Moniba Keymanesh
An Alternative to FLOPS Regularization to Effectively Productionize SPLADE-Doc
May 21, 2025Abstract:Learned Sparse Retrieval (LSR) models encode text as weighted term vectors, which need to be sparse to leverage inverted index structures during retrieval. SPLADE, the most popular LSR model, uses FLOPS regularization to encourage vector sparsity during training. However, FLOPS regularization does not ensure sparsity among terms - only within a given query or document. Terms with very high Document Frequencies (DFs) substantially increase latency in production retrieval engines, such as Apache Solr, due to their lengthy posting lists. To address the issue of high DFs, we present a new variant of FLOPS regularization: DF-FLOPS. This new regularization technique penalizes the usage of high-DF terms, thereby shortening posting lists and reducing retrieval latency. Unlike other inference-time sparsification methods, such as stopword removal, DF-FLOPS regularization allows for the selective inclusion of high-frequency terms in cases where the terms are truly salient. We find that DF-FLOPS successfully reduces the prevalence of high-DF terms and lowers retrieval latency (around 10x faster) in a production-grade engine while maintaining effectiveness both in-domain (only a 2.2-point drop in MRR@10) and cross-domain (improved performance in 12 out of 13 tasks on which we tested). With retrieval latencies on par with BM25, this work provides an important step towards making LSR practical for deployment in production-grade search engines.
What Makes Data-to-Text Generation Hard for Pretrained Language Models?
May 23, 2022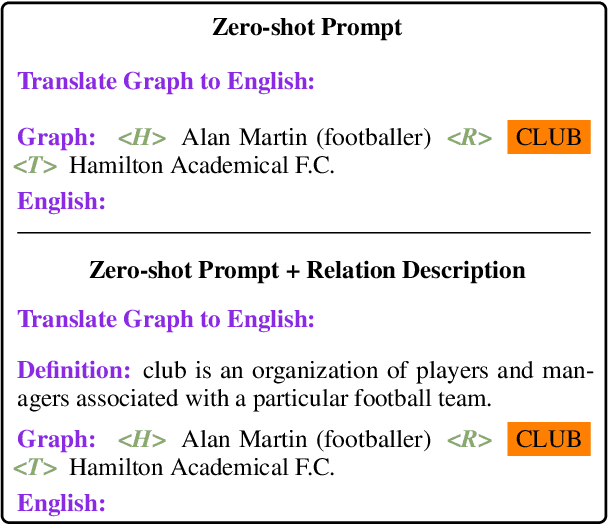
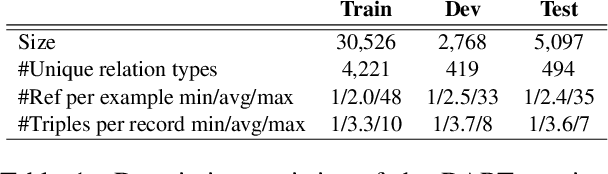
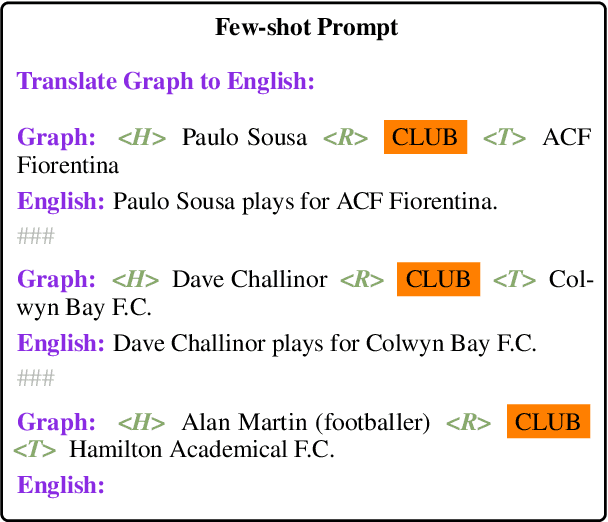
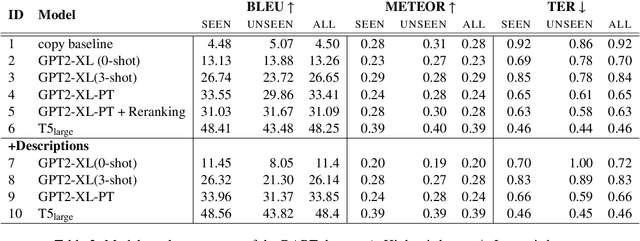
Abstract:Expressing natural language descriptions of structured facts or relations -- data-to-text generation (D2T) -- increases the accessibility of structured knowledge repositories. Previous work shows that pre-trained language models(PLMs) perform remarkably well on this task after fine-tuning on a significant amount of task-specific training data. On the other hand, while auto-regressive PLMs can generalize from a few task examples, their efficacy at D2T is largely unexplored. Furthermore, we have an incomplete understanding of the limits of PLMs on D2T. In this work, we conduct an empirical study of both fine-tuned and auto-regressive PLMs on the DART multi-domain D2T dataset. We consider their performance as a function of the amount of task-specific data and how these data are incorporated into the models: zero and few-shot learning, and fine-tuning of model weights. In addition, we probe the limits of PLMs by measuring performance on subsets of the evaluation data: novel predicates and abstractive test examples. To improve the performance on these subsets, we investigate two techniques: providing predicate descriptions in the context and re-ranking generated candidates by information reflected in the source. Finally, we conduct a human evaluation of model errors and show that D2T generation tasks would benefit from datasets with more careful manual curation.
Privacy Policy Question Answering Assistant: A Query-Guided Extractive Summarization Approach
Sep 29, 2021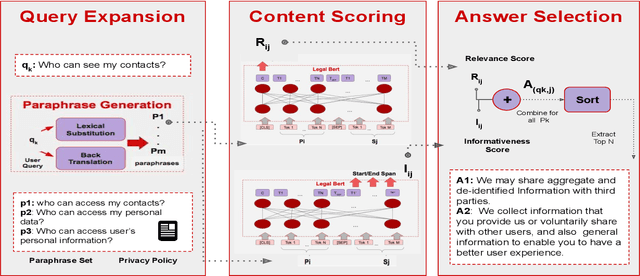
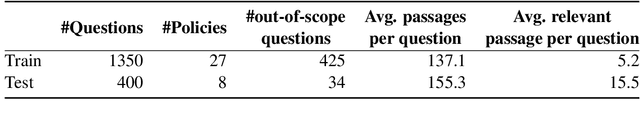
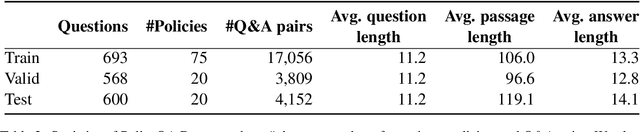
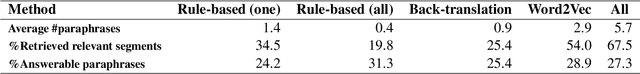
Abstract:Existing work on making privacy policies accessible has explored new presentation forms such as color-coding based on the risk factors or summarization to assist users with conscious agreement. To facilitate a more personalized interaction with the policies, in this work, we propose an automated privacy policy question answering assistant that extracts a summary in response to the input user query. This is a challenging task because users articulate their privacy-related questions in a very different language than the legal language of the policy, making it difficult for the system to understand their inquiry. Moreover, existing annotated data in this domain are limited. We address these problems by paraphrasing to bring the style and language of the user's question closer to the language of privacy policies. Our content scoring module uses the existing in-domain data to find relevant information in the policy and incorporates it in a summary. Our pipeline is able to find an answer for 89% of the user queries in the privacyQA dataset.
Fairness-aware Summarization for Justified Decision-Making
Jul 13, 2021
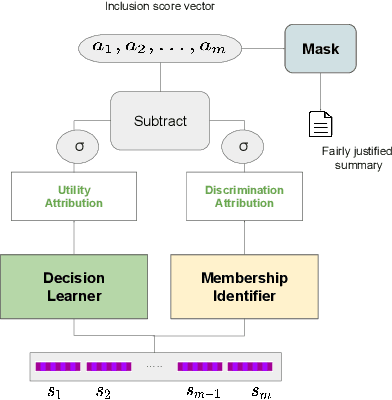
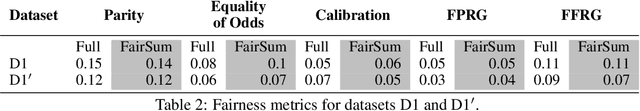
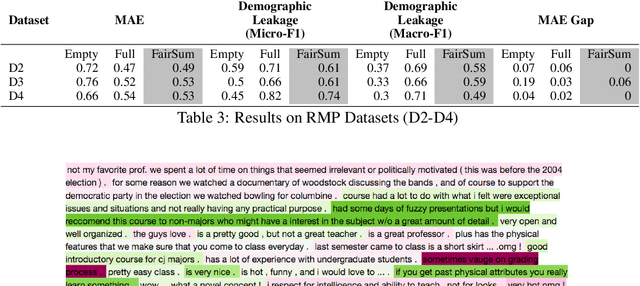
Abstract:In many applications such as recidivism prediction, facility inspection, and benefit assignment, it's important for individuals to know the decision-relevant information for the model's prediction. In addition, the model's predictions should be fairly justified. Essentially, decision-relevant features should provide sufficient information for the predicted outcome and should be independent of the membership of individuals in protected groups such as race and gender. In this work, we focus on the problem of (un)fairness in the justification of the text-based neural models. We tie the explanatory power of the model to fairness in the outcome and propose a fairness-aware summarization mechanism to detect and counteract the bias in such models. Given a potentially biased natural language explanation for a decision, we use a multi-task neural model and an attribution mechanism based on integrated gradients to extract the high-utility and discrimination-free justifications in the form of a summary. The extracted summary is then used for training a model to make decisions for individuals. Results on several real-world datasets suggests that our method: (i) assists users to understand what information is used for the model's decision and (ii) enhances the fairness in outcomes while significantly reducing the demographic leakage.
Transfer Learning for Abstractive Summarization at Controllable Budgets
Feb 18, 2020
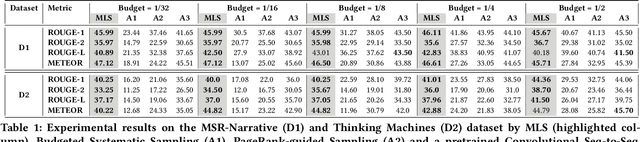
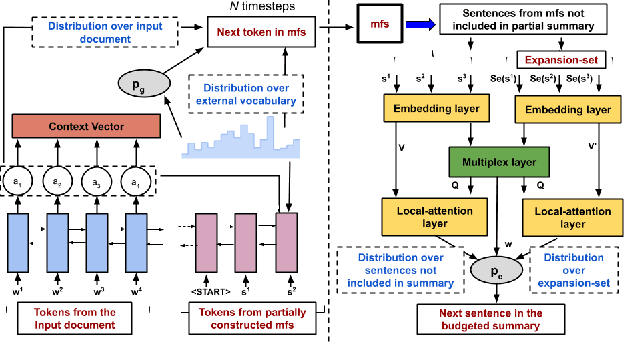
Abstract:Summarizing a document within an allocated budget while maintaining its major concepts is a challenging task. If the budget can take any arbitrary value and not known beforehand, it becomes even more difficult. Most of the existing methods for abstractive summarization, including state-of-the-art neural networks are data intensive. If the number of available training samples becomes limited, they fail to construct high-quality summaries. We propose MLS, an end-to-end framework to generate abstractive summaries with limited training data at arbitrary compression budgets. MLS employs a pair of supervised sequence-to-sequence networks. The first network called the \textit{MFS-Net} constructs a minimal feasible summary by identifying the key concepts of the input document. The second network called the Pointer-Magnifier then generates the final summary from the minimal feasible summary by leveraging an interpretable multi-headed attention model. Experiments on two cross-domain datasets show that MLS outperforms baseline methods over a range of success metrics including ROUGE and METEOR. We observed an improvement of approximately 4% in both metrics over the state-of-art convolutional network at lower budgets. Results from a human evaluation study also establish the effectiveness of MLS in generating complete coherent summaries at arbitrary compression budgets.
Network Representation Learning: Consolidation and Renewed Bearing
May 02, 2019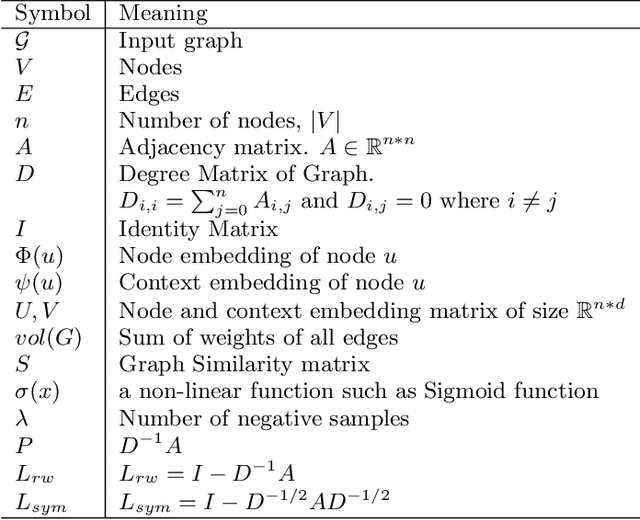
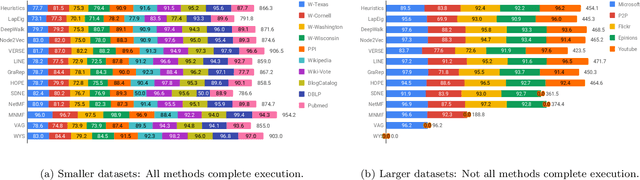

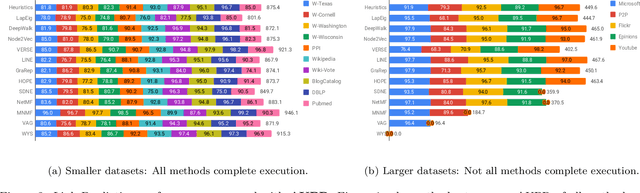
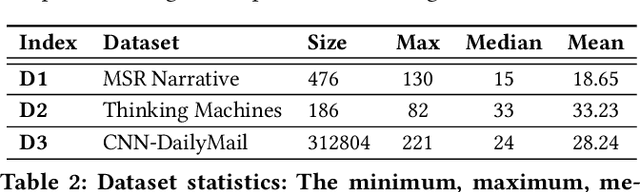
Abstract:Graphs are a natural abstraction for many problems where nodes represent entities and edges represent a relationship across entities. An important area of research that has emerged over the last decade is the use of graphs as a vehicle for non-linear dimensionality reduction in a manner akin to previous efforts based on manifold learning with uses for downstream database processing, machine learning and visualization. In this systematic yet comprehensive experimental survey, we benchmark several popular network representation learning methods operating on two key tasks: link prediction and node classification. We examine the performance of 12 unsupervised embedding methods on 15 datasets. To the best of our knowledge, the scale of our study -- both in terms of the number of methods and number of datasets -- is the largest to date. Our results reveal several key insights about work-to-date in this space. First, we find that certain baseline methods (task-specific heuristics, as well as classic manifold methods) that have often been dismissed or are not considered by previous efforts can compete on certain types of datasets if they are tuned appropriately. Second, we find that recent methods based on matrix factorization offer a small but relatively consistent advantage over alternative methods (e.g., random-walk based methods) from a qualitative standpoint. Specifically, we find that MNMF, a community preserving embedding method, is the most competitive method for the link prediction task. While NetMF is the most competitive baseline for node classification. Third, no single method completely outperforms other embedding methods on both node classification and link prediction tasks. We also present several drill-down analysis that reveals settings under which certain algorithms perform well (e.g., the role of neighborhood context on performance) -- guiding the end-user.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge