creativity in various tasks, but the methods for assessing such creativity are inadequate. The assessment of LLM creativity needs to consider differences from humans, requiring multi-dimensional measurement while balancing accuracy and efficiency. This paper aims to establish an efficient framework for assessing the level of creativity in LLMs. By adapting the modified Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking, the research evaluates the creative performance of various LLMs across 7 tasks, emphasizing 4 criteria including Fluency, Flexibility, Originality, and Elaboration. In this context, we develop a comprehensive dataset of 700 questions for testing and an LLM-based evaluation method. In addition, this study presents a novel analysis of LLMs' responses to diverse prompts and role-play situations. We found that the creativity of LLMs primarily falls short in originality, while excelling in elaboration. Besides, the use of prompts and the role-play settings of the model significantly influence creativity. Additionally, the experimental results also indicate that collaboration among multiple LLMs can enhance originality. Notably, our findings reveal a consensus between human evaluations and LLMs regarding the personality traits that influence creativity. The findings underscore the significant impact of LLM design on creativity and bridges artificial intelligence and human creativity, offering insights into LLMs' creativity and potential applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge