Wangyou Zhang
Representation-Regularized Convolutional Audio Transformer for Audio Understanding
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Bootstrap-based Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) has achieved remarkable progress in audio understanding. However, existing methods typically operate at a single level of granularity, limiting their ability to model the diverse temporal and spectral structures inherent in complex audio signals. Furthermore, bootstrapping representations from scratch is computationally expensive, often requiring extensive training to converge. In this work, we propose the Convolutional Audio Transformer (CAT), a unified framework designed to address these challenges. First, to capture hierarchical audio features, CAT incorporates a Multi-resolution Block that aggregates information across varying granularities. Second, to enhance training efficiency, we introduce a Representation Regularization objective. Drawing inspiration from generative modeling, this auxiliary task guides the student model by aligning its predictions with high-quality semantic representations from frozen, pre-trained external encoders. Experimental results demonstrate that CAT significantly outperforms baselines on audio understanding benchmarks. Notably, it achieves competitive performance on the AudioSet 20k dataset with 5 times faster convergence than existing methods. Codes and checkpoints will be released soon at https://github.com/realzhouchushu/CAT.
ICASSP 2026 URGENT Speech Enhancement Challenge
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:The ICASSP 2026 URGENT Challenge advances the series by focusing on universal speech enhancement (SE) systems that handle diverse distortions, domains, and input conditions. This overview paper details the challenge's motivation, task definitions, datasets, baseline systems, evaluation protocols, and results. The challenge is divided into two complementary tracks. Track 1 focuses on universal speech enhancement, while Track 2 introduces speech quality assessment for enhanced speech. The challenge attracted over 80 team registrations, with 29 submitting valid entries, demonstrating significant community interest in robust SE technologies.
Improving Speech Enhancement with Multi-Metric Supervision from Learned Quality Assessment
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Speech quality assessment (SQA) aims to predict the perceived quality of speech signals under a wide range of distortions. It is inherently connected to speech enhancement (SE), which seeks to improve speech quality by removing unwanted signal components. While SQA models are widely used to evaluate SE performance, their potential to guide SE training remains underexplored. In this work, we investigate a training framework that leverages a SQA model, trained to predict multiple evaluation metrics from a public SE leaderboard, as a supervisory signal for SE. This approach addresses a key limitation of conventional SE objectives, such as SI-SNR, which often fail to align with perceptual quality and generalize poorly across evaluation metrics. Moreover, it enables training on real-world data where clean references are unavailable. Experiments on both simulated and real-world test sets show that SQA-guided training consistently improves performance across a range of quality metrics.
Interspeech 2025 URGENT Speech Enhancement Challenge
May 29, 2025Abstract:There has been a growing effort to develop universal speech enhancement (SE) to handle inputs with various speech distortions and recording conditions. The URGENT Challenge series aims to foster such universal SE by embracing a broad range of distortion types, increasing data diversity, and incorporating extensive evaluation metrics. This work introduces the Interspeech 2025 URGENT Challenge, the second edition of the series, to explore several aspects that have received limited attention so far: language dependency, universality for more distortion types, data scalability, and the effectiveness of using noisy training data. We received 32 submissions, where the best system uses a discriminative model, while most other competitive ones are hybrid methods. Analysis reveals some key findings: (i) some generative or hybrid approaches are preferred in subjective evaluations over the top discriminative model, and (ii) purely generative SE models can exhibit language dependency.
ASVspoof 5: Design, Collection and Validation of Resources for Spoofing, Deepfake, and Adversarial Attack Detection Using Crowdsourced Speech
Feb 13, 2025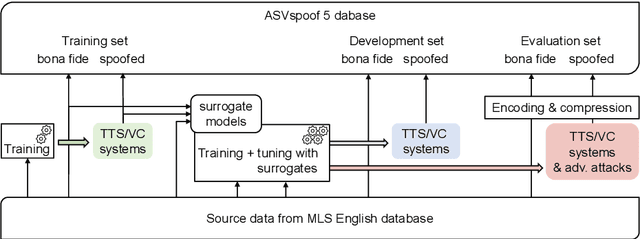

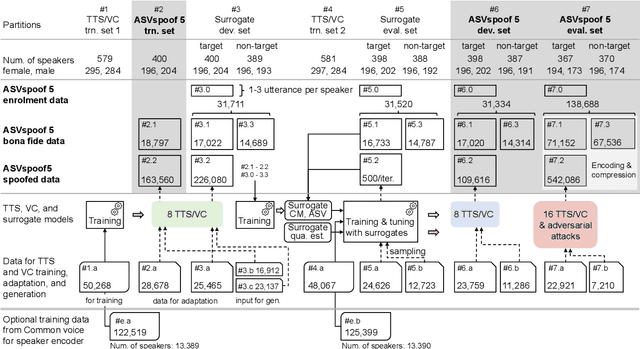
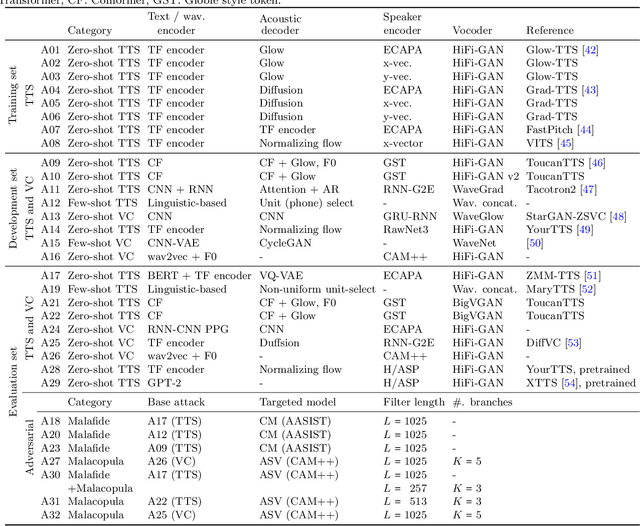
Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake attacks as well as the design of detection solutions. We introduce the ASVspoof 5 database which is generated in crowdsourced fashion from data collected in diverse acoustic conditions (cf. studio-quality data for earlier ASVspoof databases) and from ~2,000 speakers (cf. ~100 earlier). The database contains attacks generated with 32 different algorithms, also crowdsourced, and optimised to varying degrees using new surrogate detection models. Among them are attacks generated with a mix of legacy and contemporary text-to-speech synthesis and voice conversion models, in addition to adversarial attacks which are incorporated for the first time. ASVspoof 5 protocols comprise seven speaker-disjoint partitions. They include two distinct partitions for the training of different sets of attack models, two more for the development and evaluation of surrogate detection models, and then three additional partitions which comprise the ASVspoof 5 training, development and evaluation sets. An auxiliary set of data collected from an additional 30k speakers can also be used to train speaker encoders for the implementation of attack algorithms. Also described herein is an experimental validation of the new ASVspoof 5 database using a set of automatic speaker verification and spoof/deepfake baseline detectors. With the exception of protocols and tools for the generation of spoofed/deepfake speech, the resources described in this paper, already used by participants of the ASVspoof 5 challenge in 2024, are now all freely available to the community.
Advanced Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech for Background Removal and Preservation with Controllable Masked Speech Prediction
Feb 11, 2025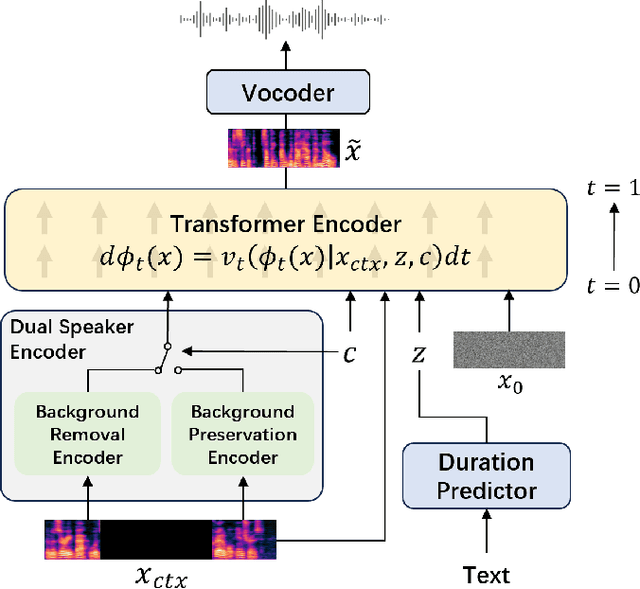
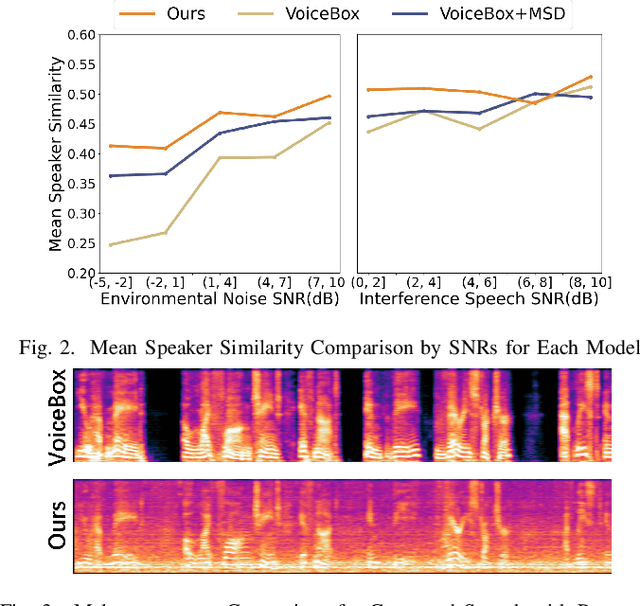
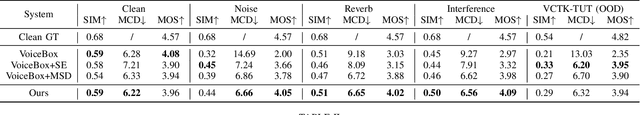
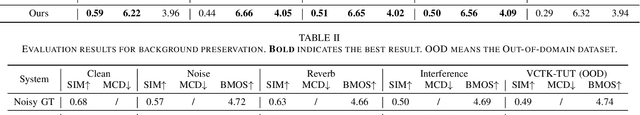
Abstract:The acoustic background plays a crucial role in natural conversation. It provides context and helps listeners understand the environment, but a strong background makes it difficult for listeners to understand spoken words. The appropriate handling of these backgrounds is situation-dependent: Although it may be necessary to remove background to ensure speech clarity, preserving the background is sometimes crucial to maintaining the contextual integrity of the speech. Despite recent advancements in zero-shot Text-to-Speech technologies, current systems often struggle with speech prompts containing backgrounds. To address these challenges, we propose a Controllable Masked Speech Prediction strategy coupled with a dual-speaker encoder, utilizing a task-related control signal to guide the prediction of dual background removal and preservation targets. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach enables precise control over the removal or preservation of background across various acoustic conditions and exhibits strong generalization capabilities in unseen scenarios.
VERSA: A Versatile Evaluation Toolkit for Speech, Audio, and Music
Dec 23, 2024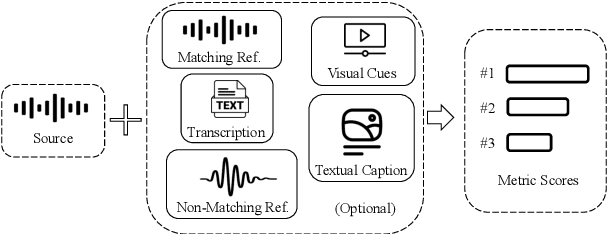
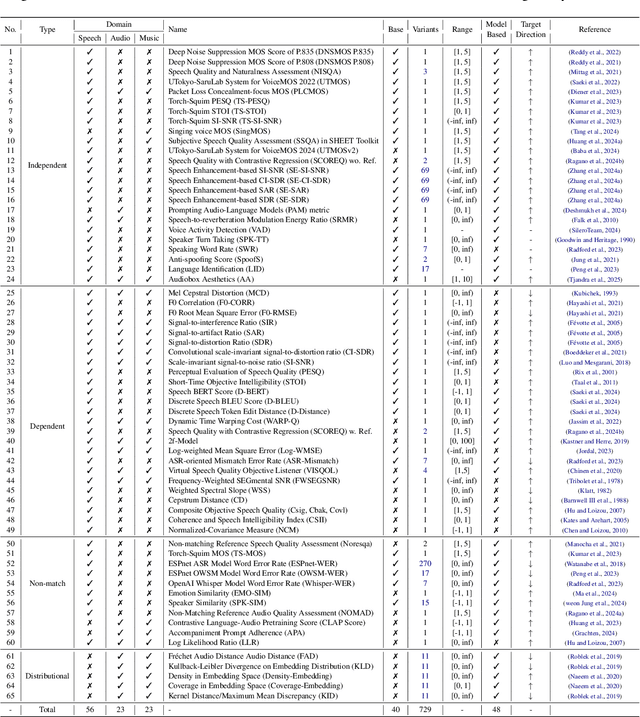

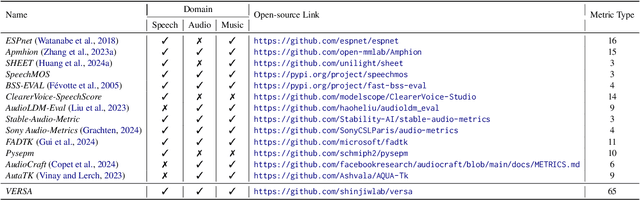
Abstract:In this work, we introduce VERSA, a unified and standardized evaluation toolkit designed for various speech, audio, and music signals. The toolkit features a Pythonic interface with flexible configuration and dependency control, making it user-friendly and efficient. With full installation, VERSA offers 63 metrics with 711 metric variations based on different configurations. These metrics encompass evaluations utilizing diverse external resources, including matching and non-matching reference audio, text transcriptions, and text captions. As a lightweight yet comprehensive toolkit, VERSA is versatile to support the evaluation of a wide range of downstream scenarios. To demonstrate its capabilities, this work highlights example use cases for VERSA, including audio coding, speech synthesis, speech enhancement, singing synthesis, and music generation. The toolkit is available at https://github.com/shinjiwlab/versa.
Scale This, Not That: Investigating Key Dataset Attributes for Efficient Speech Enhancement Scaling
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Recent speech enhancement models have shown impressive performance gains by scaling up model complexity and training data. However, the impact of dataset variability (e.g. text, language, speaker, and noise) has been underexplored. Analyzing each attribute individually is often challenging, as multiple attributes are usually entangled in commonly used datasets, posing a significant obstacle in understanding the distinct contributions of each attribute to the model's performance. To address this challenge, we propose a generation-training-evaluation framework that leverages zero-shot text-to-speech systems to investigate the impact of controlled attribute variations on speech enhancement performance. It enables us to synthesize training datasets in a scalable manner while carefully altering each attribute. Based on the proposed framework, we analyze the scaling effects of various dataset attributes on the performance of both discriminative and generative SE models. Extensive experiments on multi-domain corpora imply that acoustic attributes (e.g., speaker and noise) are much more important to current speech enhancement models than semantic attributes (e.g., language and text), offering new insights for future research.
Text-To-Speech Synthesis In The Wild
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:Text-to-speech (TTS) systems are traditionally trained using modest databases of studio-quality, prompted or read speech collected in benign acoustic environments such as anechoic rooms. The recent literature nonetheless shows efforts to train TTS systems using data collected in the wild. While this approach allows for the use of massive quantities of natural speech, until now, there are no common datasets. We introduce the TTS In the Wild (TITW) dataset, the result of a fully automated pipeline, in this case, applied to the VoxCeleb1 dataset commonly used for speaker recognition. We further propose two training sets. TITW-Hard is derived from the transcription, segmentation, and selection of VoxCeleb1 source data. TITW-Easy is derived from the additional application of enhancement and additional data selection based on DNSMOS. We show that a number of recent TTS models can be trained successfully using TITW-Easy, but that it remains extremely challenging to produce similar results using TITW-Hard. Both the dataset and protocols are publicly available and support the benchmarking of TTS systems trained using TITW data.
Towards Robust Speech Representation Learning for Thousands of Languages
Jul 02, 2024Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) has helped extend speech technologies to more languages by reducing the need for labeled data. However, models are still far from supporting the world's 7000+ languages. We propose XEUS, a Cross-lingual Encoder for Universal Speech, trained on over 1 million hours of data across 4057 languages, extending the language coverage of SSL models 4-fold. We combine 1 million hours of speech from existing publicly accessible corpora with a newly created corpus of 7400+ hours from 4057 languages, which will be publicly released. To handle the diverse conditions of multilingual speech data, we augment the typical SSL masked prediction approach with a novel dereverberation objective, increasing robustness. We evaluate XEUS on several benchmarks, and show that it consistently outperforms or achieves comparable results to state-of-the-art (SOTA) SSL models across a variety of tasks. XEUS sets a new SOTA on the ML-SUPERB benchmark: it outperforms MMS 1B and w2v-BERT 2.0 v2 by 0.8% and 4.4% respectively, despite having less parameters or pre-training data. Checkpoints, code, and data are found in https://www.wavlab.org/activities/2024/xeus/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge