Susan Liang
Mark
Omni-Judge: Can Omni-LLMs Serve as Human-Aligned Judges for Text-Conditioned Audio-Video Generation?
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:State-of-the-art text-to-video generation models such as Sora 2 and Veo 3 can now produce high-fidelity videos with synchronized audio directly from a textual prompt, marking a new milestone in multi-modal generation. However, evaluating such tri-modal outputs remains an unsolved challenge. Human evaluation is reliable but costly and difficult to scale, while traditional automatic metrics, such as FVD, CLAP, and ViCLIP, focus on isolated modality pairs, struggle with complex prompts, and provide limited interpretability. Omni-modal large language models (omni-LLMs) present a promising alternative: they naturally process audio, video, and text, support rich reasoning, and offer interpretable chain-of-thought feedback. Driven by this, we introduce Omni-Judge, a study assessing whether omni-LLMs can serve as human-aligned judges for text-conditioned audio-video generation. Across nine perceptual and alignment metrics, Omni-Judge achieves correlation comparable to traditional metrics and excels on semantically demanding tasks such as audio-text alignment, video-text alignment, and audio-video-text coherence. It underperforms on high-FPS perceptual metrics, including video quality and audio-video synchronization, due to limited temporal resolution. Omni-Judge provides interpretable explanations that expose semantic or physical inconsistencies, enabling practical downstream uses such as feedback-based refinement. Our findings highlight both the potential and current limitations of omni-LLMs as unified evaluators for multi-modal generation.
When to Think and When to Look: Uncertainty-Guided Lookback
Nov 19, 2025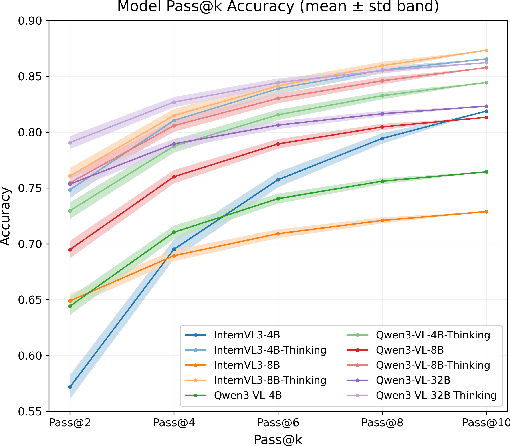
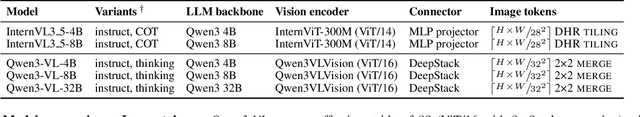
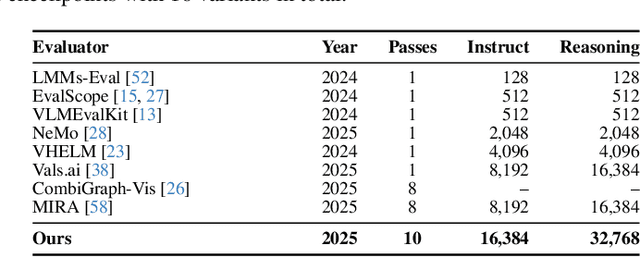
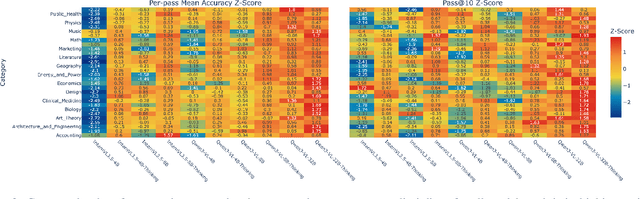
Abstract:Test-time thinking (that is, generating explicit intermediate reasoning chains) is known to boost performance in large language models and has recently shown strong gains for large vision language models (LVLMs). However, despite these promising results, there is still no systematic analysis of how thinking actually affects visual reasoning. We provide the first such analysis with a large scale, controlled comparison of thinking for LVLMs, evaluating ten variants from the InternVL3.5 and Qwen3-VL families on MMMU-val under generous token budgets and multi pass decoding. We show that more thinking is not always better; long chains often yield long wrong trajectories that ignore the image and underperform the same models run in standard instruct mode. A deeper analysis reveals that certain short lookback phrases, which explicitly refer back to the image, are strongly enriched in successful trajectories and correlate with better visual grounding. Building on this insight, we propose uncertainty guided lookback, a training free decoding strategy that combines an uncertainty signal with adaptive lookback prompts and breadth search. Our method improves overall MMMU performance, delivers the largest gains in categories where standard thinking is weak, and outperforms several strong decoding baselines, setting a new state of the art under fixed model families and token budgets. We further show that this decoding strategy generalizes, yielding consistent improvements on five additional benchmarks, including two broad multimodal suites and math focused visual reasoning datasets.
Video-LMM Post-Training: A Deep Dive into Video Reasoning with Large Multimodal Models
Oct 06, 2025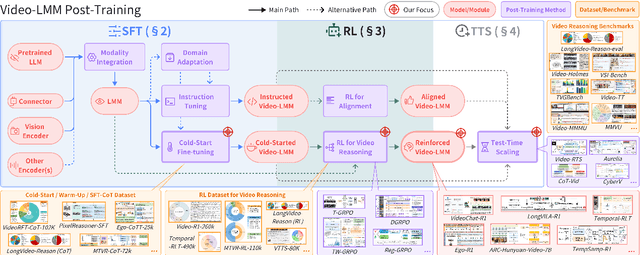
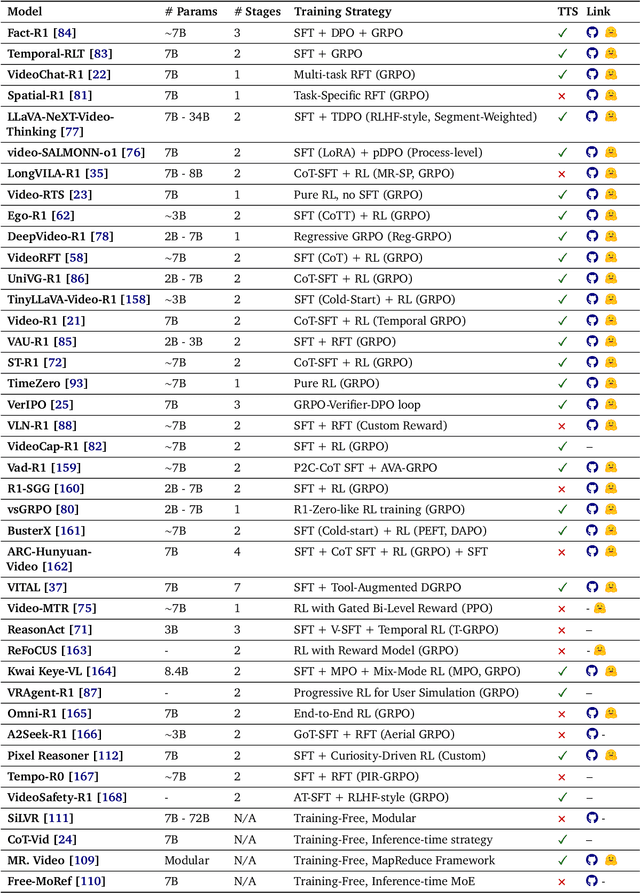
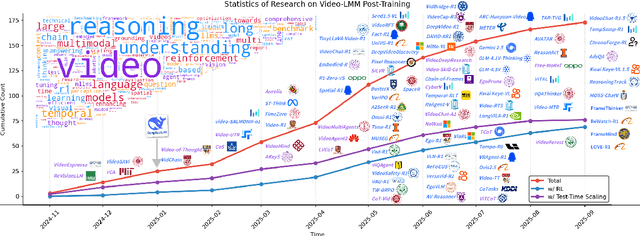
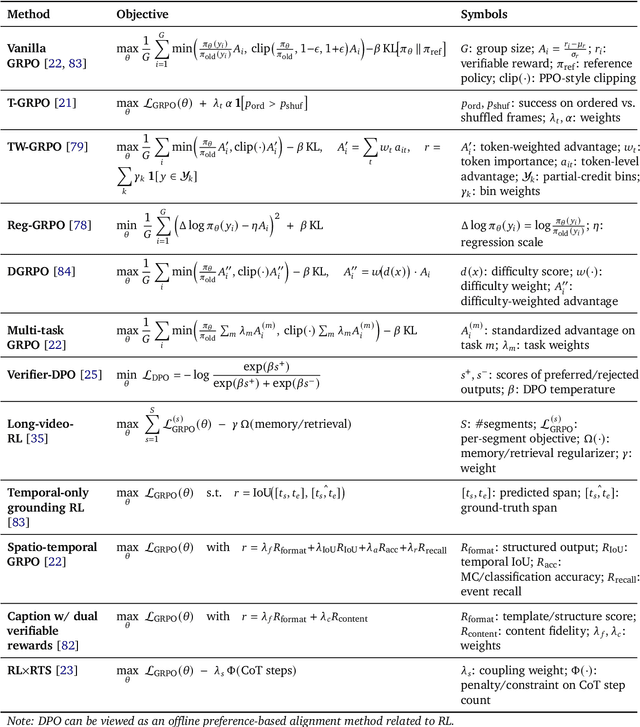
Abstract:Video understanding represents the most challenging frontier in computer vision, requiring models to reason about complex spatiotemporal relationships, long-term dependencies, and multimodal evidence. The recent emergence of Video-Large Multimodal Models (Video-LMMs), which integrate visual encoders with powerful decoder-based language models, has demonstrated remarkable capabilities in video understanding tasks. However, the critical phase that transforms these models from basic perception systems into sophisticated reasoning engines, post-training, remains fragmented across the literature. This survey provides the first comprehensive examination of post-training methodologies for Video-LMMs, encompassing three fundamental pillars: supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with chain-of-thought, reinforcement learning (RL) from verifiable objectives, and test-time scaling (TTS) through enhanced inference computation. We present a structured taxonomy that clarifies the roles, interconnections, and video-specific adaptations of these techniques, addressing unique challenges such as temporal localization, spatiotemporal grounding, long video efficiency, and multimodal evidence integration. Through systematic analysis of representative methods, we synthesize key design principles, insights, and evaluation protocols while identifying critical open challenges in reward design, scalability, and cost-performance optimization. We further curate essential benchmarks, datasets, and metrics to facilitate rigorous assessment of post-training effectiveness. This survey aims to provide researchers and practitioners with a unified framework for advancing Video-LMM capabilities. Additional resources and updates are maintained at: https://github.com/yunlong10/Awesome-Video-LMM-Post-Training
High-Quality Sound Separation Across Diverse Categories via Visually-Guided Generative Modeling
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:We propose DAVIS, a Diffusion-based Audio-VIsual Separation framework that solves the audio-visual sound source separation task through generative learning. Existing methods typically frame sound separation as a mask-based regression problem, achieving significant progress. However, they face limitations in capturing the complex data distribution required for high-quality separation of sounds from diverse categories. In contrast, DAVIS circumvents these issues by leveraging potent generative modeling paradigms, specifically Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM) and the more recent Flow Matching (FM), integrated within a specialized Separation U-Net architecture. Our framework operates by synthesizing the desired separated sound spectrograms directly from a noise distribution, conditioned concurrently on the mixed audio input and associated visual information. The inherent nature of its generative objective makes DAVIS particularly adept at producing high-quality sound separations for diverse sound categories. We present comparative evaluations of DAVIS, encompassing both its DDPM and Flow Matching variants, against leading methods on the standard AVE and MUSIC datasets. The results affirm that both variants surpass existing approaches in separation quality, highlighting the efficacy of our generative framework for tackling the audio-visual source separation task.
ZeroSep: Separate Anything in Audio with Zero Training
May 29, 2025Abstract:Audio source separation is fundamental for machines to understand complex acoustic environments and underpins numerous audio applications. Current supervised deep learning approaches, while powerful, are limited by the need for extensive, task-specific labeled data and struggle to generalize to the immense variability and open-set nature of real-world acoustic scenes. Inspired by the success of generative foundation models, we investigate whether pre-trained text-guided audio diffusion models can overcome these limitations. We make a surprising discovery: zero-shot source separation can be achieved purely through a pre-trained text-guided audio diffusion model under the right configuration. Our method, named ZeroSep, works by inverting the mixed audio into the diffusion model's latent space and then using text conditioning to guide the denoising process to recover individual sources. Without any task-specific training or fine-tuning, ZeroSep repurposes the generative diffusion model for a discriminative separation task and inherently supports open-set scenarios through its rich textual priors. ZeroSep is compatible with a variety of pre-trained text-guided audio diffusion backbones and delivers strong separation performance on multiple separation benchmarks, surpassing even supervised methods.
BinauralFlow: A Causal and Streamable Approach for High-Quality Binaural Speech Synthesis with Flow Matching Models
May 28, 2025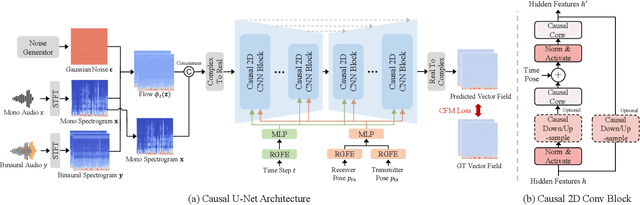
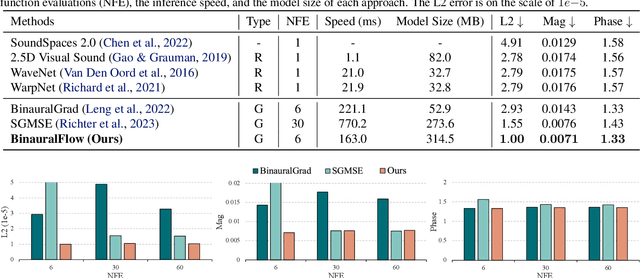
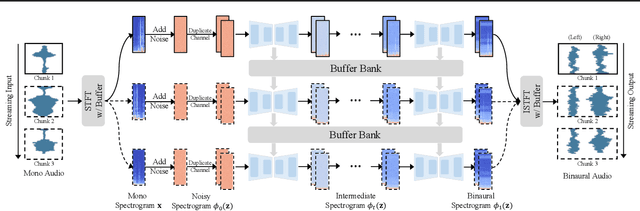
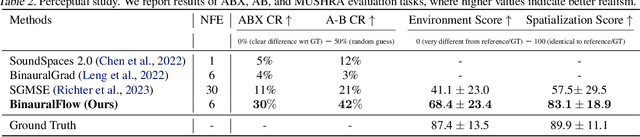
Abstract:Binaural rendering aims to synthesize binaural audio that mimics natural hearing based on a mono audio and the locations of the speaker and listener. Although many methods have been proposed to solve this problem, they struggle with rendering quality and streamable inference. Synthesizing high-quality binaural audio that is indistinguishable from real-world recordings requires precise modeling of binaural cues, room reverb, and ambient sounds. Additionally, real-world applications demand streaming inference. To address these challenges, we propose a flow matching based streaming binaural speech synthesis framework called BinauralFlow. We consider binaural rendering to be a generation problem rather than a regression problem and design a conditional flow matching model to render high-quality audio. Moreover, we design a causal U-Net architecture that estimates the current audio frame solely based on past information to tailor generative models for streaming inference. Finally, we introduce a continuous inference pipeline incorporating streaming STFT/ISTFT operations, a buffer bank, a midpoint solver, and an early skip schedule to improve rendering continuity and speed. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate the superiority of our method over SOTA approaches. A perceptual study further reveals that our model is nearly indistinguishable from real-world recordings, with a $42\%$ confusion rate.
MMPerspective: Do MLLMs Understand Perspective? A Comprehensive Benchmark for Perspective Perception, Reasoning, and Robustness
May 26, 2025Abstract:Understanding perspective is fundamental to human visual perception, yet the extent to which multimodal large language models (MLLMs) internalize perspective geometry remains unclear. We introduce MMPerspective, the first benchmark specifically designed to systematically evaluate MLLMs' understanding of perspective through 10 carefully crafted tasks across three complementary dimensions: Perspective Perception, Reasoning, and Robustness. Our benchmark comprises 2,711 real-world and synthetic image instances with 5,083 question-answer pairs that probe key capabilities, such as vanishing point perception and counting, perspective type reasoning, line relationship understanding in 3D space, invariance to perspective-preserving transformations, etc. Through a comprehensive evaluation of 43 state-of-the-art MLLMs, we uncover significant limitations: while models demonstrate competence on surface-level perceptual tasks, they struggle with compositional reasoning and maintaining spatial consistency under perturbations. Our analysis further reveals intriguing patterns between model architecture, scale, and perspective capabilities, highlighting both robustness bottlenecks and the benefits of chain-of-thought prompting. MMPerspective establishes a valuable testbed for diagnosing and advancing spatial understanding in vision-language systems. Resources available at: https://yunlong10.github.io/MMPerspective/
The Sword of Damocles in ViTs: Computational Redundancy Amplifies Adversarial Transferability
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have demonstrated impressive performance across a range of applications, including many safety-critical tasks. However, their unique architectural properties raise new challenges and opportunities in adversarial robustness. In particular, we observe that adversarial examples crafted on ViTs exhibit higher transferability compared to those crafted on CNNs, suggesting that ViTs contain structural characteristics favorable for transferable attacks. In this work, we investigate the role of computational redundancy in ViTs and its impact on adversarial transferability. Unlike prior studies that aim to reduce computation for efficiency, we propose to exploit this redundancy to improve the quality and transferability of adversarial examples. Through a detailed analysis, we identify two forms of redundancy, including the data-level and model-level, that can be harnessed to amplify attack effectiveness. Building on this insight, we design a suite of techniques, including attention sparsity manipulation, attention head permutation, clean token regularization, ghost MoE diversification, and test-time adversarial training. Extensive experiments on the ImageNet-1k dataset validate the effectiveness of our approach, showing that our methods significantly outperform existing baselines in both transferability and generality across diverse model architectures.
Caption Anything in Video: Fine-grained Object-centric Captioning via Spatiotemporal Multimodal Prompting
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:We present CAT-V (Caption AnyThing in Video), a training-free framework for fine-grained object-centric video captioning that enables detailed descriptions of user-selected objects through time. CAT-V integrates three key components: a Segmenter based on SAMURAI for precise object segmentation across frames, a Temporal Analyzer powered by TRACE-Uni for accurate event boundary detection and temporal analysis, and a Captioner using InternVL-2.5 for generating detailed object-centric descriptions. Through spatiotemporal visual prompts and chain-of-thought reasoning, our framework generates detailed, temporally-aware descriptions of objects' attributes, actions, statuses, interactions, and environmental contexts without requiring additional training data. CAT-V supports flexible user interactions through various visual prompts (points, bounding boxes, and irregular regions) and maintains temporal sensitivity by tracking object states and interactions across different time segments. Our approach addresses limitations of existing video captioning methods, which either produce overly abstract descriptions or lack object-level precision, enabling fine-grained, object-specific descriptions while maintaining temporal coherence and spatial accuracy. The GitHub repository for this project is available at https://github.com/yunlong10/CAT-V
Why Reasoning Matters? A Survey of Advancements in Multimodal Reasoning (v1)
Apr 04, 2025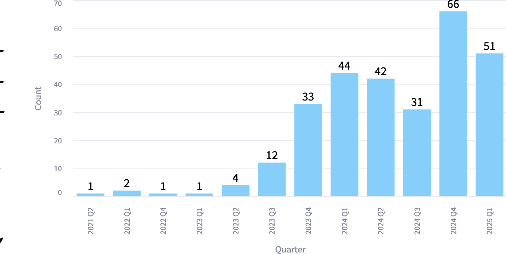
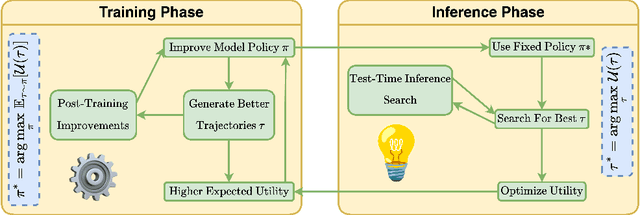
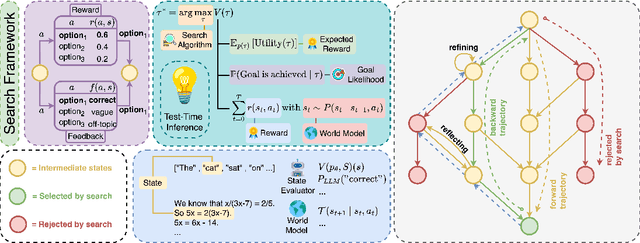
Abstract:Reasoning is central to human intelligence, enabling structured problem-solving across diverse tasks. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have greatly enhanced their reasoning abilities in arithmetic, commonsense, and symbolic domains. However, effectively extending these capabilities into multimodal contexts-where models must integrate both visual and textual inputs-continues to be a significant challenge. Multimodal reasoning introduces complexities, such as handling conflicting information across modalities, which require models to adopt advanced interpretative strategies. Addressing these challenges involves not only sophisticated algorithms but also robust methodologies for evaluating reasoning accuracy and coherence. This paper offers a concise yet insightful overview of reasoning techniques in both textual and multimodal LLMs. Through a thorough and up-to-date comparison, we clearly formulate core reasoning challenges and opportunities, highlighting practical methods for post-training optimization and test-time inference. Our work provides valuable insights and guidance, bridging theoretical frameworks and practical implementations, and sets clear directions for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge