Junxuan Huang
ZeroSep: Separate Anything in Audio with Zero Training
May 29, 2025Abstract:Audio source separation is fundamental for machines to understand complex acoustic environments and underpins numerous audio applications. Current supervised deep learning approaches, while powerful, are limited by the need for extensive, task-specific labeled data and struggle to generalize to the immense variability and open-set nature of real-world acoustic scenes. Inspired by the success of generative foundation models, we investigate whether pre-trained text-guided audio diffusion models can overcome these limitations. We make a surprising discovery: zero-shot source separation can be achieved purely through a pre-trained text-guided audio diffusion model under the right configuration. Our method, named ZeroSep, works by inverting the mixed audio into the diffusion model's latent space and then using text conditioning to guide the denoising process to recover individual sources. Without any task-specific training or fine-tuning, ZeroSep repurposes the generative diffusion model for a discriminative separation task and inherently supports open-set scenarios through its rich textual priors. ZeroSep is compatible with a variety of pre-trained text-guided audio diffusion backbones and delivers strong separation performance on multiple separation benchmarks, surpassing even supervised methods.
PointACL:Adversarial Contrastive Learning for Robust Point Clouds Representation under Adversarial Attack
Sep 14, 2022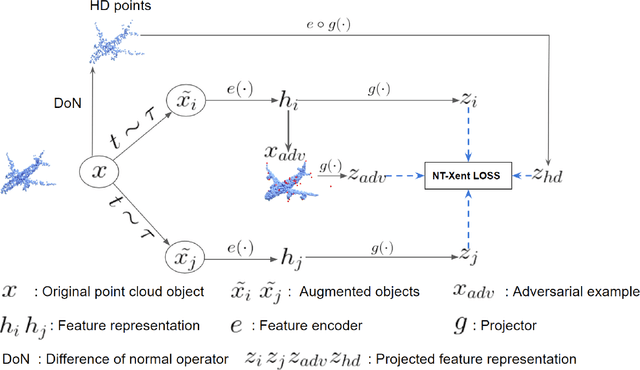
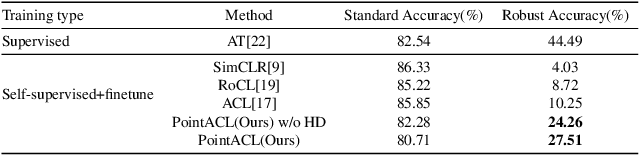

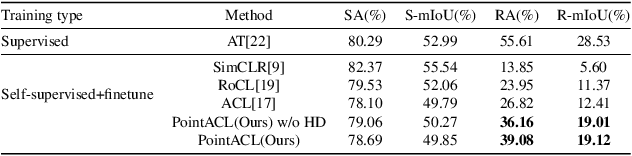
Abstract:Despite recent success of self-supervised based contrastive learning model for 3D point clouds representation, the adversarial robustness of such pre-trained models raised concerns. Adversarial contrastive learning (ACL) is considered an effective way to improve the robustness of pre-trained models. In contrastive learning, the projector is considered an effective component for removing unnecessary feature information during contrastive pretraining and most ACL works also use contrastive loss with projected feature representations to generate adversarial examples in pretraining, while "unprojected " feature representations are used in generating adversarial inputs during inference.Because of the distribution gap between projected and "unprojected" features, their models are constrained of obtaining robust feature representations for downstream tasks. We introduce a new method to generate high-quality 3D adversarial examples for adversarial training by utilizing virtual adversarial loss with "unprojected" feature representations in contrastive learning framework. We present our robust aware loss function to train self-supervised contrastive learning framework adversarially. Furthermore, we find selecting high difference points with the Difference of Normal (DoN) operator as additional input for adversarial self-supervised contrastive learning can significantly improve the adversarial robustness of the pre-trained model. We validate our method, PointACL on downstream tasks, including 3D classification and 3D segmentation with multiple datasets. It obtains comparable robust accuracy over state-of-the-art contrastive adversarial learning methods.
Generation For Adaption: A GAN-Based Approach for 3D Domain Adaption with Point Cloud Data
Feb 26, 2021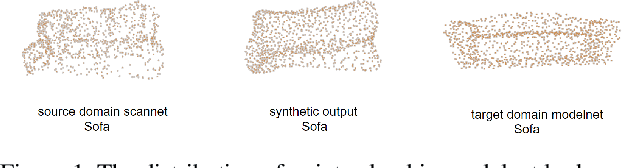
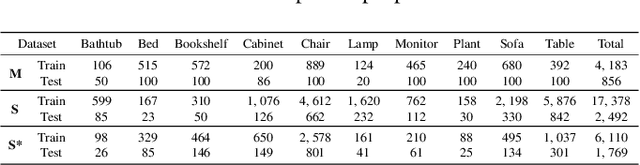
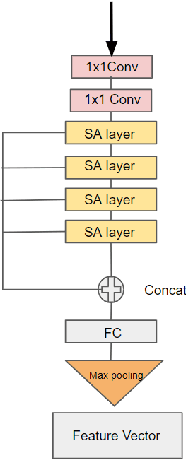
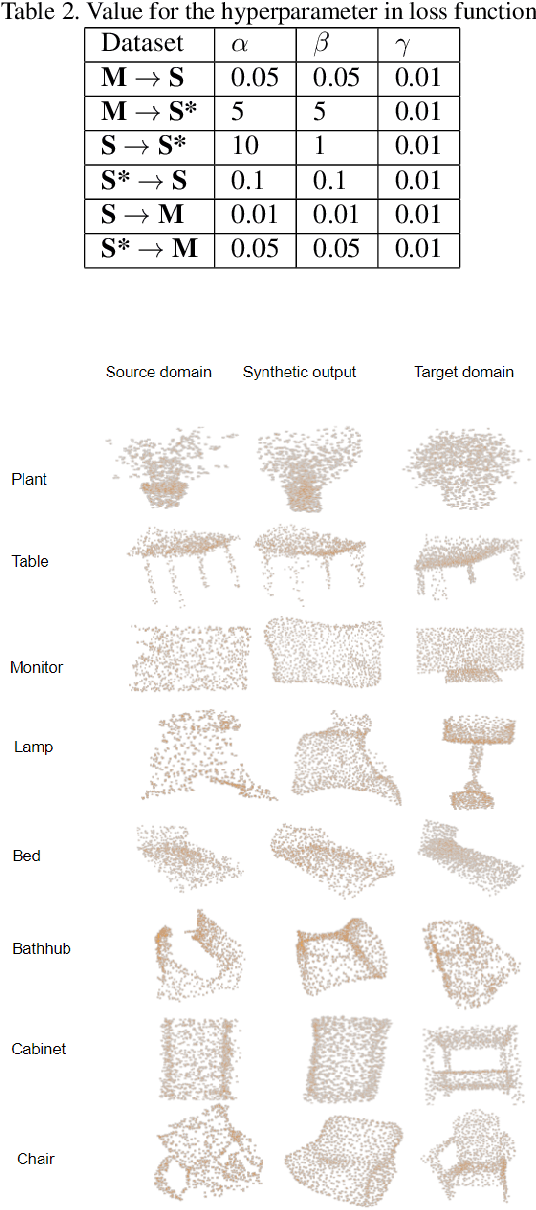
Abstract:Recent deep networks have achieved good performance on a variety of 3d points classification tasks. However, these models often face challenges in "wild tasks".There are considerable differences between the labeled training/source data collected by one Lidar and unseen test/target data collected by a different Lidar. Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) seeks to overcome such a problem without target domain labels.Instead of aligning features between source data and target data,we propose a method that use a Generative adversarial network to generate synthetic data from the source domain so that the output is close to the target domain.Experiments show that our approach performs better than other state-of-the-art UDA methods in three popular 3D object/scene datasets (i.e., ModelNet, ShapeNet and ScanNet) for cross-domain 3D objects classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge