Hanwu Sun
I4U System Description for NIST SRE'20 CTS Challenge
Nov 02, 2022



Abstract:This manuscript describes the I4U submission to the 2020 NIST Speaker Recognition Evaluation (SRE'20) Conversational Telephone Speech (CTS) Challenge. The I4U's submission was resulted from active collaboration among researchers across eight research teams - I$^2$R (Singapore), UEF (Finland), VALPT (Italy, Spain), NEC (Japan), THUEE (China), LIA (France), NUS (Singapore), INRIA (France) and TJU (China). The submission was based on the fusion of top performing sub-systems and sub-fusion systems contributed by individual teams. Efforts have been spent on the use of common development and validation sets, submission schedule and milestone, minimizing inconsistency in trial list and score file format across sites.
I4U Submission to NIST SRE 2018: Leveraging from a Decade of Shared Experiences
Apr 16, 2019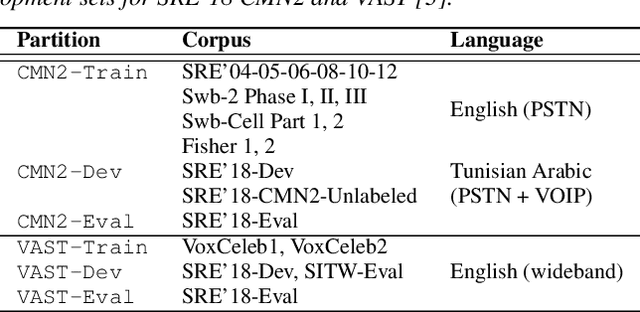
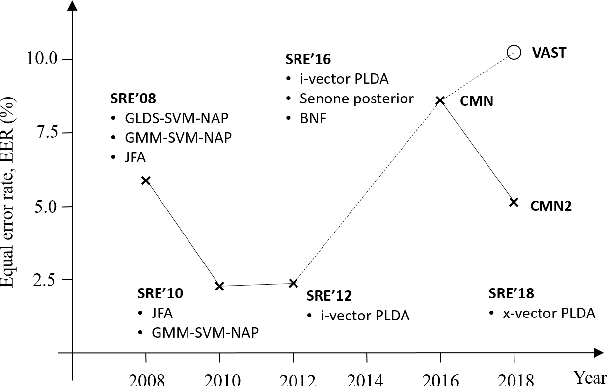
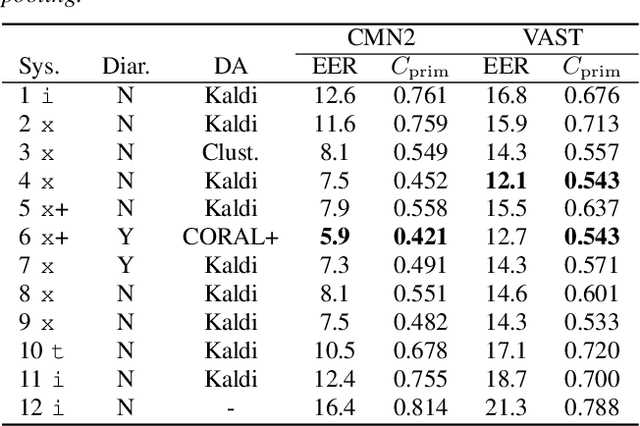
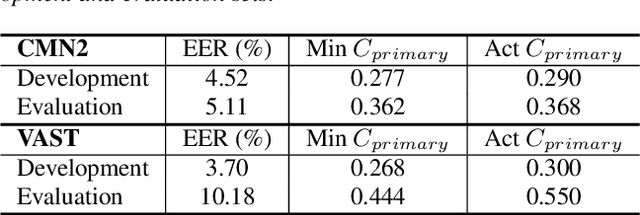
Abstract:The I4U consortium was established to facilitate a joint entry to NIST speaker recognition evaluations (SRE). The latest edition of such joint submission was in SRE 2018, in which the I4U submission was among the best-performing systems. SRE'18 also marks the 10-year anniversary of I4U consortium into NIST SRE series of evaluation. The primary objective of the current paper is to summarize the results and lessons learned based on the twelve sub-systems and their fusion submitted to SRE'18. It is also our intention to present a shared view on the advancements, progresses, and major paradigm shifts that we have witnessed as an SRE participant in the past decade from SRE'08 to SRE'18. In this regard, we have seen, among others, a paradigm shift from supervector representation to deep speaker embedding, and a switch of research challenge from channel compensation to domain adaptation.
Fantastic 4 system for NIST 2015 Language Recognition Evaluation
Feb 05, 2016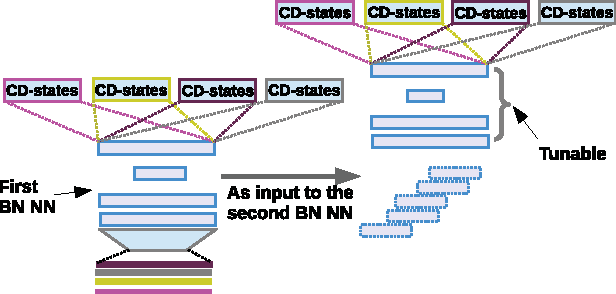
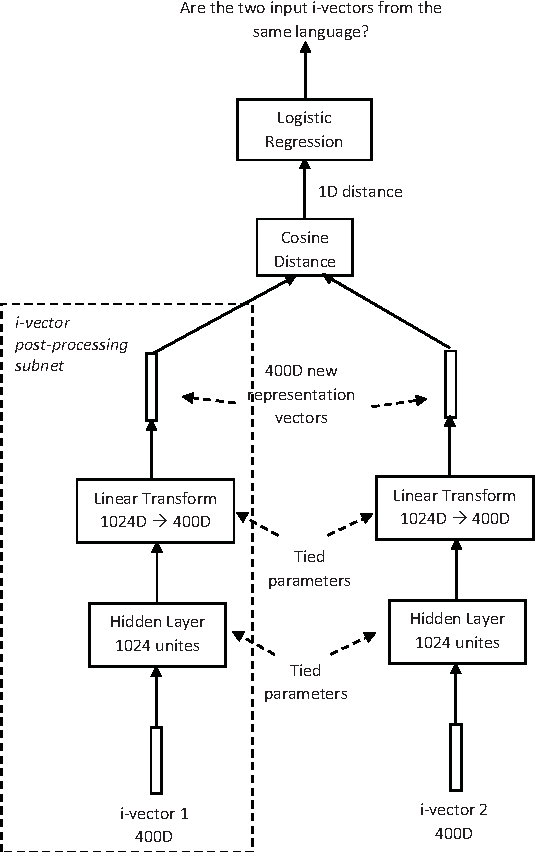
Abstract:This article describes the systems jointly submitted by Institute for Infocomm (I$^2$R), the Laboratoire d'Informatique de l'Universit\'e du Maine (LIUM), Nanyang Technology University (NTU) and the University of Eastern Finland (UEF) for 2015 NIST Language Recognition Evaluation (LRE). The submitted system is a fusion of nine sub-systems based on i-vectors extracted from different types of features. Given the i-vectors, several classifiers are adopted for the language detection task including support vector machines (SVM), multi-class logistic regression (MCLR), Probabilistic Linear Discriminant Analysis (PLDA) and Deep Neural Networks (DNN).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge