Xuechen Liu
ASVspoof 5: Evaluation of Spoofing, Deepfake, and Adversarial Attack Detection Using Crowdsourced Speech
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake detection solutions. A significant change from previous challenge editions is a new crowdsourced database collected from a substantially greater number of speakers under diverse recording conditions, and a mix of cutting-edge and legacy generative speech technology. With the new database described elsewhere, we provide in this paper an overview of the ASVspoof 5 challenge results for the submissions of 53 participating teams. While many solutions perform well, performance degrades under adversarial attacks and the application of neural encoding/compression schemes. Together with a review of post-challenge results, we also report a study of calibration in addition to other principal challenges and outline a road-map for the future of ASVspoof.
Enabling MoE on the Edge via Importance-Driven Expert Scheduling
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture has emerged as a key technique for scaling Large Language Models by activating only a subset of experts per query. Deploying MoE on consumer-grade edge hardware, however, is constrained by limited device memory, making dynamic expert offloading essential. Unlike prior work that treats offloading purely as a scheduling problem, we leverage expert importance to guide decisions, substituting low-importance activated experts with functionally similar ones already cached in GPU memory, thereby preserving accuracy. As a result, this design reduces memory usage and data transfer, while largely eliminating PCIe overhead. In addition, we introduce a scheduling policy that maximizes the reuse ratio of GPU-cached experts, further boosting efficiency. Extensive evaluations show that our approach delivers 48% lower decoding latency with over 60% expert cache hit rate, while maintaining nearly lossless accuracy.
From Sharpness to Better Generalization for Speech Deepfake Detection
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Generalization remains a critical challenge in speech deepfake detection (SDD). While various approaches aim to improve robustness, generalization is typically assessed through performance metrics like equal error rate without a theoretical framework to explain model performance. This work investigates sharpness as a theoretical proxy for generalization in SDD. We analyze how sharpness responds to domain shifts and find it increases in unseen conditions, indicating higher model sensitivity. Based on this, we apply Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) to reduce sharpness explicitly, leading to better and more stable performance across diverse unseen test sets. Furthermore, correlation analysis confirms a statistically significant relationship between sharpness and generalization in most test settings. These findings suggest that sharpness can serve as a theoretical indicator for generalization in SDD and that sharpness-aware training offers a promising strategy for improving robustness.
A Hierarchical Probabilistic Framework for Incremental Knowledge Tracing in Classroom Settings
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Knowledge tracing (KT) aims to estimate a student's evolving knowledge state and predict their performance on new exercises based on performance history. Many realistic classroom settings for KT are typically low-resource in data and require online updates as students' exercise history grows, which creates significant challenges for existing KT approaches. To restore strong performance under low-resource conditions, we revisit the hierarchical knowledge concept (KC) information, which is typically available in many classroom settings and can provide strong prior when data are sparse. We therefore propose Knowledge-Tree-based Knowledge Tracing (KT$^2$), a probabilistic KT framework that models student understanding over a tree-structured hierarchy of knowledge concepts using a Hidden Markov Tree Model. KT$^2$ estimates student mastery via an EM algorithm and supports personalized prediction through an incremental update mechanism as new responses arrive. Our experiments show that KT$^2$ consistently outperforms strong baselines in realistic online, low-resource settings.
Quantifying Source Speaker Leakage in One-to-One Voice Conversion
Apr 22, 2025
Abstract:Using a multi-accented corpus of parallel utterances for use with commercial speech devices, we present a case study to show that it is possible to quantify a degree of confidence about a source speaker's identity in the case of one-to-one voice conversion. Following voice conversion using a HiFi-GAN vocoder, we compare information leakage for a range speaker characteristics; assuming a "worst-case" white-box scenario, we quantify our confidence to perform inference and narrow the pool of likely source speakers, reinforcing the regulatory obligation and moral duty that providers of synthetic voices have to ensure the privacy of their speakers' data.
ASVspoof 5: Design, Collection and Validation of Resources for Spoofing, Deepfake, and Adversarial Attack Detection Using Crowdsourced Speech
Feb 13, 2025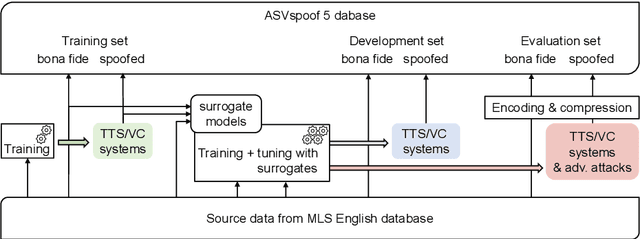

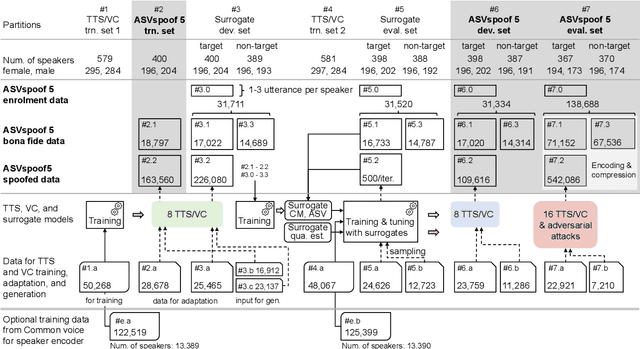
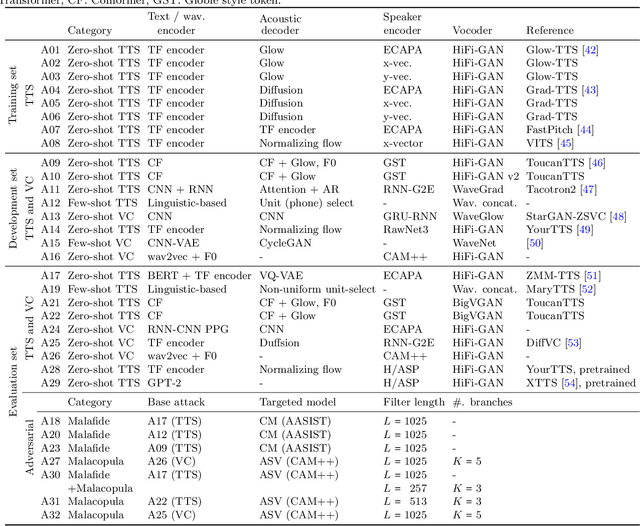
Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake attacks as well as the design of detection solutions. We introduce the ASVspoof 5 database which is generated in crowdsourced fashion from data collected in diverse acoustic conditions (cf. studio-quality data for earlier ASVspoof databases) and from ~2,000 speakers (cf. ~100 earlier). The database contains attacks generated with 32 different algorithms, also crowdsourced, and optimised to varying degrees using new surrogate detection models. Among them are attacks generated with a mix of legacy and contemporary text-to-speech synthesis and voice conversion models, in addition to adversarial attacks which are incorporated for the first time. ASVspoof 5 protocols comprise seven speaker-disjoint partitions. They include two distinct partitions for the training of different sets of attack models, two more for the development and evaluation of surrogate detection models, and then three additional partitions which comprise the ASVspoof 5 training, development and evaluation sets. An auxiliary set of data collected from an additional 30k speakers can also be used to train speaker encoders for the implementation of attack algorithms. Also described herein is an experimental validation of the new ASVspoof 5 database using a set of automatic speaker verification and spoof/deepfake baseline detectors. With the exception of protocols and tools for the generation of spoofed/deepfake speech, the resources described in this paper, already used by participants of the ASVspoof 5 challenge in 2024, are now all freely available to the community.
Explaining Speaker and Spoof Embeddings via Probing
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:This study investigates the explainability of embedding representations, specifically those used in modern audio spoofing detection systems based on deep neural networks, known as spoof embeddings. Building on established work in speaker embedding explainability, we examine how well these spoof embeddings capture speaker-related information. We train simple neural classifiers using either speaker or spoof embeddings as input, with speaker-related attributes as target labels. These attributes are categorized into two groups: metadata-based traits (e.g., gender, age) and acoustic traits (e.g., fundamental frequency, speaking rate). Our experiments on the ASVspoof 2019 LA evaluation set demonstrate that spoof embeddings preserve several key traits, including gender, speaking rate, F0, and duration. Further analysis of gender and speaking rate indicates that the spoofing detector partially preserves these traits, potentially to ensure the decision process remains robust against them.
Libri2Vox Dataset: Target Speaker Extraction with Diverse Speaker Conditions and Synthetic Data
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Target speaker extraction (TSE) is essential in speech processing applications, particularly in scenarios with complex acoustic environments. Current TSE systems face challenges in limited data diversity and a lack of robustness in real-world conditions, primarily because they are trained on artificially mixed datasets with limited speaker variability and unrealistic noise profiles. To address these challenges, we propose Libri2Vox, a new dataset that combines clean target speech from the LibriTTS dataset with interference speech from the noisy VoxCeleb2 dataset, providing a large and diverse set of speakers under realistic noisy conditions. We also augment Libri2Vox with synthetic speakers generated using state-of-the-art speech generative models to enhance speaker diversity. Additionally, to further improve the effectiveness of incorporating synthetic data, curriculum learning is implemented to progressively train TSE models with increasing levels of difficulty. Extensive experiments across multiple TSE architectures reveal varying degrees of improvement, with SpeakerBeam demonstrating the most substantial gains: a 1.39 dB improvement in signal-to-distortion ratio (SDR) on the Libri2Talker test set compared to baseline training. Building upon these results, we further enhanced performance through our speaker similarity-based curriculum learning approach with the Conformer architecture, achieving an additional 0.78 dB improvement over conventional random sampling methods in which data samples are randomly selected from the entire dataset. These results demonstrate the complementary benefits of diverse real-world data, synthetic speaker augmentation, and structured training strategies in building robust TSE systems.
Improving curriculum learning for target speaker extraction with synthetic speakers
Oct 01, 2024



Abstract:Target speaker extraction (TSE) aims to isolate individual speaker voices from complex speech environments. The effectiveness of TSE systems is often compromised when the speaker characteristics are similar to each other. Recent research has introduced curriculum learning (CL), in which TSE models are trained incrementally on speech samples of increasing complexity. In CL training, the model is first trained on samples with low speaker similarity between the target and interference speakers, and then on samples with high speaker similarity. To further improve CL, this paper uses a $k$-nearest neighbor-based voice conversion method to simulate and generate speech of diverse interference speakers, and then uses the generated data as part of the CL. Experiments demonstrate that training data based on synthetic speakers can effectively enhance the model's capabilities and significantly improve the performance of multiple TSE systems.
AfriHuBERT: A self-supervised speech representation model for African languages
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we present AfriHuBERT, an extension of mHuBERT-147, a state-of-the-art (SOTA) and compact self-supervised learning (SSL) model, originally pretrained on 147 languages. While mHuBERT-147 was pretrained on 16 African languages, we expand this to cover 39 African languages through continued pretraining on 6,500+ hours of speech data aggregated from diverse sources, including 23 newly added languages. We evaluate AfriHuBERT on two key speech tasks: Language Identification (LID) and Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) using FLEURS dataset. Our results show a +4% F1 score improvement on average for LID and a -1.2% average Word Error Rate (WER) reduction for ASR. Further analysis shows that ASR models trained on AfriHuBERT exhibit improved cross-corpus generalization. Additionally, the analysis indicates that the FLEURS have data quality limitations that may affect their suitability for evaluating low-resource African languages, suggesting the need for better evaluation benchmarks for these languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge