Ivan Kukanov
ASVspoof 5: Evaluation of Spoofing, Deepfake, and Adversarial Attack Detection Using Crowdsourced Speech
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake detection solutions. A significant change from previous challenge editions is a new crowdsourced database collected from a substantially greater number of speakers under diverse recording conditions, and a mix of cutting-edge and legacy generative speech technology. With the new database described elsewhere, we provide in this paper an overview of the ASVspoof 5 challenge results for the submissions of 53 participating teams. While many solutions perform well, performance degrades under adversarial attacks and the application of neural encoding/compression schemes. Together with a review of post-challenge results, we also report a study of calibration in addition to other principal challenges and outline a road-map for the future of ASVspoof.
Mixture of Low-Rank Adapter Experts in Generalizable Audio Deepfake Detection
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Foundation models such as Wav2Vec2 excel at representation learning in speech tasks, including audio deepfake detection. However, after being fine-tuned on a fixed set of bonafide and spoofed audio clips, they often fail to generalize to novel deepfake methods not represented in training. To address this, we propose a mixture-of-LoRA-experts approach that integrates multiple low-rank adapters (LoRA) into the model's attention layers. A routing mechanism selectively activates specialized experts, enhancing adaptability to evolving deepfake attacks. Experimental results show that our method outperforms standard fine-tuning in both in-domain and out-of-domain scenarios, reducing equal error rates relative to baseline models. Notably, our best MoE-LoRA model lowers the average out-of-domain EER from 8.55\% to 6.08\%, demonstrating its effectiveness in achieving generalizable audio deepfake detection.
KLASSify to Verify: Audio-Visual Deepfake Detection Using SSL-based Audio and Handcrafted Visual Features
Aug 10, 2025



Abstract:The rapid development of audio-driven talking head generators and advanced Text-To-Speech (TTS) models has led to more sophisticated temporal deepfakes. These advances highlight the need for robust methods capable of detecting and localizing deepfakes, even under novel, unseen attack scenarios. Current state-of-the-art deepfake detectors, while accurate, are often computationally expensive and struggle to generalize to novel manipulation techniques. To address these challenges, we propose multimodal approaches for the AV-Deepfake1M 2025 challenge. For the visual modality, we leverage handcrafted features to improve interpretability and adaptability. For the audio modality, we adapt a self-supervised learning (SSL) backbone coupled with graph attention networks to capture rich audio representations, improving detection robustness. Our approach strikes a balance between performance and real-world deployment, focusing on resilience and potential interpretability. On the AV-Deepfake1M++ dataset, our multimodal system achieves AUC of 92.78% for deepfake classification task and IoU of 0.3536 for temporal localization using only the audio modality.
ASVspoof 5: Design, Collection and Validation of Resources for Spoofing, Deepfake, and Adversarial Attack Detection Using Crowdsourced Speech
Feb 13, 2025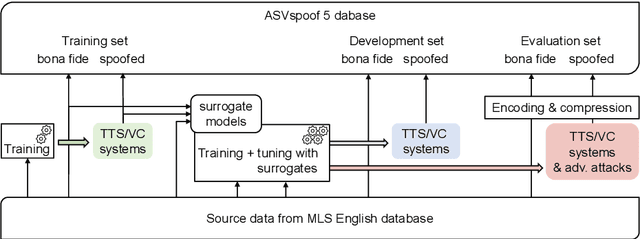

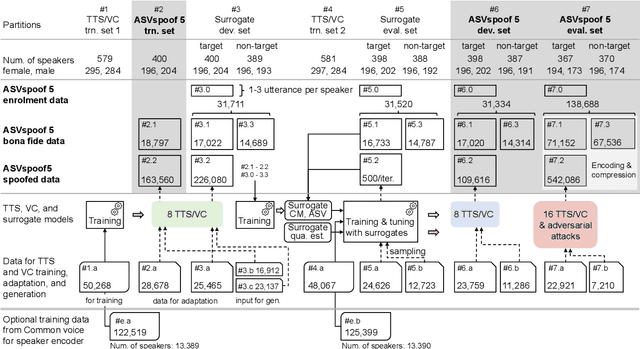
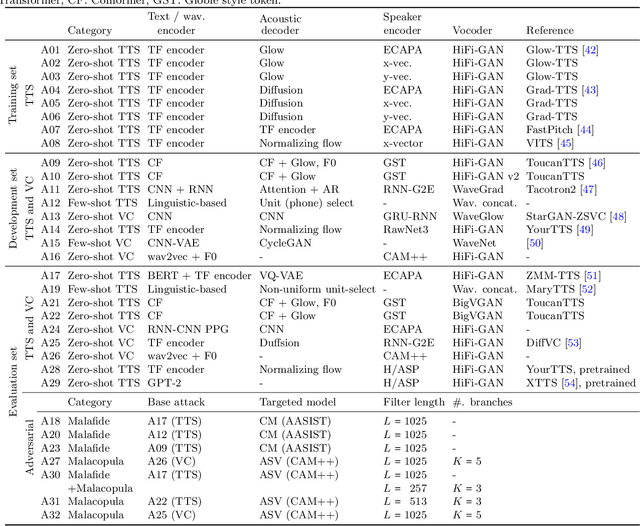
Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake attacks as well as the design of detection solutions. We introduce the ASVspoof 5 database which is generated in crowdsourced fashion from data collected in diverse acoustic conditions (cf. studio-quality data for earlier ASVspoof databases) and from ~2,000 speakers (cf. ~100 earlier). The database contains attacks generated with 32 different algorithms, also crowdsourced, and optimised to varying degrees using new surrogate detection models. Among them are attacks generated with a mix of legacy and contemporary text-to-speech synthesis and voice conversion models, in addition to adversarial attacks which are incorporated for the first time. ASVspoof 5 protocols comprise seven speaker-disjoint partitions. They include two distinct partitions for the training of different sets of attack models, two more for the development and evaluation of surrogate detection models, and then three additional partitions which comprise the ASVspoof 5 training, development and evaluation sets. An auxiliary set of data collected from an additional 30k speakers can also be used to train speaker encoders for the implementation of attack algorithms. Also described herein is an experimental validation of the new ASVspoof 5 database using a set of automatic speaker verification and spoof/deepfake baseline detectors. With the exception of protocols and tools for the generation of spoofed/deepfake speech, the resources described in this paper, already used by participants of the ASVspoof 5 challenge in 2024, are now all freely available to the community.
Meta-Learning Approaches for Improving Detection of Unseen Speech Deepfakes
Oct 27, 2024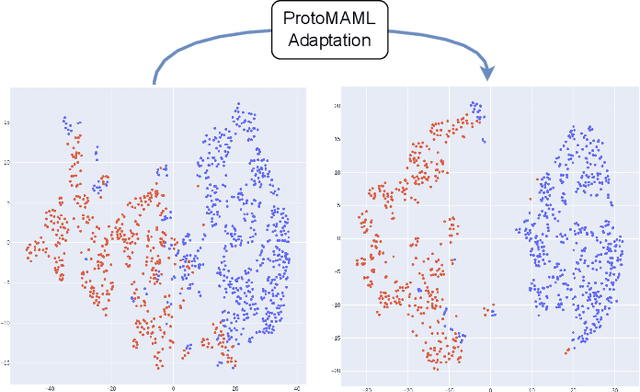
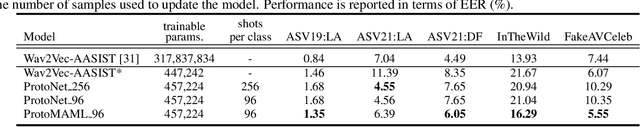
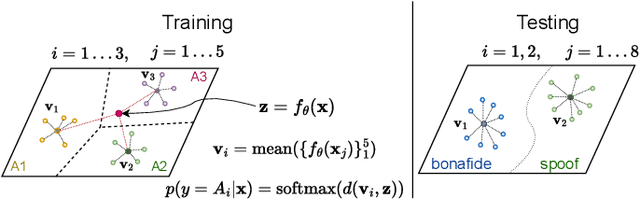
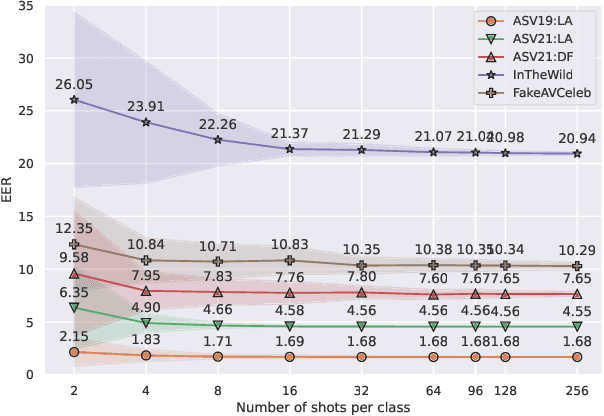
Abstract:Current speech deepfake detection approaches perform satisfactorily against known adversaries; however, generalization to unseen attacks remains an open challenge. The proliferation of speech deepfakes on social media underscores the need for systems that can generalize to unseen attacks not observed during training. We address this problem from the perspective of meta-learning, aiming to learn attack-invariant features to adapt to unseen attacks with very few samples available. This approach is promising since generating of a high-scale training dataset is often expensive or infeasible. Our experiments demonstrated an improvement in the Equal Error Rate (EER) from 21.67% to 10.42% on the InTheWild dataset, using just 96 samples from the unseen dataset. Continuous few-shot adaptation ensures that the system remains up-to-date.
Towards Quantifying and Reducing Language Mismatch Effects in Cross-Lingual Speech Anti-Spoofing
Sep 12, 2024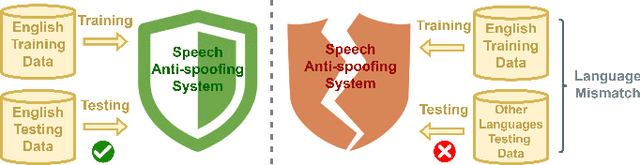
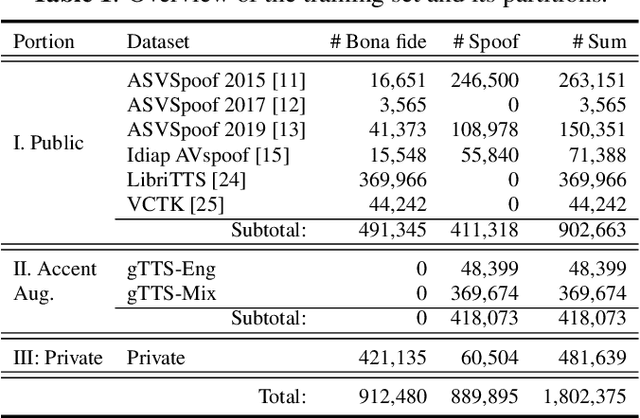
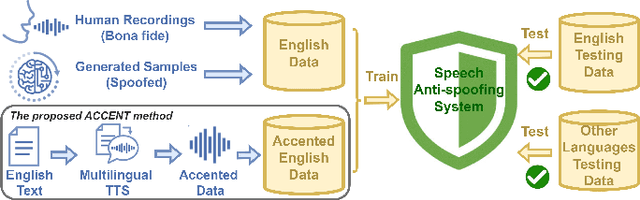
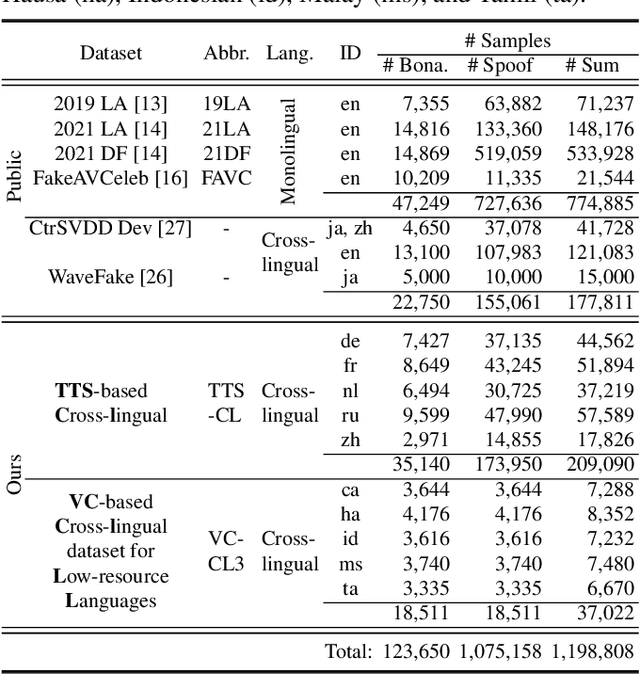
Abstract:The effects of language mismatch impact speech anti-spoofing systems, while investigations and quantification of these effects remain limited. Existing anti-spoofing datasets are mainly in English, and the high cost of acquiring multilingual datasets hinders training language-independent models. We initiate this work by evaluating top-performing speech anti-spoofing systems that are trained on English data but tested on other languages, observing notable performance declines. We propose an innovative approach - Accent-based data expansion via TTS (ACCENT), which introduces diverse linguistic knowledge to monolingual-trained models, improving their cross-lingual capabilities. We conduct experiments on a large-scale dataset consisting of over 3 million samples, including 1.8 million training samples and nearly 1.2 million testing samples across 12 languages. The language mismatch effects are preliminarily quantified and remarkably reduced over 15% by applying the proposed ACCENT. This easily implementable method shows promise for multilingual and low-resource language scenarios.
ASVspoof 5: Crowdsourced Speech Data, Deepfakes, and Adversarial Attacks at Scale
Aug 16, 2024



Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges that promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake attacks, and the design of detection solutions. Compared to previous challenges, the ASVspoof 5 database is built from crowdsourced data collected from a vastly greater number of speakers in diverse acoustic conditions. Attacks, also crowdsourced, are generated and tested using surrogate detection models, while adversarial attacks are incorporated for the first time. New metrics support the evaluation of spoofing-robust automatic speaker verification (SASV) as well as stand-alone detection solutions, i.e., countermeasures without ASV. We describe the two challenge tracks, the new database, the evaluation metrics, baselines, and the evaluation platform, and present a summary of the results. Attacks significantly compromise the baseline systems, while submissions bring substantial improvements.
Analysis of Joint Speech-Text Embeddings for Semantic Matching
Apr 04, 2022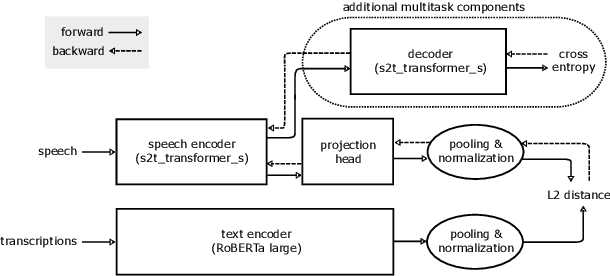
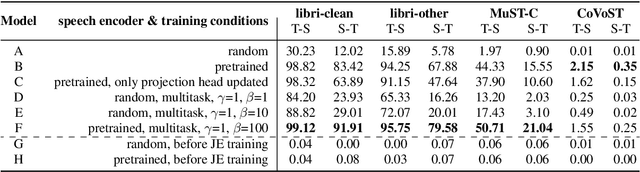
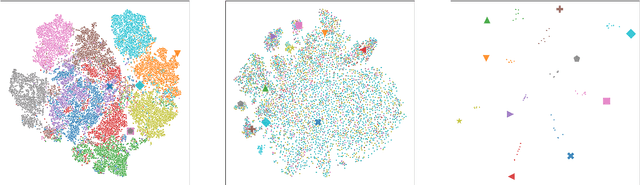
Abstract:Embeddings play an important role in many recent end-to-end solutions for language processing problems involving more than one data modality. Although there has been some effort to understand the properties of single-modality embedding spaces, particularly that of text, their cross-modal counterparts are less understood. In this work, we study a joint speech-text embedding space trained for semantic matching by minimizing the distance between paired utterance and transcription inputs. This was done through dual encoders in a teacher-student model setup, with a pretrained language model acting as the teacher and a transformer-based speech encoder as the student. We extend our method to incorporate automatic speech recognition through both pretraining and multitask scenarios and found that both approaches improve semantic matching. Multiple techniques were utilized to analyze and evaluate cross-modal semantic alignment of the embeddings: a quantitative retrieval accuracy metric, zero-shot classification to investigate generalizability, and probing of the encoders to observe the extent of knowledge transfer from one modality to another.
Cost Sensitive Optimization of Deepfake Detector
Dec 08, 2020
Abstract:Since the invention of cinema, the manipulated videos have existed. But generating manipulated videos that can fool the viewer has been a time-consuming endeavor. With the dramatic improvements in the deep generative modeling, generating believable looking fake videos has become a reality. In the present work, we concentrate on the so-called deepfake videos, where the source face is swapped with the targets. We argue that deepfake detection task should be viewed as a screening task, where the user, such as the video streaming platform, will screen a large number of videos daily. It is clear then that only a small fraction of the uploaded videos are deepfakes, so the detection performance needs to be measured in a cost-sensitive way. Preferably, the model parameters also need to be estimated in the same way. This is precisely what we propose here.
I4U Submission to NIST SRE 2018: Leveraging from a Decade of Shared Experiences
Apr 16, 2019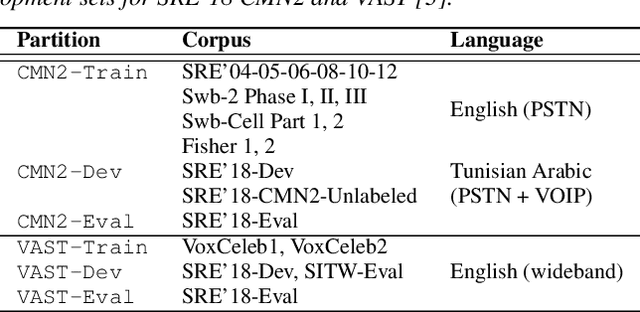
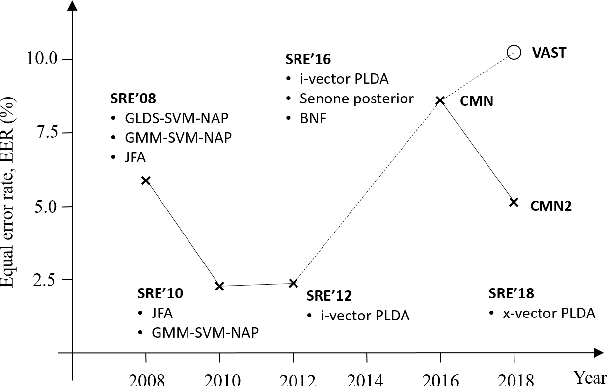
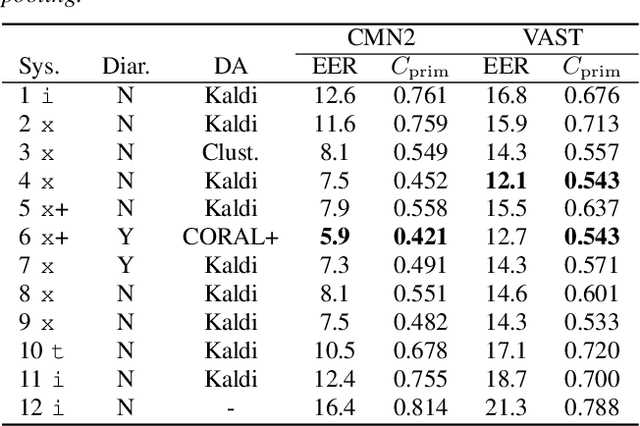
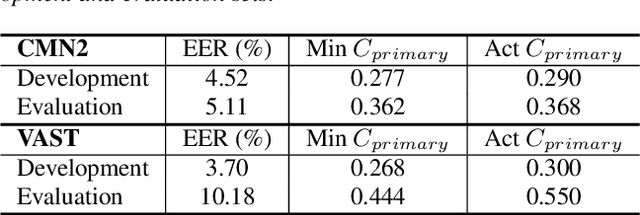
Abstract:The I4U consortium was established to facilitate a joint entry to NIST speaker recognition evaluations (SRE). The latest edition of such joint submission was in SRE 2018, in which the I4U submission was among the best-performing systems. SRE'18 also marks the 10-year anniversary of I4U consortium into NIST SRE series of evaluation. The primary objective of the current paper is to summarize the results and lessons learned based on the twelve sub-systems and their fusion submitted to SRE'18. It is also our intention to present a shared view on the advancements, progresses, and major paradigm shifts that we have witnessed as an SRE participant in the past decade from SRE'08 to SRE'18. In this regard, we have seen, among others, a paradigm shift from supervector representation to deep speaker embedding, and a switch of research challenge from channel compensation to domain adaptation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge