Yanmin Qian
Representation-Regularized Convolutional Audio Transformer for Audio Understanding
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Bootstrap-based Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) has achieved remarkable progress in audio understanding. However, existing methods typically operate at a single level of granularity, limiting their ability to model the diverse temporal and spectral structures inherent in complex audio signals. Furthermore, bootstrapping representations from scratch is computationally expensive, often requiring extensive training to converge. In this work, we propose the Convolutional Audio Transformer (CAT), a unified framework designed to address these challenges. First, to capture hierarchical audio features, CAT incorporates a Multi-resolution Block that aggregates information across varying granularities. Second, to enhance training efficiency, we introduce a Representation Regularization objective. Drawing inspiration from generative modeling, this auxiliary task guides the student model by aligning its predictions with high-quality semantic representations from frozen, pre-trained external encoders. Experimental results demonstrate that CAT significantly outperforms baselines on audio understanding benchmarks. Notably, it achieves competitive performance on the AudioSet 20k dataset with 5 times faster convergence than existing methods. Codes and checkpoints will be released soon at https://github.com/realzhouchushu/CAT.
SLM-SS: Speech Language Model for Generative Speech Separation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Speech separation (SS) has advanced significantly with neural network-based methods, showing improved performance on signal-level metrics. However, these methods often struggle to maintain speech intelligibility in the separated signals, which can negatively affect the performance of downstream tasks such as speech recognition. In this work, we propose SLM-SS, a novel approach that applies speech language models to SS, aiming to enhance the intelligibility and coherence of the separated signals. We frame SS as discrete multi-codebook sequence generation, using Encoder-Decoder models to map quantized speech mixtures to target tokens. In addition to the autoregressive modeling strategy, we introduce a non-autoregressive model to improve decoding efficiency for residual tokens. Experimental results on the LibriMix dataset demonstrate that our approach shows significantly better preservation of speech intelligibility, leading to improved linguistic consistency in a variety of downstream tasks compared to existing approaches.
DeepASMR: LLM-Based Zero-Shot ASMR Speech Generation for Anyone of Any Voice
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:While modern Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems achieve high fidelity for read-style speech, they struggle to generate Autonomous Sensory Meridian Response (ASMR), a specialized, low-intensity speech style essential for relaxation. The inherent challenges include ASMR's subtle, often unvoiced characteristics and the demand for zero-shot speaker adaptation. In this paper, we introduce DeepASMR, the first framework designed for zero-shot ASMR generation. We demonstrate that a single short snippet of a speaker's ordinary, read-style speech is sufficient to synthesize high-fidelity ASMR in their voice, eliminating the need for whispered training data from the target speaker. Methodologically, we first identify that discrete speech tokens provide a soft factorization of ASMR style from speaker timbre. Leveraging this insight, we propose a two-stage pipeline incorporating a Large Language Model (LLM) for content-style encoding and a flow-matching acoustic decoder for timbre reconstruction. Furthermore, we contribute DeepASMR-DB, a comprehensive 670-hour English-Chinese multi-speaker ASMR speech corpus, and introduce a novel evaluation protocol integrating objective metrics, human listening tests, LLM-based scoring and unvoiced speech analysis. Extensive experiments confirm that DeepASMR achieves state-of-the-art naturalness and style fidelity in ASMR generation for anyone of any voice, while maintaining competitive performance on normal speech synthesis.
ICASSP 2026 URGENT Speech Enhancement Challenge
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:The ICASSP 2026 URGENT Challenge advances the series by focusing on universal speech enhancement (SE) systems that handle diverse distortions, domains, and input conditions. This overview paper details the challenge's motivation, task definitions, datasets, baseline systems, evaluation protocols, and results. The challenge is divided into two complementary tracks. Track 1 focuses on universal speech enhancement, while Track 2 introduces speech quality assessment for enhanced speech. The challenge attracted over 80 team registrations, with 29 submitting valid entries, demonstrating significant community interest in robust SE technologies.
A Data-Centric Approach to Generalizable Speech Deepfake Detection
Dec 24, 2025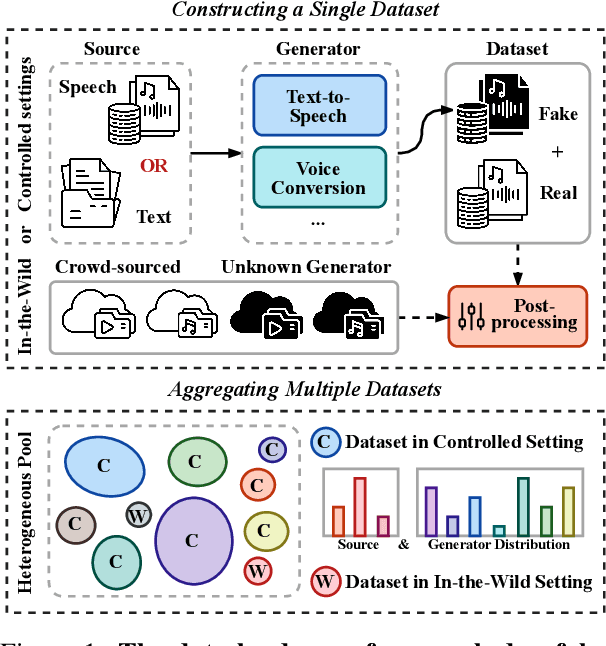
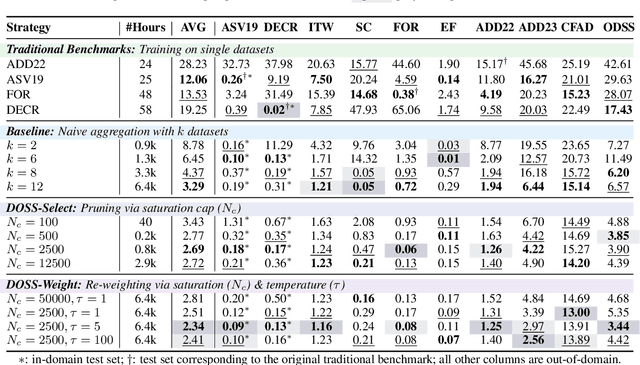
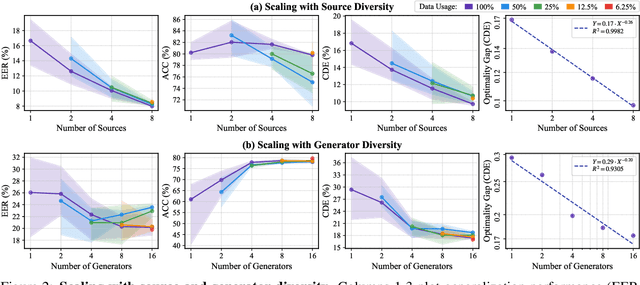
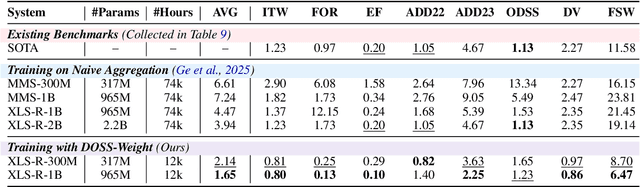
Abstract:Achieving robust generalization in speech deepfake detection (SDD) remains a primary challenge, as models often fail to detect unseen forgery methods. While research has focused on model-centric and algorithm-centric solutions, the impact of data composition is often underexplored. This paper proposes a data-centric approach, analyzing the SDD data landscape from two practical perspectives: constructing a single dataset and aggregating multiple datasets. To address the first perspective, we conduct a large-scale empirical study to characterize the data scaling laws for SDD, quantifying the impact of source and generator diversity. To address the second, we propose the Diversity-Optimized Sampling Strategy (DOSS), a principled framework for mixing heterogeneous data with two implementations: DOSS-Select (pruning) and DOSS-Weight (re-weighting). Our experiments show that DOSS-Select outperforms the naive aggregation baseline while using only 3% of the total available data. Furthermore, our final model, trained on a 12k-hour curated data pool using the optimal DOSS-Weight strategy, achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming large-scale baselines with greater data and model efficiency on both public benchmarks and a new challenge set of various commercial APIs.
USE: A Unified Model for Universal Sound Separation and Extraction
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Sound separation (SS) and target sound extraction (TSE) are fundamental techniques for addressing complex acoustic scenarios. While existing SS methods struggle with determining the unknown number of sound sources, TSE approaches require precisely specified clues to achieve optimal performance. This paper proposes a unified framework that synergistically combines SS and TSE to overcome their individual limitations. Our architecture employs two complementary components: 1) An Encoder-Decoder Attractor (EDA) network that automatically infers both the source count and corresponding acoustic clues for SS, and 2) A multi-modal fusion network that precisely interprets diverse user-provided clues (acoustic, semantic, or visual) for TSE. Through joint training with cross-task consistency constraints, we establish a unified latent space that bridges both paradigms. During inference, the system adaptively operates in either fully autonomous SS mode or clue-driven TSE mode. Experiments demonstrate remarkable performance in both tasks, with notable improvements of 1.4 dB SDR improvement in SS compared to baseline and 86\% TSE accuracy.
What Does the Speaker Embedding Encode?
Dec 20, 2025



Abstract:Developing a good speaker embedding has received tremendous interest in the speech community, with representations such as i-vector and d-vector demonstrating remarkable performance across various tasks. Despite their widespread adoption, a fundamental question remains largely unexplored: what properties are actually encoded in these embeddings? To address this gap, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of three prominent speaker embedding methods: i-vector, d-vector, and RNN/LSTM-based sequence-vector (s-vector). Through carefully designed classification tasks, we systematically investigate their encoding capabilities across multiple dimensions, including speaker identity, gender, speaking rate, text content, word order, and channel information. Our analysis reveals distinct strengths and limitations of each embedding type: i-vector excels at speaker discrimination but encodes limited sequential information; s-vector captures text content and word order effectively but struggles with speaker identity; d-vector shows balanced performance but loses sequential information through averaging. Based on these insights, we propose a novel multi-task learning framework that integrates i-vector and s-vector, resulting in a new speaker embedding (i-s-vector) that combines their complementary advantages. Experimental results on RSR2015 demonstrate that the proposed i-s-vector achieves more than 50% EER reduction compared to the i-vector baseline on content mismatch trials, validating the effectiveness of our approach.
Exploring Self-Supervised Audio Models for Generalized Anomalous Sound Detection
Aug 17, 2025
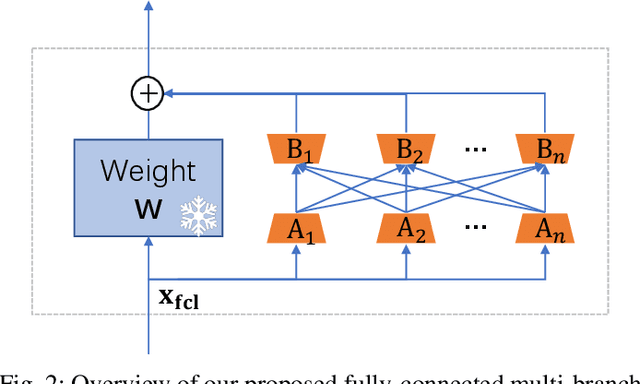
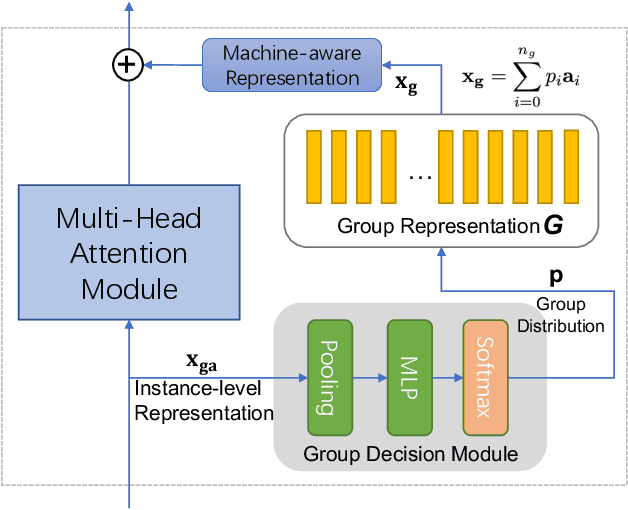
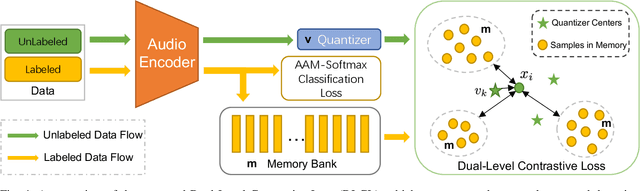
Abstract:Machine anomalous sound detection (ASD) is a valuable technique across various applications. However, its generalization performance is often limited due to challenges in data collection and the complexity of acoustic environments. Inspired by the success of large pre-trained models in numerous fields, this paper introduces a robust ASD model that leverages self-supervised pre-trained models trained on large-scale speech and audio datasets. Although there are inconsistencies between the pre-training datasets and the ASD task, our findings indicate that pre-training still provides substantial benefits for ASD. To mitigate overfitting and retain learned knowledge when fine-tuning with limited data, we explore Fully-Connected Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) as an alternative to full fine-tuning. Additionally, we propose a Machine-aware Group Adapter module, which enables the model to capture differences between various machines within a unified framework, thereby enhancing the generalization performance of ASD systems. To address the challenge of missing attribute labels, we design a novel objective function that dynamically clusters unattributed data using vector quantization and optimizes through a dual-level contrastive learning loss. The proposed methods are evaluated on all benchmark datasets, including the DCASE 2020-2024 five ASD challenges, and the experimental results show significant improvements of our new approach and demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed strategies.
FISHER: A Foundation Model for Multi-Modal Industrial Signal Comprehensive Representation
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:With the rapid deployment of SCADA systems, how to effectively analyze industrial signals and detect abnormal states is an urgent need for the industry. Due to the significant heterogeneity of these signals, which we summarize as the M5 problem, previous works only focus on small sub-problems and employ specialized models, failing to utilize the synergies between modalities and the powerful scaling law. However, we argue that the M5 signals can be modeled in a unified manner due to the intrinsic similarity. As a result, we propose FISHER, a Foundation model for multi-modal Industrial Signal compreHEnsive Representation. To support arbitrary sampling rates, FISHER considers the increment of sampling rate as the concatenation of sub-band information. Specifically, FISHER takes the STFT sub-band as the modeling unit and adopts a teacher student SSL framework for pre-training. We also develop the RMIS benchmark, which evaluates the representations of M5 industrial signals on multiple health management tasks. Compared with top SSL models, FISHER showcases versatile and outstanding capabilities with a general performance gain up to 5.03%, along with much more efficient scaling curves. We also investigate the scaling law on downstream tasks and derive potential avenues for future works. FISHER is now open-sourced on https://github.com/jianganbai/FISHER
From Sharpness to Better Generalization for Speech Deepfake Detection
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Generalization remains a critical challenge in speech deepfake detection (SDD). While various approaches aim to improve robustness, generalization is typically assessed through performance metrics like equal error rate without a theoretical framework to explain model performance. This work investigates sharpness as a theoretical proxy for generalization in SDD. We analyze how sharpness responds to domain shifts and find it increases in unseen conditions, indicating higher model sensitivity. Based on this, we apply Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) to reduce sharpness explicitly, leading to better and more stable performance across diverse unseen test sets. Furthermore, correlation analysis confirms a statistically significant relationship between sharpness and generalization in most test settings. These findings suggest that sharpness can serve as a theoretical indicator for generalization in SDD and that sharpness-aware training offers a promising strategy for improving robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge