Zhiyang Dou
GeoPT: Scaling Physics Simulation via Lifted Geometric Pre-Training
Feb 23, 2026Abstract:Neural simulators promise efficient surrogates for physics simulation, but scaling them is bottlenecked by the prohibitive cost of generating high-fidelity training data. Pre-training on abundant off-the-shelf geometries offers a natural alternative, yet faces a fundamental gap: supervision on static geometry alone ignores dynamics and can lead to negative transfer on physics tasks. We present GeoPT, a unified pre-trained model for general physics simulation based on lifted geometric pre-training. The core idea is to augment geometry with synthetic dynamics, enabling dynamics-aware self-supervision without physics labels. Pre-trained on over one million samples, GeoPT consistently improves industrial-fidelity benchmarks spanning fluid mechanics for cars, aircraft, and ships, and solid mechanics in crash simulation, reducing labeled data requirements by 20-60% and accelerating convergence by 2$\times$. These results show that lifting with synthetic dynamics bridges the geometry-physics gap, unlocking a scalable path for neural simulation and potentially beyond. Code is available at https://github.com/Physics-Scaling/GeoPT.
CoMoVi: Co-Generation of 3D Human Motions and Realistic Videos
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we find that the generation of 3D human motions and 2D human videos is intrinsically coupled. 3D motions provide the structural prior for plausibility and consistency in videos, while pre-trained video models offer strong generalization capabilities for motions, which necessitate coupling their generation processes. Based on this, we present CoMoVi, a co-generative framework that couples two video diffusion models (VDMs) to generate 3D human motions and videos synchronously within a single diffusion denoising loop. To achieve this, we first propose an effective 2D human motion representation that can inherit the powerful prior of pre-trained VDMs. Then, we design a dual-branch diffusion model to couple human motion and video generation process with mutual feature interaction and 3D-2D cross attentions. Moreover, we curate CoMoVi Dataset, a large-scale real-world human video dataset with text and motion annotations, covering diverse and challenging human motions. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in both 3D human motion and video generation tasks.
EgoReAct: Egocentric Video-Driven 3D Human Reaction Generation
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Humans exhibit adaptive, context-sensitive responses to egocentric visual input. However, faithfully modeling such reactions from egocentric video remains challenging due to the dual requirements of strictly causal generation and precise 3D spatial alignment. To tackle this problem, we first construct the Human Reaction Dataset (HRD) to address data scarcity and misalignment by building a spatially aligned egocentric video-reaction dataset, as existing datasets (e.g., ViMo) suffer from significant spatial inconsistency between the egocentric video and reaction motion, e.g., dynamically moving motions are always paired with fixed-camera videos. Leveraging HRD, we present EgoReAct, the first autoregressive framework that generates 3D-aligned human reaction motions from egocentric video streams in real-time. We first compress the reaction motion into a compact yet expressive latent space via a Vector Quantised-Variational AutoEncoder and then train a Generative Pre-trained Transformer for reaction generation from the visual input. EgoReAct incorporates 3D dynamic features, i.e., metric depth, and head dynamics during the generation, which effectively enhance spatial grounding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EgoReAct achieves remarkably higher realism, spatial consistency, and generation efficiency compared with prior methods, while maintaining strict causality during generation. We will release code, models, and data upon acceptance.
TrackingWorld: World-centric Monocular 3D Tracking of Almost All Pixels
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Monocular 3D tracking aims to capture the long-term motion of pixels in 3D space from a single monocular video and has witnessed rapid progress in recent years. However, we argue that the existing monocular 3D tracking methods still fall short in separating the camera motion from foreground dynamic motion and cannot densely track newly emerging dynamic subjects in the videos. To address these two limitations, we propose TrackingWorld, a novel pipeline for dense 3D tracking of almost all pixels within a world-centric 3D coordinate system. First, we introduce a tracking upsampler that efficiently lifts the arbitrary sparse 2D tracks into dense 2D tracks. Then, to generalize the current tracking methods to newly emerging objects, we apply the upsampler to all frames and reduce the redundancy of 2D tracks by eliminating the tracks in overlapped regions. Finally, we present an efficient optimization-based framework to back-project dense 2D tracks into world-centric 3D trajectories by estimating the camera poses and the 3D coordinates of these 2D tracks. Extensive evaluations on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our system achieves accurate and dense 3D tracking in a world-centric coordinate frame.
SyncHuman: Synchronizing 2D and 3D Generative Models for Single-view Human Reconstruction
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Photorealistic 3D full-body human reconstruction from a single image is a critical yet challenging task for applications in films and video games due to inherent ambiguities and severe self-occlusions. While recent approaches leverage SMPL estimation and SMPL-conditioned image generative models to hallucinate novel views, they suffer from inaccurate 3D priors estimated from SMPL meshes and have difficulty in handling difficult human poses and reconstructing fine details. In this paper, we propose SyncHuman, a novel framework that combines 2D multiview generative model and 3D native generative model for the first time, enabling high-quality clothed human mesh reconstruction from single-view images even under challenging human poses. Multiview generative model excels at capturing fine 2D details but struggles with structural consistency, whereas 3D native generative model generates coarse yet structurally consistent 3D shapes. By integrating the complementary strengths of these two approaches, we develop a more effective generation framework. Specifically, we first jointly fine-tune the multiview generative model and the 3D native generative model with proposed pixel-aligned 2D-3D synchronization attention to produce geometrically aligned 3D shapes and 2D multiview images. To further improve details, we introduce a feature injection mechanism that lifts fine details from 2D multiview images onto the aligned 3D shapes, enabling accurate and high-fidelity reconstruction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SyncHuman achieves robust and photo-realistic 3D human reconstruction, even for images with challenging poses. Our method outperforms baseline methods in geometric accuracy and visual fidelity, demonstrating a promising direction for future 3D generation models.
PartSAM: A Scalable Promptable Part Segmentation Model Trained on Native 3D Data
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Segmenting 3D objects into parts is a long-standing challenge in computer vision. To overcome taxonomy constraints and generalize to unseen 3D objects, recent works turn to open-world part segmentation. These approaches typically transfer supervision from 2D foundation models, such as SAM, by lifting multi-view masks into 3D. However, this indirect paradigm fails to capture intrinsic geometry, leading to surface-only understanding, uncontrolled decomposition, and limited generalization. We present PartSAM, the first promptable part segmentation model trained natively on large-scale 3D data. Following the design philosophy of SAM, PartSAM employs an encoder-decoder architecture in which a triplane-based dual-branch encoder produces spatially structured tokens for scalable part-aware representation learning. To enable large-scale supervision, we further introduce a model-in-the-loop annotation pipeline that curates over five million 3D shape-part pairs from online assets, providing diverse and fine-grained labels. This combination of scalable architecture and diverse 3D data yields emergent open-world capabilities: with a single prompt, PartSAM achieves highly accurate part identification, and in a Segment-Every-Part mode, it automatically decomposes shapes into both surface and internal structures. Extensive experiments show that PartSAM outperforms state-of-the-art methods by large margins across multiple benchmarks, marking a decisive step toward foundation models for 3D part understanding. Our code and model will be released soon.
Motion2Motion: Cross-topology Motion Transfer with Sparse Correspondence
Aug 18, 2025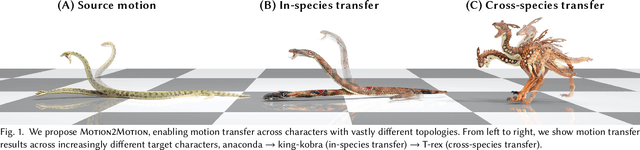
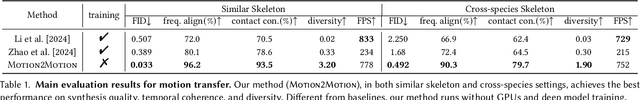
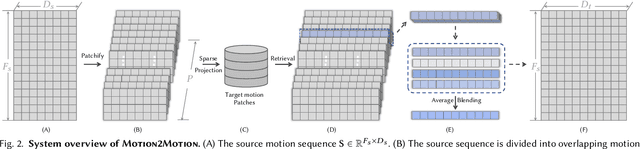

Abstract:This work studies the challenge of transfer animations between characters whose skeletal topologies differ substantially. While many techniques have advanced retargeting techniques in decades, transfer motions across diverse topologies remains less-explored. The primary obstacle lies in the inherent topological inconsistency between source and target skeletons, which restricts the establishment of straightforward one-to-one bone correspondences. Besides, the current lack of large-scale paired motion datasets spanning different topological structures severely constrains the development of data-driven approaches. To address these limitations, we introduce Motion2Motion, a novel, training-free framework. Simply yet effectively, Motion2Motion works with only one or a few example motions on the target skeleton, by accessing a sparse set of bone correspondences between the source and target skeletons. Through comprehensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations, we demonstrate that Motion2Motion achieves efficient and reliable performance in both similar-skeleton and cross-species skeleton transfer scenarios. The practical utility of our approach is further evidenced by its successful integration in downstream applications and user interfaces, highlighting its potential for industrial applications. Code and data are available at https://lhchen.top/Motion2Motion.
MOSPA: Human Motion Generation Driven by Spatial Audio
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Enabling virtual humans to dynamically and realistically respond to diverse auditory stimuli remains a key challenge in character animation, demanding the integration of perceptual modeling and motion synthesis. Despite its significance, this task remains largely unexplored. Most previous works have primarily focused on mapping modalities like speech, audio, and music to generate human motion. As of yet, these models typically overlook the impact of spatial features encoded in spatial audio signals on human motion. To bridge this gap and enable high-quality modeling of human movements in response to spatial audio, we introduce the first comprehensive Spatial Audio-Driven Human Motion (SAM) dataset, which contains diverse and high-quality spatial audio and motion data. For benchmarking, we develop a simple yet effective diffusion-based generative framework for human MOtion generation driven by SPatial Audio, termed MOSPA, which faithfully captures the relationship between body motion and spatial audio through an effective fusion mechanism. Once trained, MOSPA could generate diverse realistic human motions conditioned on varying spatial audio inputs. We perform a thorough investigation of the proposed dataset and conduct extensive experiments for benchmarking, where our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on this task. Our model and dataset will be open-sourced upon acceptance. Please refer to our supplementary video for more details.
Go to Zero: Towards Zero-shot Motion Generation with Million-scale Data
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Generating diverse and natural human motion sequences based on textual descriptions constitutes a fundamental and challenging research area within the domains of computer vision, graphics, and robotics. Despite significant advancements in this field, current methodologies often face challenges regarding zero-shot generalization capabilities, largely attributable to the limited size of training datasets. Moreover, the lack of a comprehensive evaluation framework impedes the advancement of this task by failing to identify directions for improvement. In this work, we aim to push text-to-motion into a new era, that is, to achieve the generalization ability of zero-shot. To this end, firstly, we develop an efficient annotation pipeline and introduce MotionMillion-the largest human motion dataset to date, featuring over 2,000 hours and 2 million high-quality motion sequences. Additionally, we propose MotionMillion-Eval, the most comprehensive benchmark for evaluating zero-shot motion generation. Leveraging a scalable architecture, we scale our model to 7B parameters and validate its performance on MotionMillion-Eval. Our results demonstrate strong generalization to out-of-domain and complex compositional motions, marking a significant step toward zero-shot human motion generation. The code is available at https://github.com/VankouF/MotionMillion-Codes.
Vid2Sim: Generalizable, Video-based Reconstruction of Appearance, Geometry and Physics for Mesh-free Simulation
Jun 06, 2025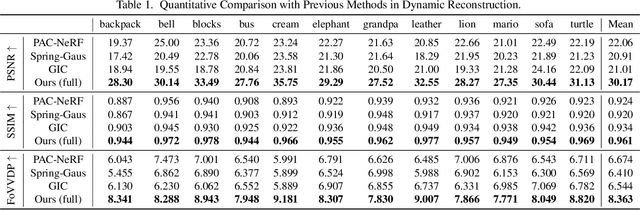
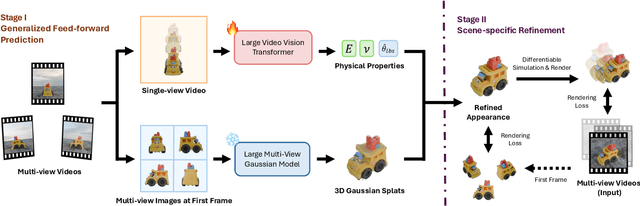
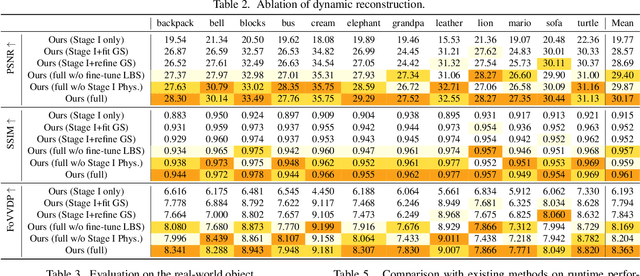

Abstract:Faithfully reconstructing textured shapes and physical properties from videos presents an intriguing yet challenging problem. Significant efforts have been dedicated to advancing such a system identification problem in this area. Previous methods often rely on heavy optimization pipelines with a differentiable simulator and renderer to estimate physical parameters. However, these approaches frequently necessitate extensive hyperparameter tuning for each scene and involve a costly optimization process, which limits both their practicality and generalizability. In this work, we propose a novel framework, Vid2Sim, a generalizable video-based approach for recovering geometry and physical properties through a mesh-free reduced simulation based on Linear Blend Skinning (LBS), offering high computational efficiency and versatile representation capability. Specifically, Vid2Sim first reconstructs the observed configuration of the physical system from video using a feed-forward neural network trained to capture physical world knowledge. A lightweight optimization pipeline then refines the estimated appearance, geometry, and physical properties to closely align with video observations within just a few minutes. Additionally, after the reconstruction, Vid2Sim enables high-quality, mesh-free simulation with high efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves superior accuracy and efficiency in reconstructing geometry and physical properties from video data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge