Anurag Kumar
PhaseCoder: Microphone Geometry-Agnostic Spatial Audio Understanding for Multimodal LLMs
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Current multimodal LLMs process audio as a mono stream, ignoring the rich spatial information essential for embodied AI. Existing spatial audio models, conversely, are constrained to fixed microphone geometries, preventing deployment across diverse devices. We present PhaseCoder, a transformer-only spatial audio encoder that is agnostic to microphone geometry. PhaseCoder takes raw multichannel audio and microphone coordinates as inputs to perform localization and produces robust spatial embeddings. We demonstrate that Gemma 3n LLM can be fine-tuned to reason over "Spatial Audio Tokens" produced by PhaseCoder. We show our encoder achieves state-of-the-art results on microphone-invariant localization benchmarks and, for the first time, enables an LLM to perform complex spatial reasoning and targeted transcription tasks from an arbitrary microphone array.
High-Quality Sound Separation Across Diverse Categories via Visually-Guided Generative Modeling
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:We propose DAVIS, a Diffusion-based Audio-VIsual Separation framework that solves the audio-visual sound source separation task through generative learning. Existing methods typically frame sound separation as a mask-based regression problem, achieving significant progress. However, they face limitations in capturing the complex data distribution required for high-quality separation of sounds from diverse categories. In contrast, DAVIS circumvents these issues by leveraging potent generative modeling paradigms, specifically Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM) and the more recent Flow Matching (FM), integrated within a specialized Separation U-Net architecture. Our framework operates by synthesizing the desired separated sound spectrograms directly from a noise distribution, conditioned concurrently on the mixed audio input and associated visual information. The inherent nature of its generative objective makes DAVIS particularly adept at producing high-quality sound separations for diverse sound categories. We present comparative evaluations of DAVIS, encompassing both its DDPM and Flow Matching variants, against leading methods on the standard AVE and MUSIC datasets. The results affirm that both variants surpass existing approaches in separation quality, highlighting the efficacy of our generative framework for tackling the audio-visual source separation task.
Interspeech 2025 URGENT Speech Enhancement Challenge
May 29, 2025Abstract:There has been a growing effort to develop universal speech enhancement (SE) to handle inputs with various speech distortions and recording conditions. The URGENT Challenge series aims to foster such universal SE by embracing a broad range of distortion types, increasing data diversity, and incorporating extensive evaluation metrics. This work introduces the Interspeech 2025 URGENT Challenge, the second edition of the series, to explore several aspects that have received limited attention so far: language dependency, universality for more distortion types, data scalability, and the effectiveness of using noisy training data. We received 32 submissions, where the best system uses a discriminative model, while most other competitive ones are hybrid methods. Analysis reveals some key findings: (i) some generative or hybrid approaches are preferred in subjective evaluations over the top discriminative model, and (ii) purely generative SE models can exhibit language dependency.
Learning to Highlight Audio by Watching Movies
May 17, 2025
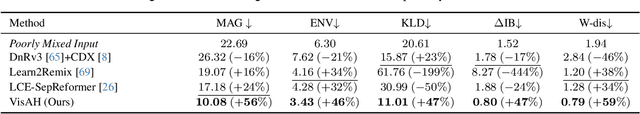
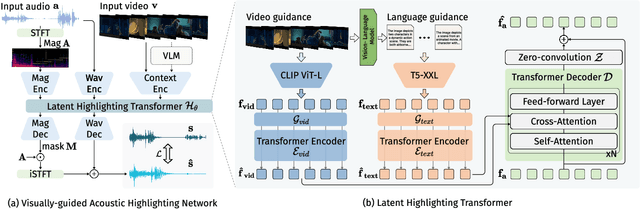
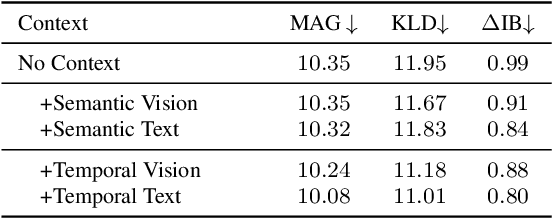
Abstract:Recent years have seen a significant increase in video content creation and consumption. Crafting engaging content requires the careful curation of both visual and audio elements. While visual cue curation, through techniques like optimal viewpoint selection or post-editing, has been central to media production, its natural counterpart, audio, has not undergone equivalent advancements. This often results in a disconnect between visual and acoustic saliency. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel task: visually-guided acoustic highlighting, which aims to transform audio to deliver appropriate highlighting effects guided by the accompanying video, ultimately creating a more harmonious audio-visual experience. We propose a flexible, transformer-based multimodal framework to solve this task. To train our model, we also introduce a new dataset -- the muddy mix dataset, leveraging the meticulous audio and video crafting found in movies, which provides a form of free supervision. We develop a pseudo-data generation process to simulate poorly mixed audio, mimicking real-world scenarios through a three-step process -- separation, adjustment, and remixing. Our approach consistently outperforms several baselines in both quantitative and subjective evaluation. We also systematically study the impact of different types of contextual guidance and difficulty levels of the dataset. Our project page is here: https://wikichao.github.io/VisAH/.
Hearing Anywhere in Any Environment
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:In mixed reality applications, a realistic acoustic experience in spatial environments is as crucial as the visual experience for achieving true immersion. Despite recent advances in neural approaches for Room Impulse Response (RIR) estimation, most existing methods are limited to the single environment on which they are trained, lacking the ability to generalize to new rooms with different geometries and surface materials. We aim to develop a unified model capable of reconstructing the spatial acoustic experience of any environment with minimum additional measurements. To this end, we present xRIR, a framework for cross-room RIR prediction. The core of our generalizable approach lies in combining a geometric feature extractor, which captures spatial context from panorama depth images, with a RIR encoder that extracts detailed acoustic features from only a few reference RIR samples. To evaluate our method, we introduce ACOUSTICROOMS, a new dataset featuring high-fidelity simulation of over 300,000 RIRs from 260 rooms. Experiments show that our method strongly outperforms a series of baselines. Furthermore, we successfully perform sim-to-real transfer by evaluating our model on four real-world environments, demonstrating the generalizability of our approach and the realism of our dataset.
Quickest change detection for UAV-based sensing
Apr 10, 2025



Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of quickest change detection (QCD) at two spatially separated locations monitored by a single unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) equipped with a sensor. At any location, the UAV observes i.i.d. data sequentially in discrete time instants. The distribution of the observation data changes at some unknown, arbitrary time and the UAV has to detect this change in the shortest possible time. Change can occur at most at one location over the entire infinite time horizon. The UAV switches between these two locations in order to quickly detect the change. To this end, we propose Location Switching and Change Detection (LS-CD) algorithm which uses a repeated one-sided sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) based mechanism for observation-driven location switching and change detection. The primary goal is to minimize the worst-case average detection delay (WADD) while meeting constraints on the average run length to false alarm (ARL2FA) and the UAV's time-averaged energy consumption. We provide a rigorous theoretical analysis of the algorithm's performance by using theory of random walk. Specifically, we derive tight upper and lower bounds to its ARL2FA and a tight upper bound to its WADD. In the special case of a symmetrical setting, our analysis leads to a new asymptotic upper bound to the ARL2FA of the standard CUSUM algorithm, a novel contribution not available in the literature, to our knowledge. Numerical simulations demonstrate the efficacy of LS-CD.
Efficient Audiovisual Speech Processing via MUTUD: Multimodal Training and Unimodal Deployment
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Building reliable speech systems often requires combining multiple modalities, like audio and visual cues. While such multimodal solutions frequently lead to improvements in performance and may even be critical in certain cases, they come with several constraints such as increased sensory requirements, computational cost, and modality synchronization, to mention a few. These challenges constrain the direct uses of these multimodal solutions in real-world applications. In this work, we develop approaches where the learning happens with all available modalities but the deployment or inference is done with just one or reduced modalities. To do so, we propose a Multimodal Training and Unimodal Deployment (MUTUD) framework which includes a Temporally Aligned Modality feature Estimation (TAME) module that can estimate information from missing modality using modalities present during inference. This innovative approach facilitates the integration of information across different modalities, enhancing the overall inference process by leveraging the strengths of each modality to compensate for the absence of certain modalities during inference. We apply MUTUD to various audiovisual speech tasks and show that it can reduce the performance gap between the multimodal and corresponding unimodal models to a considerable extent. MUTUD can achieve this while reducing the model size and compute compared to multimodal models, in some cases by almost 80%.
SEAL: Speaker Error Correction using Acoustic-conditioned Large Language Models
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:Speaker Diarization (SD) is a crucial component of modern end-to-end ASR pipelines. Traditional SD systems, which are typically audio-based and operate independently of ASR, often introduce speaker errors, particularly during speaker transitions and overlapping speech. Recently, language models including fine-tuned large language models (LLMs) have shown to be effective as a second-pass speaker error corrector by leveraging lexical context in the transcribed output. In this work, we introduce a novel acoustic conditioning approach to provide more fine-grained information from the acoustic diarizer to the LLM. We also show that a simpler constrained decoding strategy reduces LLM hallucinations, while avoiding complicated post-processing. Our approach significantly reduces the speaker error rates by 24-43% across Fisher, Callhome, and RT03-CTS datasets, compared to the first-pass Acoustic SD.
Bridging Context Gaps: Enhancing Comprehension in Long-Form Social Conversations Through Contextualized Excerpts
Dec 28, 2024Abstract:We focus on enhancing comprehension in small-group recorded conversations, which serve as a medium to bring people together and provide a space for sharing personal stories and experiences on crucial social matters. One way to parse and convey information from these conversations is by sharing highlighted excerpts in subsequent conversations. This can help promote a collective understanding of relevant issues, by highlighting perspectives and experiences to other groups of people who might otherwise be unfamiliar with and thus unable to relate to these experiences. The primary challenge that arises then is that excerpts taken from one conversation and shared in another setting might be missing crucial context or key elements that were previously introduced in the original conversation. This problem is exacerbated when conversations become lengthier and richer in themes and shared experiences. To address this, we explore how Large Language Models (LLMs) can enrich these excerpts by providing socially relevant context. We present approaches for effective contextualization to improve comprehension, readability, and empathy. We show significant improvements in understanding, as assessed through subjective and objective evaluations. While LLMs can offer valuable context, they struggle with capturing key social aspects. We release the Human-annotated Salient Excerpts (HSE) dataset to support future work. Additionally, we show how context-enriched excerpts can provide more focused and comprehensive conversation summaries.
Scaling Concept With Text-Guided Diffusion Models
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:Text-guided diffusion models have revolutionized generative tasks by producing high-fidelity content from text descriptions. They have also enabled an editing paradigm where concepts can be replaced through text conditioning (e.g., a dog to a tiger). In this work, we explore a novel approach: instead of replacing a concept, can we enhance or suppress the concept itself? Through an empirical study, we identify a trend where concepts can be decomposed in text-guided diffusion models. Leveraging this insight, we introduce ScalingConcept, a simple yet effective method to scale decomposed concepts up or down in real input without introducing new elements. To systematically evaluate our approach, we present the WeakConcept-10 dataset, where concepts are imperfect and need to be enhanced. More importantly, ScalingConcept enables a variety of novel zero-shot applications across image and audio domains, including tasks such as canonical pose generation and generative sound highlighting or removal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge