Andrew Perrault
Beyond Length: Context-Aware Expansion and Independence as Developmentally Sensitive Evaluation in Child Utterances
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Evaluating the quality of children's utterances in adult-child dialogue remains challenging due to insufficient context-sensitive metrics. Common proxies such as Mean Length of Utterance (MLU), lexical diversity (vocd-D), and readability indices (Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level, Gunning Fog Index) are dominated by length and ignore conversational context, missing aspects of response quality such as reasoning depth, topic maintenance, and discourse planning. We introduce an LLM-as-a-judge framework that first classifies the Previous Adult Utterance Type and then scores the child's response along two axes: Expansion (contextual elaboration and inferential depth) and Independence (the child's contribution to advancing the discourse). These axes reflect fundamental dimensions in child language development, where Expansion captures elaboration, clause combining, and causal and contrastive connectives. Independence captures initiative, topic control, decreasing reliance on adult scaffolding through growing self-regulation, and audience design. We establish developmental validity by showing age-related patterns and demonstrate predictive value by improving age estimation over common baselines. We further confirm semantic sensitivity by detecting differences tied to discourse relations. Our metrics align with human judgments, enabling large-scale evaluation. This shifts child utterance assessment from simply measuring length to evaluating how meaningfully the child's speech contributes to and advances the conversation within its context.
Learning Provably Correct Distributed Protocols Without Human Knowledge
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Provably correct distributed protocols, which are a critical component of modern distributed systems, are highly challenging to design and have often required decades of human effort. These protocols allow multiple agents to coordinate to come to a common agreement in an environment with uncertainty and failures. We formulate protocol design as a search problem over strategies in a game with imperfect information, and the desired correctness conditions are specified in Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMT). However, standard methods for solving multi-agent games fail to learn correct protocols in this setting, even when the number of agents is small. We propose a learning framework, GGMS, which integrates a specialized variant of Monte Carlo Tree Search with a transformer-based action encoder, a global depth-first search to break out of local minima, and repeated feedback from a model checker. Protocols output by GGMS are verified correct via exhaustive model checking for all executions within the bounded setting. We further prove that, under mild assumptions, the search process is complete: if a correct protocol exists, GGMS will eventually find it. In experiments, we show that GGMS can learn correct protocols for larger settings than existing methods.
VISTA Score: Verification In Sequential Turn-based Assessment
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Hallucination--defined here as generating statements unsupported or contradicted by available evidence or conversational context--remains a major obstacle to deploying conversational AI systems in settings that demand factual reliability. Existing metrics either evaluate isolated responses or treat unverifiable content as errors, limiting their use for multi-turn dialogue. We introduce VISTA (Verification In Sequential Turn-based Assessment), a framework for evaluating conversational factuality through claim-level verification and sequential consistency tracking. VISTA decomposes each assistant turn into atomic factual claims, verifies them against trusted sources and dialogue history, and categorizes unverifiable statements (subjective, contradicted, lacking evidence, or abstaining). Across eight large language models and four dialogue factuality benchmarks (AIS, BEGIN, FAITHDIAL, and FADE), VISTA substantially improves hallucination detection over FACTSCORE and LLM-as-Judge baselines. Human evaluation confirms that VISTA's decomposition improves annotator agreement and reveals inconsistencies in existing benchmarks. By modeling factuality as a dynamic property of conversation, VISTA offers a more transparent, human-aligned measure of truthfulness in dialogue systems.
Cultivating Archipelago of Forests: Evolving Robust Decision Trees through Island Coevolution
Dec 18, 2024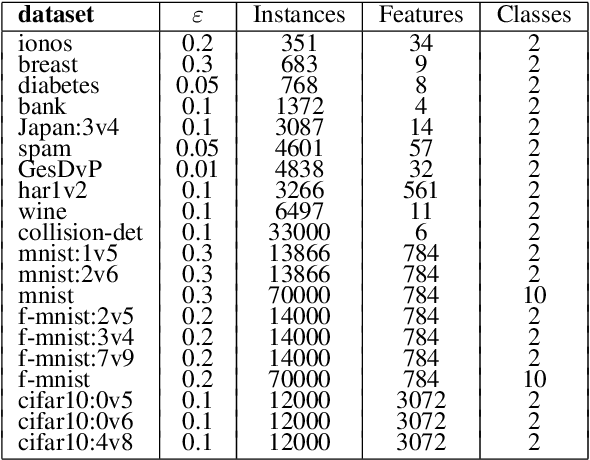
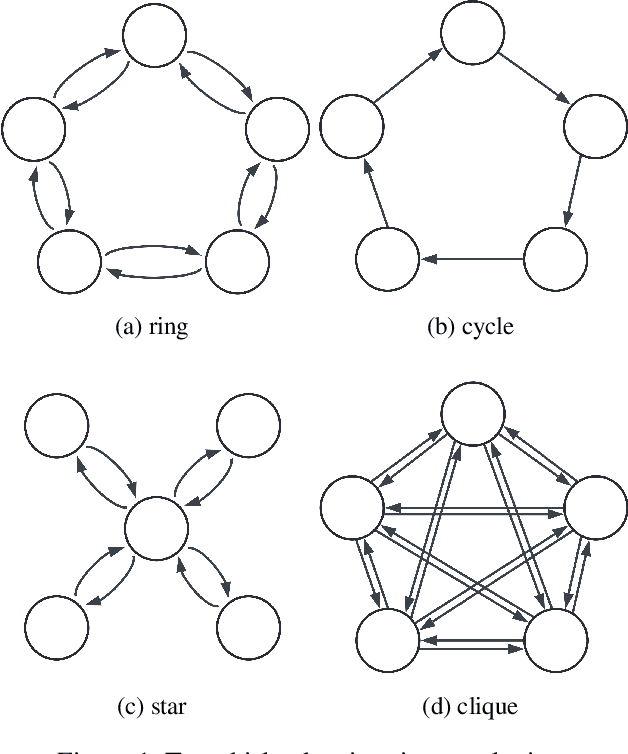
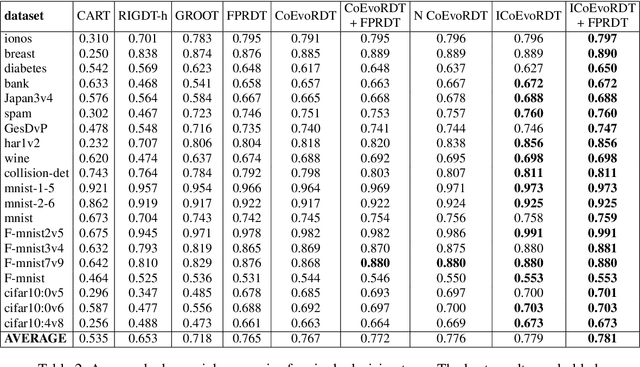
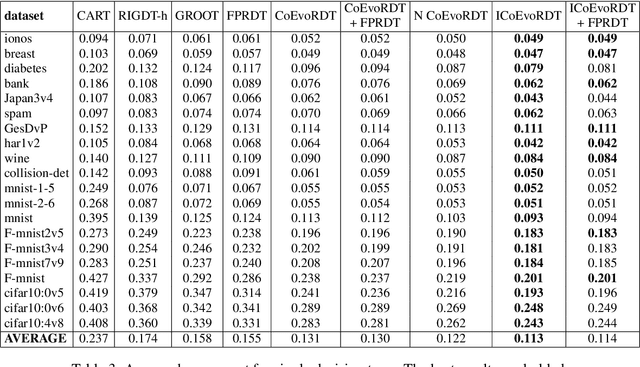
Abstract:Decision trees are widely used in machine learning due to their simplicity and interpretability, but they often lack robustness to adversarial attacks and data perturbations. The paper proposes a novel island-based coevolutionary algorithm (ICoEvoRDF) for constructing robust decision tree ensembles. The algorithm operates on multiple islands, each containing populations of decision trees and adversarial perturbations. The populations on each island evolve independently, with periodic migration of top-performing decision trees between islands. This approach fosters diversity and enhances the exploration of the solution space, leading to more robust and accurate decision tree ensembles. ICoEvoRDF utilizes a popular game theory concept of mixed Nash equilibrium for ensemble weighting, which further leads to improvement in results. ICoEvoRDF is evaluated on 20 benchmark datasets, demonstrating its superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods in optimizing both adversarial accuracy and minimax regret. The flexibility of ICoEvoRDF allows for the integration of decision trees from various existing methods, providing a unified framework for combining diverse solutions. Our approach offers a promising direction for developing robust and interpretable machine learning models
Using RLHF to align speech enhancement approaches to mean-opinion quality scores
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:Objective speech quality measures are typically used to assess speech enhancement algorithms, but it has been shown that they are sub-optimal as learning objectives because they do not always align well with human subjective ratings. This misalignment often results in noticeable distortions and artifacts that cause speech enhancement to be ineffective. To address these issues, we propose a reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) framework to fine-tune an existing speech enhancement approach by optimizing performance using a mean-opinion score (MOS)-based reward model. Our results show that the RLHF-finetuned model has the best performance across different benchmarks for both objective and MOS-based speech quality assessment metrics on the Voicebank+DEMAND dataset. Through ablation studies, we show that both policy gradient loss and supervised MSE loss are important for balanced optimization across the different metrics.
ARES: Alternating Reinforcement Learning and Supervised Fine-Tuning for Enhanced Multi-Modal Chain-of-Thought Reasoning Through Diverse AI Feedback
Jun 25, 2024Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) excel at comprehending human instructions and demonstrate remarkable results across a broad spectrum of tasks. Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and AI Feedback (RLAIF) further refine LLMs by aligning them with specific preferences. These methods primarily use ranking-based feedback for entire generations. With advanced AI models (Teacher), such as GPT-4 and Claude 3 Opus, we can request various types of detailed feedback that are expensive for humans to provide. We propose a two-stage algorithm ARES that Alternates REinforcement Learning (RL) and Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT). First, we request the Teacher to score how much each sentence contributes to solving the problem in a Chain-of-Thought (CoT). This sentence-level feedback allows us to consider individual valuable segments, providing more granular rewards for the RL procedure. Second, we ask the Teacher to correct the wrong reasoning after the RL stage. The RL procedure requires massive efforts for hyperparameter tuning and often generates errors like repetitive words and incomplete sentences. With the correction feedback, we stabilize the RL fine-tuned model through SFT. We conduct experiments on multi-model dataset ScienceQA and A-OKVQA to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposal. ARES rationale reasoning achieves around 70% win rate against baseline models judged by GPT-4o. Additionally, we observe that the improved rationale reasoning leads to a 2.5% increase in inference answer accuracy on average for the multi-modal datasets.
Symmetric Reinforcement Learning Loss for Robust Learning on Diverse Tasks and Model Scales
May 29, 2024Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) training is inherently unstable due to factors such as moving targets and high gradient variance. Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) can introduce additional difficulty. Differing preferences can complicate the alignment process, and prediction errors in a trained reward model can become more severe as the LLM generates unseen outputs. To enhance training robustness, RL has adopted techniques from supervised learning, such as ensembles and layer normalization. In this work, we improve the stability of RL training by adapting the reverse cross entropy (RCE) from supervised learning for noisy data to define a symmetric RL loss. We demonstrate performance improvements across various tasks and scales. We conduct experiments in discrete action tasks (Atari games) and continuous action space tasks (MuJoCo benchmark and Box2D) using Symmetric A2C (SA2C) and Symmetric PPO (SPPO), with and without added noise with especially notable performance in SPPO across different hyperparameters. Furthermore, we validate the benefits of the symmetric RL loss when using SPPO for large language models through improved performance in RLHF tasks, such as IMDB positive sentiment sentiment and TL;DR summarization tasks.
Reinforcement Learning for Fine-tuning Text-to-speech Diffusion Models
May 23, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in generative models have sparked significant interest within the machine learning community. Particularly, diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in synthesizing images and speech. Studies such as those by Lee et al. [19], Black et al. [4], Wang et al. [36], and Fan et al. [8] illustrate that Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) can enhance diffusion models for image synthesis. However, due to architectural differences between these models and those employed in speech synthesis, it remains uncertain whether RLHF could similarly benefit speech synthesis models. In this paper, we explore the practical application of RLHF to diffusion-based text-to-speech synthesis, leveraging the mean opinion score (MOS) as predicted by UTokyo-SaruLab MOS prediction system [29] as a proxy loss. We introduce diffusion model loss-guided RL policy optimization (DLPO) and compare it against other RLHF approaches, employing the NISQA speech quality and naturalness assessment model [21] and human preference experiments for further evaluation. Our results show that RLHF can enhance diffusion-based text-to-speech synthesis models, and, moreover, DLPO can better improve diffusion models in generating natural and high quality speech audios.
The Distributional Reward Critic Architecture for Perturbed-Reward Reinforcement Learning
Jan 11, 2024Abstract:We study reinforcement learning in the presence of an unknown reward perturbation. Existing methodologies for this problem make strong assumptions including reward smoothness, known perturbations, and/or perturbations that do not modify the optimal policy. We study the case of unknown arbitrary perturbations that discretize and shuffle reward space, but have the property that the true reward belongs to the most frequently observed class after perturbation. This class of perturbations generalizes existing classes (and, in the limit, all continuous bounded perturbations) and defeats existing methods. We introduce an adaptive distributional reward critic and show theoretically that it can recover the true rewards under technical conditions. Under the targeted perturbation in discrete and continuous control tasks, we win/tie the highest return in 40/57 settings (compared to 16/57 for the best baseline). Even under the untargeted perturbation, we still win an edge over the baseline designed especially for that setting.
Coevolutionary Algorithm for Building Robust Decision Trees under Minimax Regret
Dec 14, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, there has been growing interest in developing robust machine learning (ML) models that can withstand adversarial attacks, including one of the most widely adopted, efficient, and interpretable ML algorithms-decision trees (DTs). This paper proposes a novel coevolutionary algorithm (CoEvoRDT) designed to create robust DTs capable of handling noisy high-dimensional data in adversarial contexts. Motivated by the limitations of traditional DT algorithms, we leverage adaptive coevolution to allow DTs to evolve and learn from interactions with perturbed input data. CoEvoRDT alternately evolves competing populations of DTs and perturbed features, enabling construction of DTs with desired properties. CoEvoRDT is easily adaptable to various target metrics, allowing the use of tailored robustness criteria such as minimax regret. Furthermore, CoEvoRDT has potential to improve the results of other state-of-the-art methods by incorporating their outcomes (DTs they produce) into the initial population and optimize them in the process of coevolution. Inspired by the game theory, CoEvoRDT utilizes mixed Nash equilibrium to enhance convergence. The method is tested on 20 popular datasets and shows superior performance compared to 4 state-of-the-art algorithms. It outperformed all competing methods on 13 datasets with adversarial accuracy metrics, and on all 20 considered datasets with minimax regret. Strong experimental results and flexibility in choosing the error measure make CoEvoRDT a promising approach for constructing robust DTs in real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge