Micha Elsner
Shortcomings of LLMs for Low-Resource Translation: Retrieval and Understanding are Both the Problem
Jun 21, 2024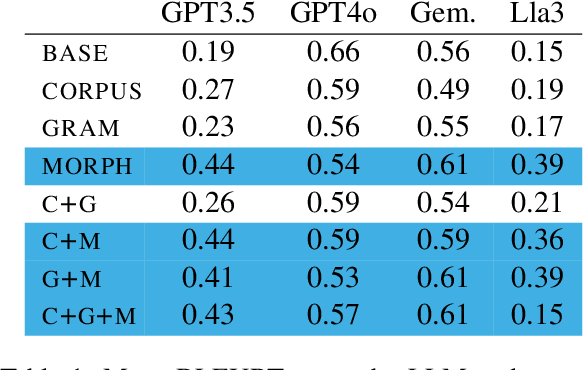
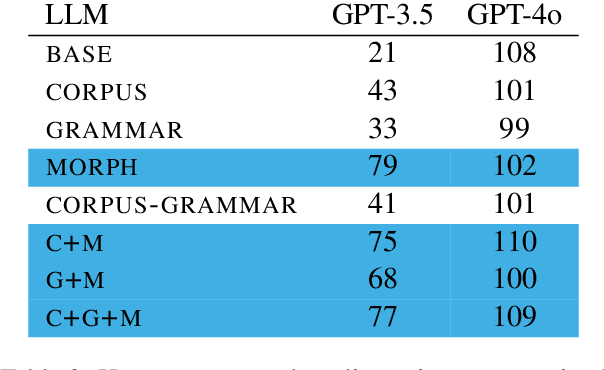
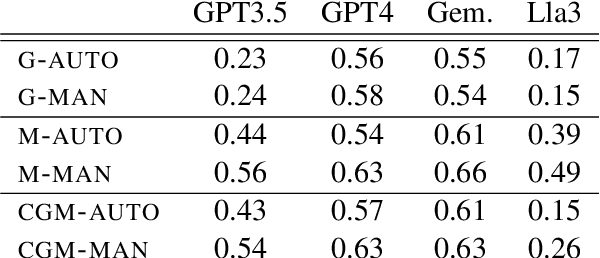
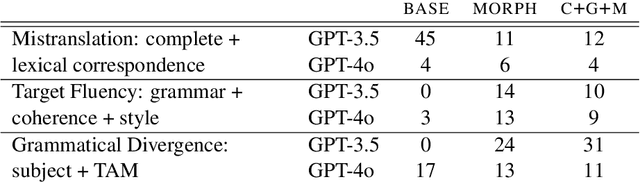
Abstract:This work investigates the in-context learning abilities of pretrained large language models (LLMs) when instructed to translate text from a low-resource language into a high-resource language as part of an automated machine translation pipeline. We conduct a set of experiments translating Southern Quechua to Spanish and examine the informativity of various types of information retrieved from a constrained database of digitized pedagogical materials (dictionaries and grammar lessons) and parallel corpora. Using both automatic and human evaluation of model output, we conduct ablation studies that manipulate (1) context type (morpheme translations, grammar descriptions, and corpus examples), (2) retrieval methods (automated vs. manual), and (3) model type. Our results suggest that even relatively small LLMs are capable of utilizing prompt context for zero-shot low-resource translation when provided a minimally sufficient amount of relevant linguistic information. However, the variable effects of prompt type, retrieval method, model type, and language-specific factors highlight the limitations of using even the best LLMs as translation systems for the majority of the world's 7,000+ languages and their speakers.
Reinforcement Learning for Fine-tuning Text-to-speech Diffusion Models
May 23, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in generative models have sparked significant interest within the machine learning community. Particularly, diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in synthesizing images and speech. Studies such as those by Lee et al. [19], Black et al. [4], Wang et al. [36], and Fan et al. [8] illustrate that Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) can enhance diffusion models for image synthesis. However, due to architectural differences between these models and those employed in speech synthesis, it remains uncertain whether RLHF could similarly benefit speech synthesis models. In this paper, we explore the practical application of RLHF to diffusion-based text-to-speech synthesis, leveraging the mean opinion score (MOS) as predicted by UTokyo-SaruLab MOS prediction system [29] as a proxy loss. We introduce diffusion model loss-guided RL policy optimization (DLPO) and compare it against other RLHF approaches, employing the NISQA speech quality and naturalness assessment model [21] and human preference experiments for further evaluation. Our results show that RLHF can enhance diffusion-based text-to-speech synthesis models, and, moreover, DLPO can better improve diffusion models in generating natural and high quality speech audios.
Exploring How Generative Adversarial Networks Learn Phonological Representations
May 21, 2023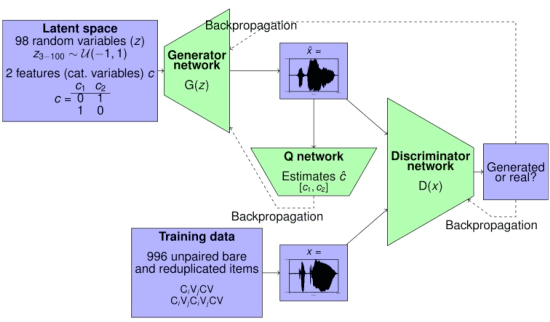
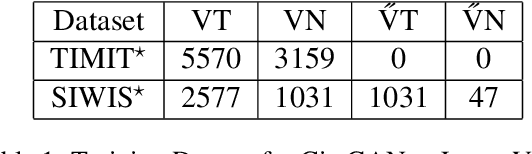
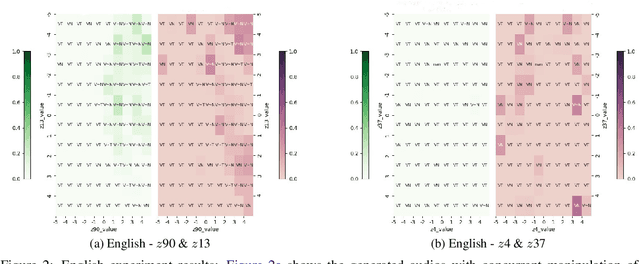
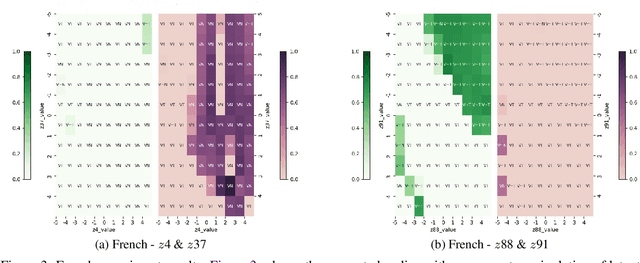
Abstract:This paper explores how Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) learn representations of phonological phenomena. We analyze how GANs encode contrastive and non-contrastive nasality in French and English vowels by applying the ciwGAN architecture (Begus 2021a). Begus claims that ciwGAN encodes linguistically meaningful representations with categorical variables in its latent space and manipulating the latent variables shows an almost one to one corresponding control of the phonological features in ciwGAN's generated outputs. However, our results show an interactive effect of latent variables on the features in the generated outputs, which suggests the learned representations in neural networks are different from the phonological representations proposed by linguists. On the other hand, ciwGAN is able to distinguish contrastive and noncontrastive features in English and French by encoding them differently. Comparing the performance of GANs learning from different languages results in a better understanding of what language specific features contribute to developing language specific phonological representations. We also discuss the role of training data frequencies in phonological feature learning.
Analogy in Contact: Modeling Maltese Plural Inflection
May 20, 2023Abstract:Maltese is often described as having a hybrid morphological system resulting from extensive contact between Semitic and Romance language varieties. Such a designation reflects an etymological divide as much as it does a larger tradition in the literature to consider concatenative and non-concatenative morphological patterns as distinct in the language architecture. Using a combination of computational modeling and information theoretic methods, we quantify the extent to which the phonology and etymology of a Maltese singular noun may predict the morphological process (affixal vs. templatic) as well as the specific plural allomorph (affix or template) relating a singular noun to its associated plural form(s) in the lexicon. The results indicate phonological pressures shape the organization of the Maltese lexicon with predictive power that extends beyond that of a word's etymology, in line with analogical theories of language change in contact.
Privacy Policy Question Answering Assistant: A Query-Guided Extractive Summarization Approach
Sep 29, 2021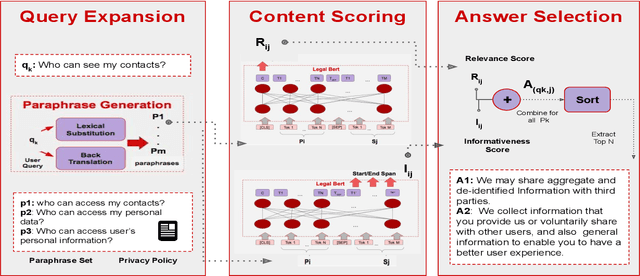
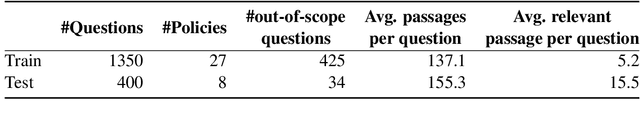
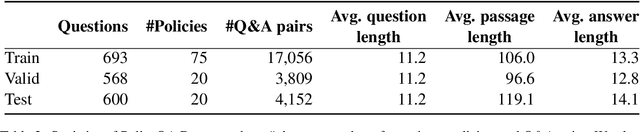
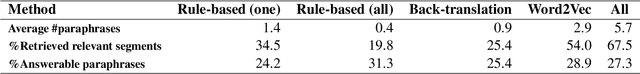
Abstract:Existing work on making privacy policies accessible has explored new presentation forms such as color-coding based on the risk factors or summarization to assist users with conscious agreement. To facilitate a more personalized interaction with the policies, in this work, we propose an automated privacy policy question answering assistant that extracts a summary in response to the input user query. This is a challenging task because users articulate their privacy-related questions in a very different language than the legal language of the policy, making it difficult for the system to understand their inquiry. Moreover, existing annotated data in this domain are limited. We address these problems by paraphrasing to bring the style and language of the user's question closer to the language of privacy policies. Our content scoring module uses the existing in-domain data to find relevant information in the policy and incorporates it in a summary. Our pipeline is able to find an answer for 89% of the user queries in the privacyQA dataset.
Fairness-aware Summarization for Justified Decision-Making
Jul 13, 2021
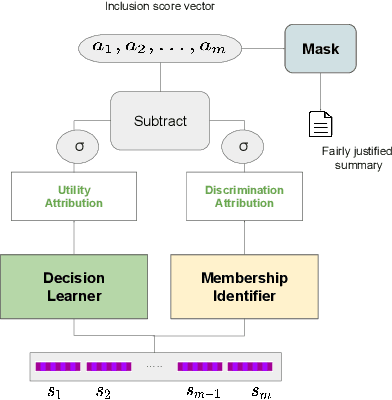
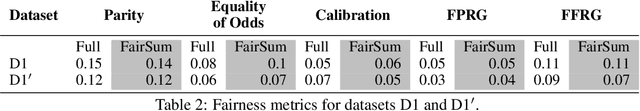
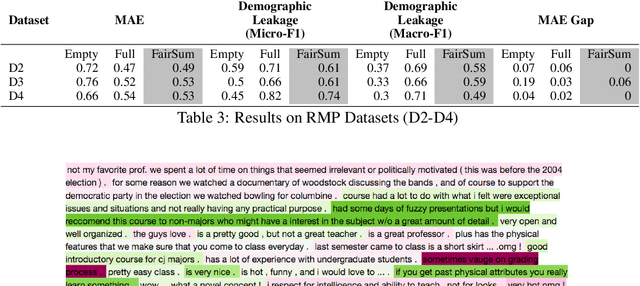
Abstract:In many applications such as recidivism prediction, facility inspection, and benefit assignment, it's important for individuals to know the decision-relevant information for the model's prediction. In addition, the model's predictions should be fairly justified. Essentially, decision-relevant features should provide sufficient information for the predicted outcome and should be independent of the membership of individuals in protected groups such as race and gender. In this work, we focus on the problem of (un)fairness in the justification of the text-based neural models. We tie the explanatory power of the model to fairness in the outcome and propose a fairness-aware summarization mechanism to detect and counteract the bias in such models. Given a potentially biased natural language explanation for a decision, we use a multi-task neural model and an attribution mechanism based on integrated gradients to extract the high-utility and discrimination-free justifications in the form of a summary. The extracted summary is then used for training a model to make decisions for individuals. Results on several real-world datasets suggests that our method: (i) assists users to understand what information is used for the model's decision and (ii) enhances the fairness in outcomes while significantly reducing the demographic leakage.
The Paradigm Discovery Problem
May 04, 2020
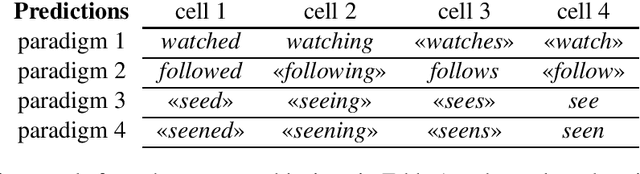
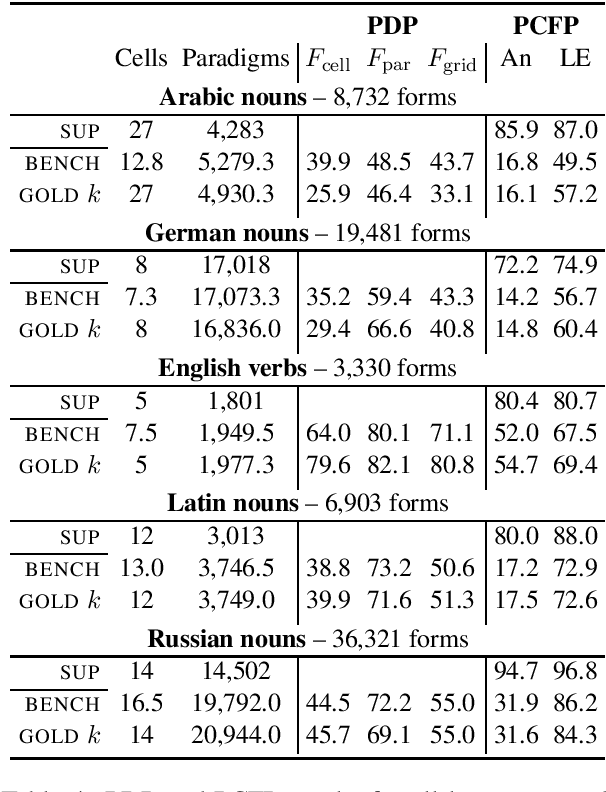
Abstract:This work treats the paradigm discovery problem (PDP), the task of learning an inflectional morphological system from unannotated sentences. We formalize the PDP and develop evaluation metrics for judging systems. Using currently available resources, we construct datasets for the task. We also devise a heuristic benchmark for the PDP and report empirical results on five diverse languages. Our benchmark system first makes use of word embeddings and string similarity to cluster forms by cell and by paradigm. Then, we bootstrap a neural transducer on top of the clustered data to predict words to realize the empty paradigm slots. An error analysis of our system suggests clustering by cell across different inflection classes is the most pressing challenge for future work. Our code and data are available for public use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge