Junichi Yamagishi
Self Voice Conversion as an Attack against Neural Audio Watermarking
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Audio watermarking embeds auxiliary information into speech while maintaining speaker identity, linguistic content, and perceptual quality. Although recent advances in neural and digital signal processing-based watermarking methods have improved imperceptibility and embedding capacity, robustness is still primarily assessed against conventional distortions such as compression, additive noise, and resampling. However, the rise of deep learning-based attacks introduces novel and significant threats to watermark security. In this work, we investigate self voice conversion as a universal, content-preserving attack against audio watermarking systems. Self voice conversion remaps a speaker's voice to the same identity while altering acoustic characteristics through a voice conversion model. We demonstrate that this attack severely degrades the reliability of state-of-the-art watermarking approaches and highlight its implications for the security of modern audio watermarking techniques.
The Third VoicePrivacy Challenge: Preserving Emotional Expressiveness and Linguistic Content in Voice Anonymization
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:We present results and analyses from the third VoicePrivacy Challenge held in 2024, which focuses on advancing voice anonymization technologies. The task was to develop a voice anonymization system for speech data that conceals a speaker's voice identity while preserving linguistic content and emotional state. We provide a systematic overview of the challenge framework, including detailed descriptions of the anonymization task and datasets used for both system development and evaluation. We outline the attack model and objective evaluation metrics for assessing privacy protection (concealing speaker voice identity) and utility (content and emotional state preservation). We describe six baseline anonymization systems and summarize the innovative approaches developed by challenge participants. Finally, we provide key insights and observations to guide the design of future VoicePrivacy challenges and identify promising directions for voice anonymization research.
ASVspoof 5: Evaluation of Spoofing, Deepfake, and Adversarial Attack Detection Using Crowdsourced Speech
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake detection solutions. A significant change from previous challenge editions is a new crowdsourced database collected from a substantially greater number of speakers under diverse recording conditions, and a mix of cutting-edge and legacy generative speech technology. With the new database described elsewhere, we provide in this paper an overview of the ASVspoof 5 challenge results for the submissions of 53 participating teams. While many solutions perform well, performance degrades under adversarial attacks and the application of neural encoding/compression schemes. Together with a review of post-challenge results, we also report a study of calibration in addition to other principal challenges and outline a road-map for the future of ASVspoof.
Human perception of audio deepfakes: the role of language and speaking style
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Audio deepfakes have reached a level of realism that makes it increasingly difficult to distinguish between human and artificial voices, which poses risks such as identity theft or spread of disinformation. Despite these concerns, research on humans' ability to identify deepfakes is limited, with most studies focusing on English and very few exploring the reasons behind listeners' perceptual decisions. This study addresses this gap through a perceptual experiment in which 54 listeners (28 native Spanish speakers and 26 native Japanese speakers) classified voices as natural or synthetic, and justified their choices. The experiment included 80 stimuli (50% artificial), organized according to three variables: language (Spanish/Japanese), speech style (audiobooks/interviews), and familiarity with the voice (familiar/unfamiliar). The goal was to examine how these variables influence detection and to analyze qualitatively the reasoning behind listeners' perceptual decisions. Results indicate an average accuracy of 59.11%, with higher performance on authentic samples. Judgments of vocal naturalness rely on a combination of linguistic and non-linguistic cues. Comparing Japanese and Spanish listeners, our qualitative analysis further reveals both shared cues and notable cross-linguistic differences in how listeners conceptualize the "humanness" of speech. Overall, participants relied primarily on suprasegmental and higher-level or extralinguistic characteristics - such as intonation, rhythm, fluency, pauses, speed, breathing, and laughter - over segmental features. These findings underscore the complexity of human perceptual strategies in distinguishing natural from artificial speech and align partly with prior research emphasizing the importance of prosody and phenomena typical of spontaneous speech, such as disfluencies.
From Sharpness to Better Generalization for Speech Deepfake Detection
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Generalization remains a critical challenge in speech deepfake detection (SDD). While various approaches aim to improve robustness, generalization is typically assessed through performance metrics like equal error rate without a theoretical framework to explain model performance. This work investigates sharpness as a theoretical proxy for generalization in SDD. We analyze how sharpness responds to domain shifts and find it increases in unseen conditions, indicating higher model sensitivity. Based on this, we apply Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) to reduce sharpness explicitly, leading to better and more stable performance across diverse unseen test sets. Furthermore, correlation analysis confirms a statistically significant relationship between sharpness and generalization in most test settings. These findings suggest that sharpness can serve as a theoretical indicator for generalization in SDD and that sharpness-aware training offers a promising strategy for improving robustness.
Quantifying Source Speaker Leakage in One-to-One Voice Conversion
Apr 22, 2025
Abstract:Using a multi-accented corpus of parallel utterances for use with commercial speech devices, we present a case study to show that it is possible to quantify a degree of confidence about a source speaker's identity in the case of one-to-one voice conversion. Following voice conversion using a HiFi-GAN vocoder, we compare information leakage for a range speaker characteristics; assuming a "worst-case" white-box scenario, we quantify our confidence to perform inference and narrow the pool of likely source speakers, reinforcing the regulatory obligation and moral duty that providers of synthetic voices have to ensure the privacy of their speakers' data.
QualiSpeech: A Speech Quality Assessment Dataset with Natural Language Reasoning and Descriptions
Mar 26, 2025



Abstract:This paper explores a novel perspective to speech quality assessment by leveraging natural language descriptions, offering richer, more nuanced insights than traditional numerical scoring methods. Natural language feedback provides instructive recommendations and detailed evaluations, yet existing datasets lack the comprehensive annotations needed for this approach. To bridge this gap, we introduce QualiSpeech, a comprehensive low-level speech quality assessment dataset encompassing 11 key aspects and detailed natural language comments that include reasoning and contextual insights. Additionally, we propose the QualiSpeech Benchmark to evaluate the low-level speech understanding capabilities of auditory large language models (LLMs). Experimental results demonstrate that finetuned auditory LLMs can reliably generate detailed descriptions of noise and distortion, effectively identifying their types and temporal characteristics. The results further highlight the potential for incorporating reasoning to enhance the accuracy and reliability of quality assessments. The dataset will be released at https://huggingface.co/datasets/tsinghua-ee/QualiSpeech.
Good practices for evaluation of synthesized speech
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:This document is provided as a guideline for reviewers of papers about speech synthesis. We outline some best practices and common pitfalls for papers about speech synthesis, with a particular focus on evaluation. We also recommend that reviewers check the guidelines for authors written in the paper kit and consider those as reviewing criteria as well. This is intended to be a living document, and it will be updated as we receive comments and feedback from readers. We note that this document is meant to provide guidance only, and that reviewers should ultimately use their own discretion when evaluating papers.
Towards Automated Fact-Checking of Real-World Claims: Exploring Task Formulation and Assessment with LLMs
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:Fact-checking is necessary to address the increasing volume of misinformation. Traditional fact-checking relies on manual analysis to verify claims, but it is slow and resource-intensive. This study establishes baseline comparisons for Automated Fact-Checking (AFC) using Large Language Models (LLMs) across multiple labeling schemes (binary, three-class, five-class) and extends traditional claim verification by incorporating analysis, verdict classification, and explanation in a structured setup to provide comprehensive justifications for real-world claims. We evaluate Llama-3 models of varying sizes (3B, 8B, 70B) on 17,856 claims collected from PolitiFact (2007-2024) using evidence retrieved via restricted web searches. We utilize TIGERScore as a reference-free evaluation metric to score the justifications. Our results show that larger LLMs consistently outperform smaller LLMs in classification accuracy and justification quality without fine-tuning. We find that smaller LLMs in a one-shot scenario provide comparable task performance to fine-tuned Small Language Models (SLMs) with large context sizes, while larger LLMs consistently surpass them. Evidence integration improves performance across all models, with larger LLMs benefiting most. Distinguishing between nuanced labels remains challenging, emphasizing the need for further exploration of labeling schemes and alignment with evidences. Our findings demonstrate the potential of retrieval-augmented AFC with LLMs.
ASVspoof 5: Design, Collection and Validation of Resources for Spoofing, Deepfake, and Adversarial Attack Detection Using Crowdsourced Speech
Feb 13, 2025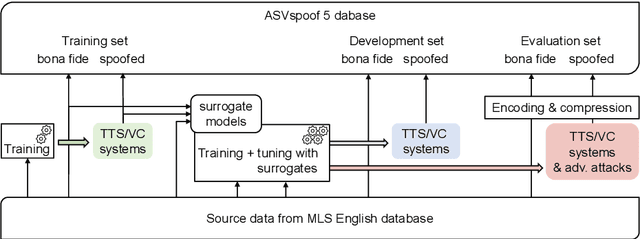

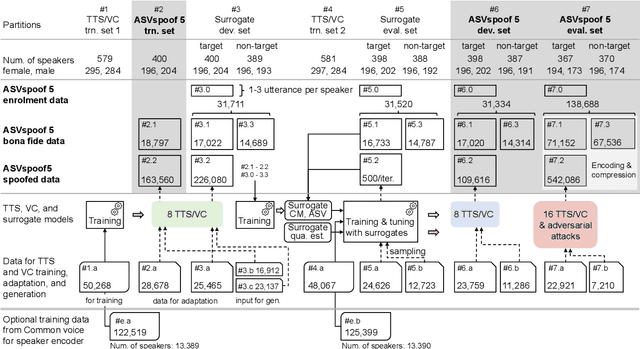
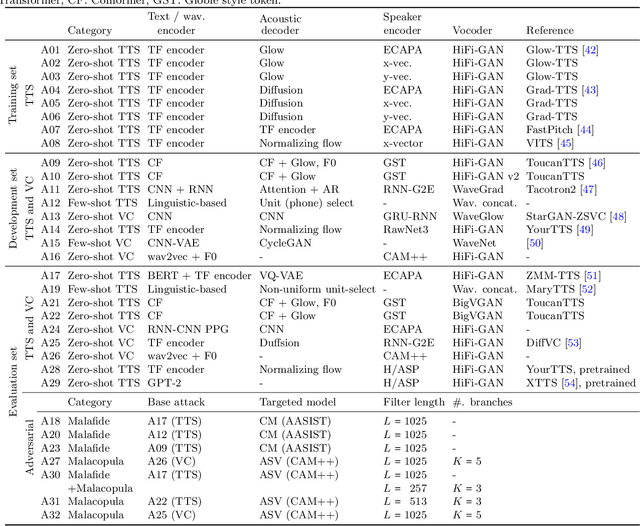
Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake attacks as well as the design of detection solutions. We introduce the ASVspoof 5 database which is generated in crowdsourced fashion from data collected in diverse acoustic conditions (cf. studio-quality data for earlier ASVspoof databases) and from ~2,000 speakers (cf. ~100 earlier). The database contains attacks generated with 32 different algorithms, also crowdsourced, and optimised to varying degrees using new surrogate detection models. Among them are attacks generated with a mix of legacy and contemporary text-to-speech synthesis and voice conversion models, in addition to adversarial attacks which are incorporated for the first time. ASVspoof 5 protocols comprise seven speaker-disjoint partitions. They include two distinct partitions for the training of different sets of attack models, two more for the development and evaluation of surrogate detection models, and then three additional partitions which comprise the ASVspoof 5 training, development and evaluation sets. An auxiliary set of data collected from an additional 30k speakers can also be used to train speaker encoders for the implementation of attack algorithms. Also described herein is an experimental validation of the new ASVspoof 5 database using a set of automatic speaker verification and spoof/deepfake baseline detectors. With the exception of protocols and tools for the generation of spoofed/deepfake speech, the resources described in this paper, already used by participants of the ASVspoof 5 challenge in 2024, are now all freely available to the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge