Transfer Learning for Abstractive Summarization at Controllable Budgets
Paper and Code
Feb 18, 2020
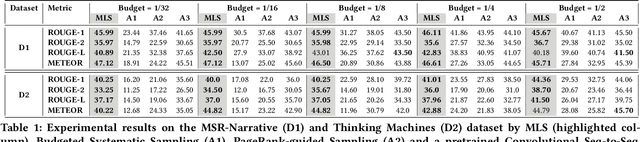
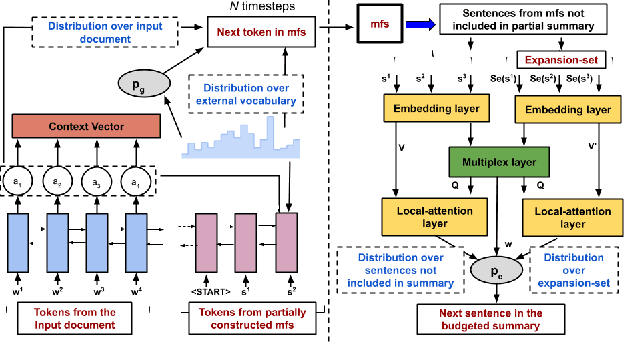
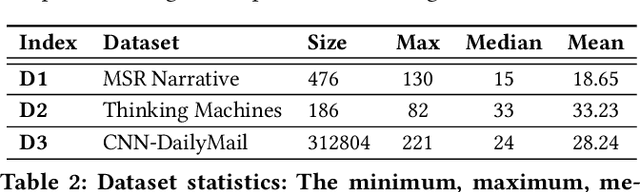
Summarizing a document within an allocated budget while maintaining its major concepts is a challenging task. If the budget can take any arbitrary value and not known beforehand, it becomes even more difficult. Most of the existing methods for abstractive summarization, including state-of-the-art neural networks are data intensive. If the number of available training samples becomes limited, they fail to construct high-quality summaries. We propose MLS, an end-to-end framework to generate abstractive summaries with limited training data at arbitrary compression budgets. MLS employs a pair of supervised sequence-to-sequence networks. The first network called the \textit{MFS-Net} constructs a minimal feasible summary by identifying the key concepts of the input document. The second network called the Pointer-Magnifier then generates the final summary from the minimal feasible summary by leveraging an interpretable multi-headed attention model. Experiments on two cross-domain datasets show that MLS outperforms baseline methods over a range of success metrics including ROUGE and METEOR. We observed an improvement of approximately 4% in both metrics over the state-of-art convolutional network at lower budgets. Results from a human evaluation study also establish the effectiveness of MLS in generating complete coherent summaries at arbitrary compression budgets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge