Ruilin Xu
E-commerce Webpage Recommendation Scheme Base on Semantic Mining and Neural Networks
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:In e-commerce websites, web mining web page recommendation technology has been widely used. However, recommendation solutions often cannot meet the actual application needs of online shopping users. To address this problem, this paper proposes an e-commerce web page recommendation solution that combines semantic web mining and BP neural networks. First, the web logs of user searches are processed, and 5 features are extracted: content priority, time consumption priority, online shopping users' explicit/implicit feedback on the website, recommendation semantics and input deviation amount. Then, these features are used as input features of the BP neural network to classify and identify the priority of the final output web page. Finally, the web pages are sorted according to priority and recommended to users. This project uses book sales webpages as samples for experiments. The results show that this solution can quickly and accurately identify the webpages required by users.
Metaknowledge Extraction Based on Multi-Modal Documents
Feb 05, 2021
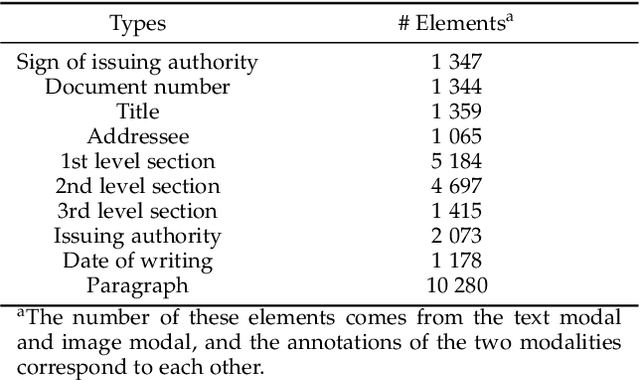


Abstract:The triple-based knowledge in large-scale knowledge bases is most likely lacking in structural logic and problematic of conducting knowledge hierarchy. In this paper, we introduce the concept of metaknowledge to knowledge engineering research for the purpose of structural knowledge construction. Therefore, the Metaknowledge Extraction Framework and Document Structure Tree model are presented to extract and organize metaknowledge elements (titles, authors, abstracts, sections, paragraphs, etc.), so that it is feasible to extract the structural knowledge from multi-modal documents. Experiment results have proved the effectiveness of metaknowledge elements extraction by our framework. Meanwhile, detailed examples are given to demonstrate what exactly metaknowledge is and how to generate it. At the end of this paper, we propose and analyze the task flow of metaknowledge applications and the associations between knowledge and metaknowledge.
Listening to Sounds of Silence for Speech Denoising
Oct 22, 2020
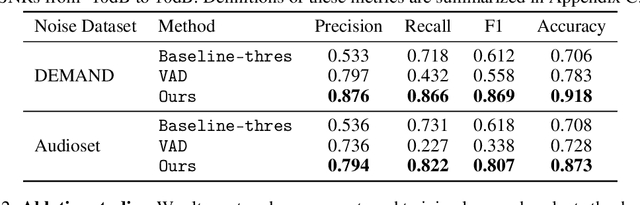


Abstract:We introduce a deep learning model for speech denoising, a long-standing challenge in audio analysis arising in numerous applications. Our approach is based on a key observation about human speech: there is often a short pause between each sentence or word. In a recorded speech signal, those pauses introduce a series of time periods during which only noise is present. We leverage these incidental silent intervals to learn a model for automatic speech denoising given only mono-channel audio. Detected silent intervals over time expose not just pure noise but its time-varying features, allowing the model to learn noise dynamics and suppress it from the speech signal. Experiments on multiple datasets confirm the pivotal role of silent interval detection for speech denoising, and our method outperforms several state-of-the-art denoising methods, including those that accept only audio input (like ours) and those that denoise based on audiovisual input (and hence require more information). We also show that our method enjoys excellent generalization properties, such as denoising spoken languages not seen during training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge