Wenhan Zhu
Multimodal Latent Diffusion Model for Complex Sewing Pattern Generation
Dec 19, 2024

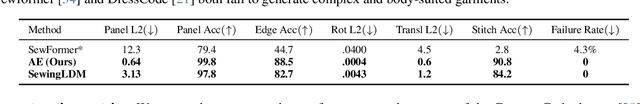

Abstract:Generating sewing patterns in garment design is receiving increasing attention due to its CG-friendly and flexible-editing nature. Previous sewing pattern generation methods have been able to produce exquisite clothing, but struggle to design complex garments with detailed control. To address these issues, we propose SewingLDM, a multi-modal generative model that generates sewing patterns controlled by text prompts, body shapes, and garment sketches. Initially, we extend the original vector of sewing patterns into a more comprehensive representation to cover more intricate details and then compress them into a compact latent space. To learn the sewing pattern distribution in the latent space, we design a two-step training strategy to inject the multi-modal conditions, \ie, body shapes, text prompts, and garment sketches, into a diffusion model, ensuring the generated garments are body-suited and detail-controlled. Comprehensive qualitative and quantitative experiments show the effectiveness of our proposed method, significantly surpassing previous approaches in terms of complex garment design and various body adaptability. Our project page: https://shengqiliu1.github.io/SewingLDM.
Monocular Identity-Conditioned Facial Reflectance Reconstruction
Mar 30, 2024Abstract:Recent 3D face reconstruction methods have made remarkable advancements, yet there remain huge challenges in monocular high-quality facial reflectance reconstruction. Existing methods rely on a large amount of light-stage captured data to learn facial reflectance models. However, the lack of subject diversity poses challenges in achieving good generalization and widespread applicability. In this paper, we learn the reflectance prior in image space rather than UV space and present a framework named ID2Reflectance. Our framework can directly estimate the reflectance maps of a single image while using limited reflectance data for training. Our key insight is that reflectance data shares facial structures with RGB faces, which enables obtaining expressive facial prior from inexpensive RGB data thus reducing the dependency on reflectance data. We first learn a high-quality prior for facial reflectance. Specifically, we pretrain multi-domain facial feature codebooks and design a codebook fusion method to align the reflectance and RGB domains. Then, we propose an identity-conditioned swapping module that injects facial identity from the target image into the pre-trained autoencoder to modify the identity of the source reflectance image. Finally, we stitch multi-view swapped reflectance images to obtain renderable assets. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method exhibits excellent generalization capability and achieves state-of-the-art facial reflectance reconstruction results for in-the-wild faces. Our project page is https://xingyuren.github.io/id2reflectance/.
ReGenNet: Towards Human Action-Reaction Synthesis
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:Humans constantly interact with their surrounding environments. Current human-centric generative models mainly focus on synthesizing humans plausibly interacting with static scenes and objects, while the dynamic human action-reaction synthesis for ubiquitous causal human-human interactions is less explored. Human-human interactions can be regarded as asymmetric with actors and reactors in atomic interaction periods. In this paper, we comprehensively analyze the asymmetric, dynamic, synchronous, and detailed nature of human-human interactions and propose the first multi-setting human action-reaction synthesis benchmark to generate human reactions conditioned on given human actions. To begin with, we propose to annotate the actor-reactor order of the interaction sequences for the NTU120, InterHuman, and Chi3D datasets. Based on them, a diffusion-based generative model with a Transformer decoder architecture called ReGenNet together with an explicit distance-based interaction loss is proposed to predict human reactions in an online manner, where the future states of actors are unavailable to reactors. Quantitative and qualitative results show that our method can generate instant and plausible human reactions compared to the baselines, and can generalize to unseen actor motions and viewpoint changes.
ITEM3D: Illumination-Aware Directional Texture Editing for 3D Models
Sep 27, 2023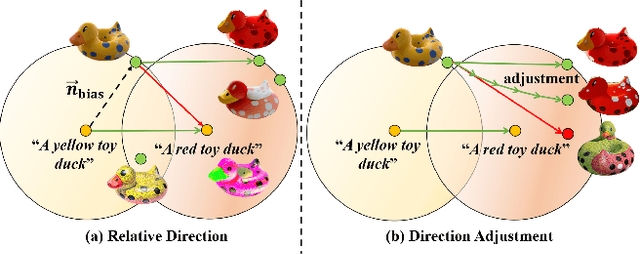
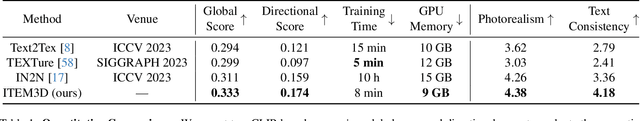
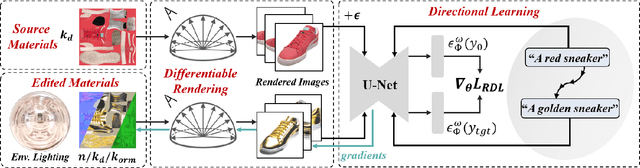

Abstract:Texture editing is a crucial task in 3D modeling that allows users to automatically manipulate the surface materials of 3D models. However, the inherent complexity of 3D models and the ambiguous text description lead to the challenge in this task. To address this challenge, we propose ITEM3D, an illumination-aware model for automatic 3D object editing according to the text prompts. Leveraging the diffusion models and the differentiable rendering, ITEM3D takes the rendered images as the bridge of text and 3D representation, and further optimizes the disentangled texture and environment map. Previous methods adopt the absolute editing direction namely score distillation sampling (SDS) as the optimization objective, which unfortunately results in the noisy appearance and text inconsistency. To solve the problem caused by the ambiguous text, we introduce a relative editing direction, an optimization objective defined by the noise difference between the source and target texts, to release the semantic ambiguity between the texts and images. Additionally, we gradually adjust the direction during optimization to further address the unexpected deviation in the texture domain. Qualitative and quantitative experiments show that our ITEM3D outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on various 3D objects. We also perform text-guided relighting to show explicit control over lighting.
HyperStyle3D: Text-Guided 3D Portrait Stylization via Hypernetworks
Apr 19, 2023Abstract:Portrait stylization is a long-standing task enabling extensive applications. Although 2D-based methods have made great progress in recent years, real-world applications such as metaverse and games often demand 3D content. On the other hand, the requirement of 3D data, which is costly to acquire, significantly impedes the development of 3D portrait stylization methods. In this paper, inspired by the success of 3D-aware GANs that bridge 2D and 3D domains with 3D fields as the intermediate representation for rendering 2D images, we propose a novel method, dubbed HyperStyle3D, based on 3D-aware GANs for 3D portrait stylization. At the core of our method is a hyper-network learned to manipulate the parameters of the generator in a single forward pass. It not only offers a strong capacity to handle multiple styles with a single model, but also enables flexible fine-grained stylization that affects only texture, shape, or local part of the portrait. While the use of 3D-aware GANs bypasses the requirement of 3D data, we further alleviate the necessity of style images with the CLIP model being the stylization guidance. We conduct an extensive set of experiments across the style, attribute, and shape, and meanwhile, measure the 3D consistency. These experiments demonstrate the superior capability of our HyperStyle3D model in rendering 3D-consistent images in diverse styles, deforming the face shape, and editing various attributes.
GANHead: Towards Generative Animatable Neural Head Avatars
Apr 08, 2023



Abstract:To bring digital avatars into people's lives, it is highly demanded to efficiently generate complete, realistic, and animatable head avatars. This task is challenging, and it is difficult for existing methods to satisfy all the requirements at once. To achieve these goals, we propose GANHead (Generative Animatable Neural Head Avatar), a novel generative head model that takes advantages of both the fine-grained control over the explicit expression parameters and the realistic rendering results of implicit representations. Specifically, GANHead represents coarse geometry, fine-gained details and texture via three networks in canonical space to obtain the ability to generate complete and realistic head avatars. To achieve flexible animation, we define the deformation filed by standard linear blend skinning (LBS), with the learned continuous pose and expression bases and LBS weights. This allows the avatars to be directly animated by FLAME parameters and generalize well to unseen poses and expressions. Compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, GANHead achieves superior performance on head avatar generation and raw scan fitting.
Head3D: Complete 3D Head Generation via Tri-plane Feature Distillation
Mar 28, 2023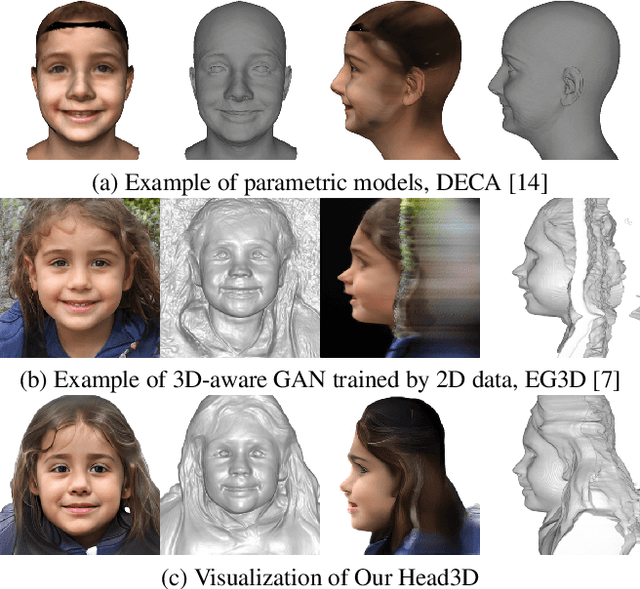
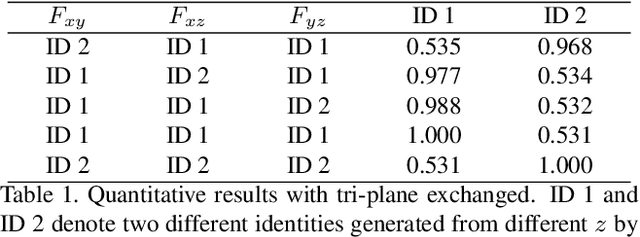
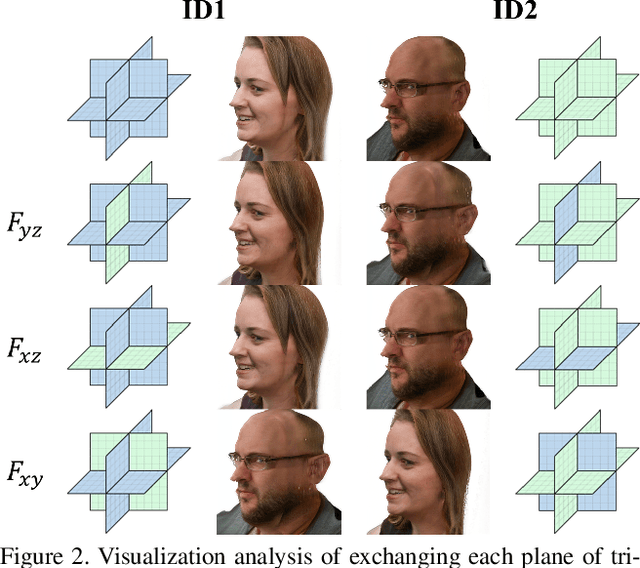
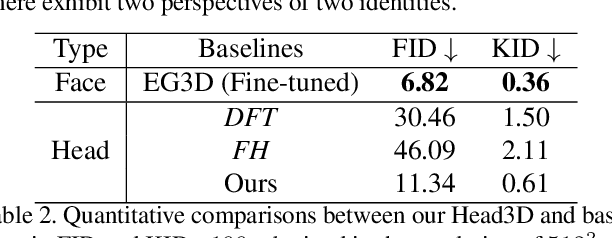
Abstract:Head generation with diverse identities is an important task in computer vision and computer graphics, widely used in multimedia applications. However, current full head generation methods require a large number of 3D scans or multi-view images to train the model, resulting in expensive data acquisition cost. To address this issue, we propose Head3D, a method to generate full 3D heads with limited multi-view images. Specifically, our approach first extracts facial priors represented by tri-planes learned in EG3D, a 3D-aware generative model, and then proposes feature distillation to deliver the 3D frontal faces into complete heads without compromising head integrity. To mitigate the domain gap between the face and head models, we present dual-discriminators to guide the frontal and back head generation, respectively. Our model achieves cost-efficient and diverse complete head generation with photo-realistic renderings and high-quality geometry representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed Head3D, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Deep Neural Network for Blind Visual Quality Assessment of 4K Content
Jun 09, 2022
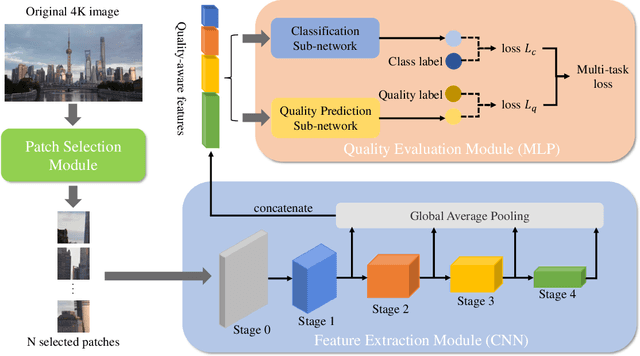

Abstract:The 4K content can deliver a more immersive visual experience to consumers due to the huge improvement of spatial resolution. However, existing blind image quality assessment (BIQA) methods are not suitable for the original and upscaled 4K contents due to the expanded resolution and specific distortions. In this paper, we propose a deep learning-based BIQA model for 4K content, which on one hand can recognize true and pseudo 4K content and on the other hand can evaluate their perceptual visual quality. Considering the characteristic that high spatial resolution can represent more abundant high-frequency information, we first propose a Grey-level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) based texture complexity measure to select three representative image patches from a 4K image, which can reduce the computational complexity and is proven to be very effective for the overall quality prediction through experiments. Then we extract different kinds of visual features from the intermediate layers of the convolutional neural network (CNN) and integrate them into the quality-aware feature representation. Finally, two multilayer perception (MLP) networks are utilized to map the quality-aware features into the class probability and the quality score for each patch respectively. The overall quality index is obtained through the average pooling of patch results. The proposed model is trained through the multi-task learning manner and we introduce an uncertainty principle to balance the losses of the classification and regression tasks. The experimental results show that the proposed model outperforms all compared BIQA metrics on four 4K content quality assessment databases.
Blind Surveillance Image Quality Assessment via Deep Neural Network Combined with the Visual Saliency
Jun 09, 2022



Abstract:The intelligent video surveillance system (IVSS) can automatically analyze the content of the surveillance image (SI) and reduce the burden of the manual labour. However, the SIs may suffer quality degradations in the procedure of acquisition, compression, and transmission, which makes IVSS hard to understand the content of SIs. In this paper, we first conduct an example experiment (i.e. the face detection task) to demonstrate that the quality of the SIs has a crucial impact on the performance of the IVSS, and then propose a saliency-based deep neural network for the blind quality assessment of the SIs, which helps IVSS to filter the low-quality SIs and improve the detection and recognition performance. Specifically, we first compute the saliency map of the SI to select the most salient local region since the salient regions usually contain rich semantic information for machine vision and thus have a great impact on the overall quality of the SIs. Next, the convolutional neural network (CNN) is adopted to extract quality-aware features for the whole image and local region, which are then mapped into the global and local quality scores through the fully connected (FC) network respectively. Finally, the overall quality score is computed as the weighted sum of the global and local quality scores. Experimental results on the SI quality database (SIQD) show that the proposed method outperforms all compared state-of-the-art BIQA methods.
A No-Reference Deep Learning Quality Assessment Method for Super-resolution Images Based on Frequency Maps
Jun 09, 2022



Abstract:To support the application scenarios where high-resolution (HR) images are urgently needed, various single image super-resolution (SISR) algorithms are developed. However, SISR is an ill-posed inverse problem, which may bring artifacts like texture shift, blur, etc. to the reconstructed images, thus it is necessary to evaluate the quality of super-resolution images (SRIs). Note that most existing image quality assessment (IQA) methods were developed for synthetically distorted images, which may not work for SRIs since their distortions are more diverse and complicated. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a no-reference deep-learning image quality assessment method based on frequency maps because the artifacts caused by SISR algorithms are quite sensitive to frequency information. Specifically, we first obtain the high-frequency map (HM) and low-frequency map (LM) of SRI by using Sobel operator and piecewise smooth image approximation. Then, a two-stream network is employed to extract the quality-aware features of both frequency maps. Finally, the features are regressed into a single quality value using fully connected layers. The experimental results show that our method outperforms all compared IQA models on the selected three super-resolution quality assessment (SRQA) databases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge