Yuko Ishiwaka
When Models Know When They Do Not Know: Calibration, Cascading, and Cleaning
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:When a model knows when it does not know, many possibilities emerge. The first question is how to enable a model to recognize that it does not know. A promising approach is to use confidence, computed from the model's internal signals, to reflect its ignorance. Prior work in specific domains has shown that calibration can provide reliable confidence estimates. In this work, we propose a simple, effective, and universal training-free method that applies to both vision and language models, performing model calibration, cascading, and data cleaning to better exploit a model's ability to recognize when it does not know. We first highlight two key empirical observations: higher confidence corresponds to higher accuracy within a single model, and models calibrated on the validation set remain calibrated on a held-out test set. These findings empirically establish the reliability and comparability of calibrated confidence. Building on this, we introduce two applications: (1) model cascading with calibrated advantage routing and (2) data cleaning based on model ensemble. Using the routing signal derived from the comparability of calibrated confidences, we cascade large and small models to improve efficiency with almost no compromise in accuracy, and we further cascade two models of comparable scale to achieve performance beyond either model alone. Leveraging multiple experts and their calibrated confidences, we design a simple yet effective data-cleaning method that balances precision and detection rate to identify mislabeled samples in ImageNet and Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) datasets. Our results demonstrate that enabling models to recognize when they do not know is a practical step toward more efficient, reliable, and trustworthy AI.
CBIL: Collective Behavior Imitation Learning for Fish from Real Videos
Mar 31, 2025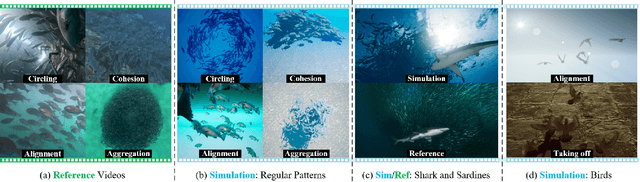
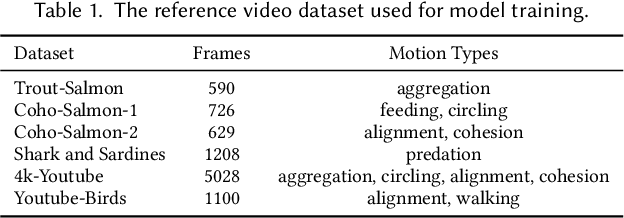
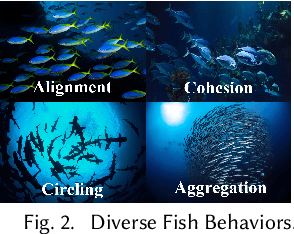
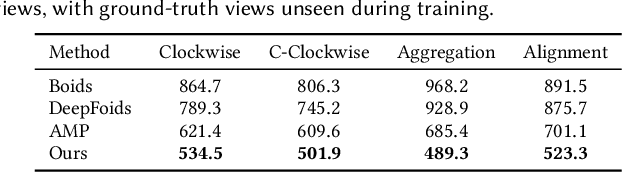
Abstract:Reproducing realistic collective behaviors presents a captivating yet formidable challenge. Traditional rule-based methods rely on hand-crafted principles, limiting motion diversity and realism in generated collective behaviors. Recent imitation learning methods learn from data but often require ground truth motion trajectories and struggle with authenticity, especially in high-density groups with erratic movements. In this paper, we present a scalable approach, Collective Behavior Imitation Learning (CBIL), for learning fish schooling behavior directly from videos, without relying on captured motion trajectories. Our method first leverages Video Representation Learning, where a Masked Video AutoEncoder (MVAE) extracts implicit states from video inputs in a self-supervised manner. The MVAE effectively maps 2D observations to implicit states that are compact and expressive for following the imitation learning stage. Then, we propose a novel adversarial imitation learning method to effectively capture complex movements of the schools of fish, allowing for efficient imitation of the distribution for motion patterns measured in the latent space. It also incorporates bio-inspired rewards alongside priors to regularize and stabilize training. Once trained, CBIL can be used for various animation tasks with the learned collective motion priors. We further show its effectiveness across different species. Finally, we demonstrate the application of our system in detecting abnormal fish behavior from in-the-wild videos.
Listening to Sounds of Silence for Speech Denoising
Oct 22, 2020
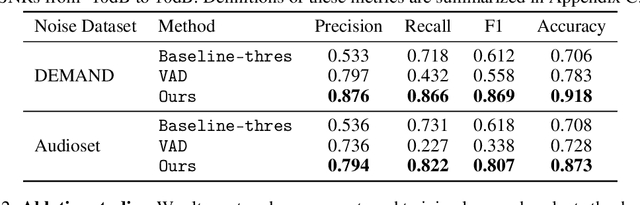


Abstract:We introduce a deep learning model for speech denoising, a long-standing challenge in audio analysis arising in numerous applications. Our approach is based on a key observation about human speech: there is often a short pause between each sentence or word. In a recorded speech signal, those pauses introduce a series of time periods during which only noise is present. We leverage these incidental silent intervals to learn a model for automatic speech denoising given only mono-channel audio. Detected silent intervals over time expose not just pure noise but its time-varying features, allowing the model to learn noise dynamics and suppress it from the speech signal. Experiments on multiple datasets confirm the pivotal role of silent interval detection for speech denoising, and our method outperforms several state-of-the-art denoising methods, including those that accept only audio input (like ours) and those that denoise based on audiovisual input (and hence require more information). We also show that our method enjoys excellent generalization properties, such as denoising spoken languages not seen during training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge