Yunkai Gao
The RoboSense Challenge: Sense Anything, Navigate Anywhere, Adapt Across Platforms
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Autonomous systems are increasingly deployed in open and dynamic environments -- from city streets to aerial and indoor spaces -- where perception models must remain reliable under sensor noise, environmental variation, and platform shifts. However, even state-of-the-art methods often degrade under unseen conditions, highlighting the need for robust and generalizable robot sensing. The RoboSense 2025 Challenge is designed to advance robustness and adaptability in robot perception across diverse sensing scenarios. It unifies five complementary research tracks spanning language-grounded decision making, socially compliant navigation, sensor configuration generalization, cross-view and cross-modal correspondence, and cross-platform 3D perception. Together, these tasks form a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating real-world sensing reliability under domain shifts, sensor failures, and platform discrepancies. RoboSense 2025 provides standardized datasets, baseline models, and unified evaluation protocols, enabling large-scale and reproducible comparison of robust perception methods. The challenge attracted 143 teams from 85 institutions across 16 countries, reflecting broad community engagement. By consolidating insights from 23 winning solutions, this report highlights emerging methodological trends, shared design principles, and open challenges across all tracks, marking a step toward building robots that can sense reliably, act robustly, and adapt across platforms in real-world environments.
Governance-Aware Hybrid Fine-Tuning for Multilingual Large Language Models
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:We present a governance-aware hybrid fine-tuning framework for multilingual, low-resource adaptation of large language models. The core algorithm combines gradient-aligned low-rank updates with structured orthogonal transformations through layer-wise mixing and introduces unitary constraints in selected sub-layers to stabilize deep optimization. In tandem with lightweight, label-free data governance steps, including language identification, near-duplicate removal, and quality filtering, the framework targets accuracy, calibration, and cross-language parity under tight compute budgets. Across XNLI and FLORES, the hybrid approach delivers consistent gains over strong PEFT baselines while maintaining directional balance and improving probability calibration, as shown in Tables II and III. It is more resilient to lightweight orthographic variants, as shown in Table IV, and benefits additively from simple governance steps, as shown in Table V. Training footprint measurements indicate modest overhead and a favorable cost-quality frontier, as shown in Table VI and Figure 2. Together, these results show that hybrid and unitary PEFT provide a stable and accessible path to resource-efficient multilingual adaptation when paired with practical data governance.
* 11 pages, 4 figures, 6 tables. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2507.18076
Policy Constraint by Only Support Constraint for Offline Reinforcement Learning
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning (RL) aims to optimize a policy by using pre-collected datasets, to maximize cumulative rewards. However, offline reinforcement learning suffers challenges due to the distributional shift between the learned and behavior policies, leading to errors when computing Q-values for out-of-distribution (OOD) actions. To mitigate this issue, policy constraint methods aim to constrain the learned policy's distribution with the distribution of the behavior policy or confine action selection within the support of the behavior policy. However, current policy constraint methods tend to exhibit excessive conservatism, hindering the policy from further surpassing the behavior policy's performance. In this work, we present Only Support Constraint (OSC) which is derived from maximizing the total probability of learned policy in the support of behavior policy, to address the conservatism of policy constraint. OSC presents a regularization term that only restricts policies to the support without imposing extra constraints on actions within the support. Additionally, to fully harness the performance of the new policy constraints, OSC utilizes a diffusion model to effectively characterize the support of behavior policies. Experimental evaluations across a variety of offline RL benchmarks demonstrate that OSC significantly enhances performance, alleviating the challenges associated with distributional shifts and mitigating conservatism of policy constraints. Code is available at https://github.com/MoreanP/OSC.
Prompt-based Visual Alignment for Zero-shot Policy Transfer
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Overfitting in RL has become one of the main obstacles to applications in reinforcement learning(RL). Existing methods do not provide explicit semantic constrain for the feature extractor, hindering the agent from learning a unified cross-domain representation and resulting in performance degradation on unseen domains. Besides, abundant data from multiple domains are needed. To address these issues, in this work, we propose prompt-based visual alignment (PVA), a robust framework to mitigate the detrimental domain bias in the image for zero-shot policy transfer. Inspired that Visual-Language Model (VLM) can serve as a bridge to connect both text space and image space, we leverage the semantic information contained in a text sequence as an explicit constraint to train a visual aligner. Thus, the visual aligner can map images from multiple domains to a unified domain and achieve good generalization performance. To better depict semantic information, prompt tuning is applied to learn a sequence of learnable tokens. With explicit constraints of semantic information, PVA can learn unified cross-domain representation under limited access to cross-domain data and achieves great zero-shot generalization ability in unseen domains. We verify PVA on a vision-based autonomous driving task with CARLA simulator. Experiments show that the agent generalizes well on unseen domains under limited access to multi-domain data.
Context Shift Reduction for Offline Meta-Reinforcement Learning
Nov 07, 2023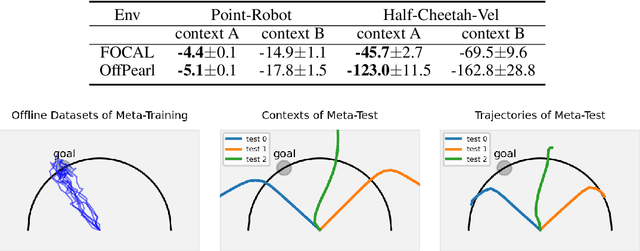
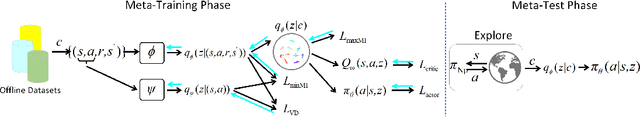
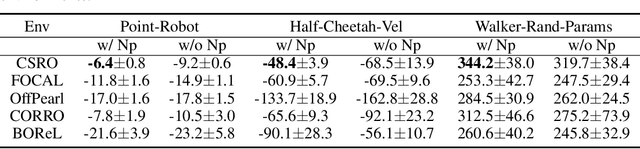
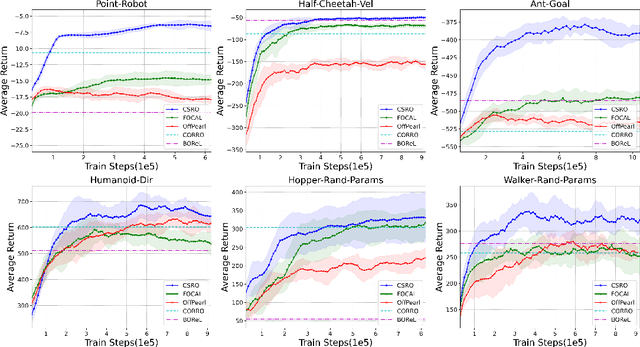
Abstract:Offline meta-reinforcement learning (OMRL) utilizes pre-collected offline datasets to enhance the agent's generalization ability on unseen tasks. However, the context shift problem arises due to the distribution discrepancy between the contexts used for training (from the behavior policy) and testing (from the exploration policy). The context shift problem leads to incorrect task inference and further deteriorates the generalization ability of the meta-policy. Existing OMRL methods either overlook this problem or attempt to mitigate it with additional information. In this paper, we propose a novel approach called Context Shift Reduction for OMRL (CSRO) to address the context shift problem with only offline datasets. The key insight of CSRO is to minimize the influence of policy in context during both the meta-training and meta-test phases. During meta-training, we design a max-min mutual information representation learning mechanism to diminish the impact of the behavior policy on task representation. In the meta-test phase, we introduce the non-prior context collection strategy to reduce the effect of the exploration policy. Experimental results demonstrate that CSRO significantly reduces the context shift and improves the generalization ability, surpassing previous methods across various challenging domains.
Contrastive Modules with Temporal Attention for Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning
Nov 02, 2023
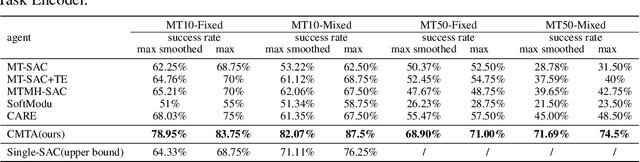
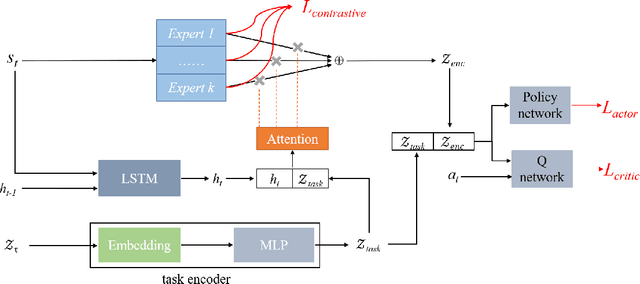
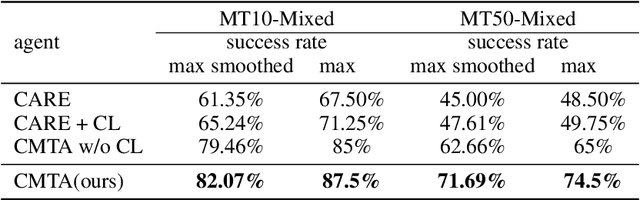
Abstract:In the field of multi-task reinforcement learning, the modular principle, which involves specializing functionalities into different modules and combining them appropriately, has been widely adopted as a promising approach to prevent the negative transfer problem that performance degradation due to conflicts between tasks. However, most of the existing multi-task RL methods only combine shared modules at the task level, ignoring that there may be conflicts within the task. In addition, these methods do not take into account that without constraints, some modules may learn similar functions, resulting in restricting the model's expressiveness and generalization capability of modular methods. In this paper, we propose the Contrastive Modules with Temporal Attention(CMTA) method to address these limitations. CMTA constrains the modules to be different from each other by contrastive learning and combining shared modules at a finer granularity than the task level with temporal attention, alleviating the negative transfer within the task and improving the generalization ability and the performance for multi-task RL. We conducted the experiment on Meta-World, a multi-task RL benchmark containing various robotics manipulation tasks. Experimental results show that CMTA outperforms learning each task individually for the first time and achieves substantial performance improvements over the baselines.
Online Prototype Alignment for Few-shot Policy Transfer
Jun 12, 2023Abstract:Domain adaptation in reinforcement learning (RL) mainly deals with the changes of observation when transferring the policy to a new environment. Many traditional approaches of domain adaptation in RL manage to learn a mapping function between the source and target domain in explicit or implicit ways. However, they typically require access to abundant data from the target domain. Besides, they often rely on visual clues to learn the mapping function and may fail when the source domain looks quite different from the target domain. To address these problems, we propose a novel framework Online Prototype Alignment (OPA) to learn the mapping function based on the functional similarity of elements and is able to achieve the few-shot policy transfer within only several episodes. The key insight of OPA is to introduce an exploration mechanism that can interact with the unseen elements of the target domain in an efficient and purposeful manner, and then connect them with the seen elements in the source domain according to their functionalities (instead of visual clues). Experimental results show that when the target domain looks visually different from the source domain, OPA can achieve better transfer performance even with much fewer samples from the target domain, outperforming prior methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge