Yunhui Guo
Learnability-Driven Submodular Optimization for Active Roadside 3D Detection
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Roadside perception datasets are typically constructed via cooperative labeling between synchronized vehicle and roadside frame pairs. However, real deployment often requires annotation of roadside-only data due to hardware and privacy constraints. Even human experts struggle to produce accurate labels without vehicle-side data (image, LIDAR), which not only increases annotation difficulty and cost, but also reveals a fundamental learnability problem: many roadside-only scenes contain distant, blurred, or occluded objects whose 3D properties are ambiguous from a single view and can only be reliably annotated by cross-checking paired vehicle--roadside frames. We refer to such cases as inherently ambiguous samples. To reduce wasted annotation effort on inherently ambiguous samples while still obtaining high-performing models, we turn to active learning. This work focuses on active learning for roadside monocular 3D object detection and proposes a learnability-driven framework that selects scenes which are both informative and reliably labelable, suppressing inherently ambiguous samples while ensuring coverage. Experiments demonstrate that our method, LH3D, achieves 86.06%, 67.32%, and 78.67% of full-performance for vehicles, pedestrians, and cyclists respectively, using only 25% of the annotation budget on DAIR-V2X-I, significantly outperforming uncertainty-based baselines. This confirms that learnability, not uncertainty, matters for roadside 3D perception.
From Pixel to Mask: A Survey of Out-of-Distribution Segmentation
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OoD) detection and segmentation have attracted growing attention as concerns about AI security rise. Conventional OoD detection methods identify the existence of OoD objects but lack spatial localization, limiting their usefulness in downstream tasks. OoD segmentation addresses this limitation by localizing anomalous objects at pixel-level granularity. This capability is crucial for safety-critical applications such as autonomous driving, where perception modules must not only detect but also precisely segment OoD objects, enabling targeted control actions and enhancing overall system robustness. In this survey, we group current OoD segmentation approaches into four categories: (i) test-time OoD segmentation, (ii) outlier exposure for supervised training, (iii) reconstruction-based methods, (iv) and approaches that leverage powerful models. We systematically review recent advances in OoD segmentation for autonomous-driving scenarios, identify emerging challenges, and discuss promising future research directions.
SafeFix: Targeted Model Repair via Controlled Image Generation
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Deep learning models for visual recognition often exhibit systematic errors due to underrepresented semantic subpopulations. Although existing debugging frameworks can pinpoint these failures by identifying key failure attributes, repairing the model effectively remains difficult. Current solutions often rely on manually designed prompts to generate synthetic training images -- an approach prone to distribution shift and semantic errors. To overcome these challenges, we introduce a model repair module that builds on an interpretable failure attribution pipeline. Our approach uses a conditional text-to-image model to generate semantically faithful and targeted images for failure cases. To preserve the quality and relevance of the generated samples, we further employ a large vision-language model (LVLM) to filter the outputs, enforcing alignment with the original data distribution and maintaining semantic consistency. By retraining vision models with this rare-case-augmented synthetic dataset, we significantly reduce errors associated with rare cases. Our experiments demonstrate that this targeted repair strategy improves model robustness without introducing new bugs. Code is available at https://github.com/oxu2/SafeFix
SELECT: A Submodular Approach for Active LiDAR Semantic Segmentation
May 06, 2025



Abstract:LiDAR-based semantic segmentation plays a vital role in autonomous driving by enabling detailed understanding of 3D environments. However, annotating LiDAR point clouds is extremely costly and requires assigning semantic labels to millions of points with complex geometric structures. Active Learning (AL) has emerged as a promising approach to reduce labeling costs by querying only the most informative samples. Yet, existing AL methods face critical challenges when applied to large-scale 3D data: outdoor scenes contain an overwhelming number of points and suffer from severe class imbalance, where rare classes have far fewer points than dominant classes. To address these issues, we propose SELECT, a voxel-centric submodular approach tailored for active LiDAR semantic segmentation. Our method targets both scalability problems and class imbalance through three coordinated stages. First, we perform Voxel-Level Submodular Subset Selection, which efficiently identifies representative voxels without pairwise comparisons, ensuring scalability. Second, we estimate Voxel-Level Model Uncertainty using Monte Carlo dropout, aggregating point-wise uncertainties to identify informative voxels. Finally, we introduce Submodular Maximization for Point-Level Class Balancing, which selects a subset of points that enhances label diversity, explicitly mitigating class imbalance. Experiments on SemanticPOSS, SemanticKITTI, and nuScenes benchmarks demonstrate that SELECT achieves superior performance compared to prior active learning approaches for 3D semantic segmentation.
H2ST: Hierarchical Two-Sample Tests for Continual Out-of-Distribution Detection
Mar 19, 2025



Abstract:Task Incremental Learning (TIL) is a specialized form of Continual Learning (CL) in which a model incrementally learns from non-stationary data streams. Existing TIL methodologies operate under the closed-world assumption, presuming that incoming data remains in-distribution (ID). However, in an open-world setting, incoming samples may originate from out-of-distribution (OOD) sources, with their task identities inherently unknown. Continually detecting OOD samples presents several challenges for current OOD detection methods: reliance on model outputs leads to excessive dependence on model performance, selecting suitable thresholds is difficult, hindering real-world deployment, and binary ID/OOD classification fails to provide task-level identification. To address these issues, we propose a novel continual OOD detection method called the Hierarchical Two-sample Tests (H2ST). H2ST eliminates the need for threshold selection through hypothesis testing and utilizes feature maps to better exploit model capabilities without excessive dependence on model performance. The proposed hierarchical architecture enables task-level detection with superior performance and lower overhead compared to non-hierarchical classifier two-sample tests. Extensive experiments and analysis validate the effectiveness of H2ST in open-world TIL scenarios and its superiority to the existing methods. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/YuhangLiuu/H2ST}{https://github.com/YuhangLiuu/H2ST}.
WonderHuman: Hallucinating Unseen Parts in Dynamic 3D Human Reconstruction
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present WonderHuman to reconstruct dynamic human avatars from a monocular video for high-fidelity novel view synthesis. Previous dynamic human avatar reconstruction methods typically require the input video to have full coverage of the observed human body. However, in daily practice, one typically has access to limited viewpoints, such as monocular front-view videos, making it a cumbersome task for previous methods to reconstruct the unseen parts of the human avatar. To tackle the issue, we present WonderHuman, which leverages 2D generative diffusion model priors to achieve high-quality, photorealistic reconstructions of dynamic human avatars from monocular videos, including accurate rendering of unseen body parts. Our approach introduces a Dual-Space Optimization technique, applying Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) in both canonical and observation spaces to ensure visual consistency and enhance realism in dynamic human reconstruction. Additionally, we present a View Selection strategy and Pose Feature Injection to enforce the consistency between SDS predictions and observed data, ensuring pose-dependent effects and higher fidelity in the reconstructed avatar. In the experiments, our method achieves SOTA performance in producing photorealistic renderings from the given monocular video, particularly for those challenging unseen parts. The project page and source code can be found at https://wyiguanw.github.io/WonderHuman/.
Modality-Inconsistent Continual Learning of Multimodal Large Language Models
Dec 17, 2024


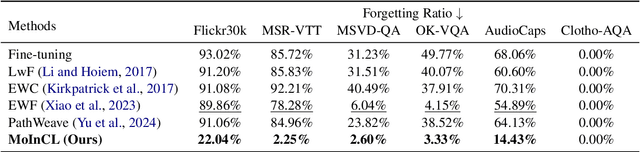
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Modality-Inconsistent Continual Learning (MICL), a new continual learning scenario for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) that involves tasks with inconsistent modalities (image, audio, or video) and varying task types (captioning or question-answering). Unlike existing vision-only or modality-incremental settings, MICL combines modality and task type shifts, both of which drive catastrophic forgetting. To address these challenges, we propose MoInCL, which employs a Pseudo Targets Generation Module to mitigate forgetting caused by task type shifts in previously seen modalities. It also incorporates Instruction-based Knowledge Distillation to preserve the model's ability to handle previously learned modalities when new ones are introduced. We benchmark MICL using a total of six tasks and conduct experiments to validate the effectiveness of our proposed MoInCL. The experimental results highlight the superiority of MoInCL, showing significant improvements over representative and state-of-the-art continual learning baselines.
Enhancing Robustness of CLIP to Common Corruptions through Bimodal Test-Time Adaptation
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Although open-vocabulary classification models like Contrastive Language Image Pretraining (CLIP) have demonstrated strong zero-shot learning capabilities, their robustness to common image corruptions remains poorly understood. Through extensive experiments, we show that zero-shot CLIP lacks robustness to common image corruptions at increasing severity levels during test-time, necessitating the adaptation of CLIP to unlabeled corrupted images using test-time adaptation (TTA). However, we found that existing TTA methods have severe limitations in adapting CLIP due to their unimodal nature. To address these limitations, we propose \framework, a bimodal TTA method specially designed to improve CLIP's robustness to common image corruptions. The key insight of our approach is not only to adapt the visual encoders for better image feature extraction but also to strengthen the alignment between image and text features by promoting a stronger association between the image class prototype, computed using pseudo-labels, and the corresponding text feature. We evaluate our approach on benchmark image corruption datasets and achieve state-of-the-art results in TTA for CLIP, specifically for domains involving image corruption. Particularly, with a ViT-B/16 vision backbone, we obtain mean accuracy improvements of 9.7%, 5.94%, and 5.12% for CIFAR-10C, CIFAR-100C, and ImageNet-C, respectively.
GradAlign for Training-free Model Performance Inference
Nov 29, 2024



Abstract:Architecture plays an important role in deciding the performance of deep neural networks. However, the search for the optimal architecture is often hindered by the vast search space, making it a time-intensive process. Recently, a novel approach known as training-free neural architecture search (NAS) has emerged, aiming to discover the ideal architecture without necessitating extensive training. Training-free NAS leverages various indicators for architecture selection, including metrics such as the count of linear regions, the density of per-sample losses, and the stability of the finite-width Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK) matrix. Despite the competitive empirical performance of current training-free NAS techniques, they suffer from certain limitations, including inconsistent performance and a lack of deep understanding. In this paper, we introduce GradAlign, a simple yet effective method designed for inferring model performance without the need for training. At its core, GradAlign quantifies the extent of conflicts within per-sample gradients during initialization, as substantial conflicts hinder model convergence and ultimately result in worse performance. We evaluate GradAlign against established training-free NAS methods using standard NAS benchmarks, showing a better overall performance. Moreover, we show that the widely adopted metric of linear region count may not suffice as a dependable criterion for selecting network architectures during at initialization.
Continual Audio-Visual Sound Separation
Nov 05, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel continual audio-visual sound separation task, aiming to continuously separate sound sources for new classes while preserving performance on previously learned classes, with the aid of visual guidance. This problem is crucial for practical visually guided auditory perception as it can significantly enhance the adaptability and robustness of audio-visual sound separation models, making them more applicable for real-world scenarios where encountering new sound sources is commonplace. The task is inherently challenging as our models must not only effectively utilize information from both modalities in current tasks but also preserve their cross-modal association in old tasks to mitigate catastrophic forgetting during audio-visual continual learning. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach named ContAV-Sep (\textbf{Cont}inual \textbf{A}udio-\textbf{V}isual Sound \textbf{Sep}aration). ContAV-Sep presents a novel Cross-modal Similarity Distillation Constraint (CrossSDC) to uphold the cross-modal semantic similarity through incremental tasks and retain previously acquired knowledge of semantic similarity in old models, mitigating the risk of catastrophic forgetting. The CrossSDC can seamlessly integrate into the training process of different audio-visual sound separation frameworks. Experiments demonstrate that ContAV-Sep can effectively mitigate catastrophic forgetting and achieve significantly better performance compared to other continual learning baselines for audio-visual sound separation. Code is available at: \url{https://github.com/weiguoPian/ContAV-Sep_NeurIPS2024}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge