Tianyu Liang
Synthesizing Reality: Leveraging the Generative AI-Powered Platform Midjourney for Construction Worker Detection
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:While recent advancements in deep neural networks (DNNs) have substantially enhanced visual AI's capabilities, the challenge of inadequate data diversity and volume remains, particularly in construction domain. This study presents a novel image synthesis methodology tailored for construction worker detection, leveraging the generative-AI platform Midjourney. The approach entails generating a collection of 12,000 synthetic images by formulating 3000 different prompts, with an emphasis on image realism and diversity. These images, after manual labeling, serve as a dataset for DNN training. Evaluation on a real construction image dataset yielded promising results, with the model attaining average precisions (APs) of 0.937 and 0.642 at intersection-over-union (IoU) thresholds of 0.5 and 0.5 to 0.95, respectively. Notably, the model demonstrated near-perfect performance on the synthetic dataset, achieving APs of 0.994 and 0.919 at the two mentioned thresholds. These findings reveal both the potential and weakness of generative AI in addressing DNN training data scarcity.
WaterHE-NeRF: Water-ray Tracing Neural Radiance Fields for Underwater Scene Reconstruction
Dec 12, 2023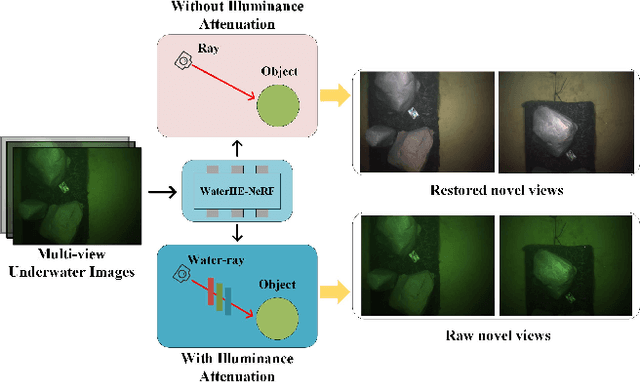
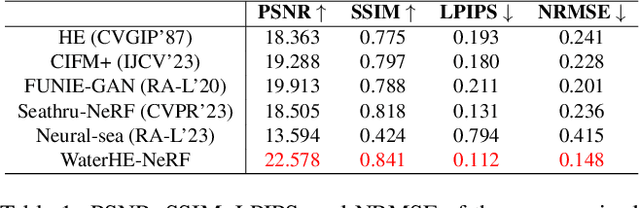
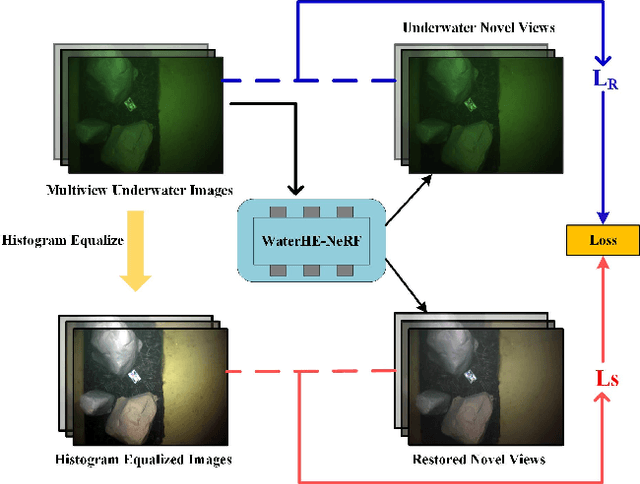
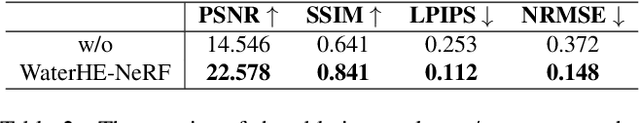
Abstract:Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) technology demonstrates immense potential in novel viewpoint synthesis tasks, due to its physics-based volumetric rendering process, which is particularly promising in underwater scenes. Addressing the limitations of existing underwater NeRF methods in handling light attenuation caused by the water medium and the lack of real Ground Truth (GT) supervision, this study proposes WaterHE-NeRF. We develop a new water-ray tracing field by Retinex theory that precisely encodes color, density, and illuminance attenuation in three-dimensional space. WaterHE-NeRF, through its illuminance attenuation mechanism, generates both degraded and clear multi-view images and optimizes image restoration by combining reconstruction loss with Wasserstein distance. Additionally, the use of histogram equalization (HE) as pseudo-GT enhances the network's accuracy in preserving original details and color distribution. Extensive experiments on real underwater datasets and synthetic datasets validate the effectiveness of WaterHE-NeRF. Our code will be made publicly available.
Classification-Aware Neural Topic Model Combined With Interpretable Analysis -- For Conflict Classification
Aug 29, 2023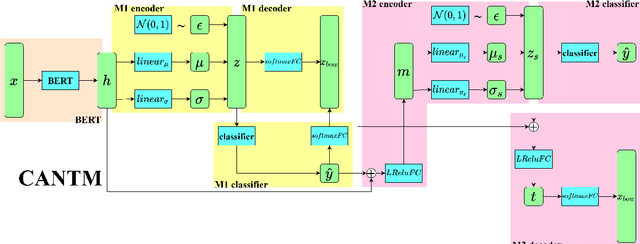
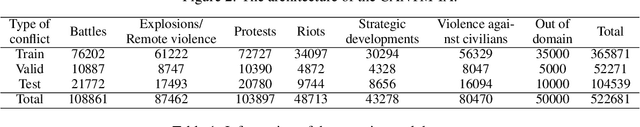
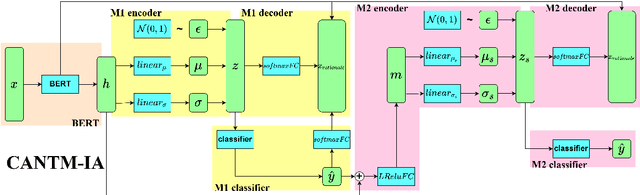
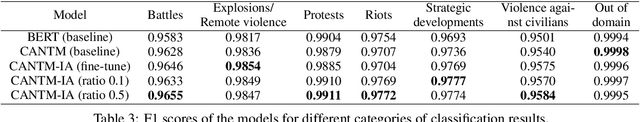
Abstract:A large number of conflict events are affecting the world all the time. In order to analyse such conflict events effectively, this paper presents a Classification-Aware Neural Topic Model (CANTM-IA) for Conflict Information Classification and Topic Discovery. The model provides a reliable interpretation of classification results and discovered topics by introducing interpretability analysis. At the same time, interpretation is introduced into the model architecture to improve the classification performance of the model and to allow interpretation to focus further on the details of the data. Finally, the model architecture is optimised to reduce the complexity of the model.
I4U System Description for NIST SRE'20 CTS Challenge
Nov 02, 2022



Abstract:This manuscript describes the I4U submission to the 2020 NIST Speaker Recognition Evaluation (SRE'20) Conversational Telephone Speech (CTS) Challenge. The I4U's submission was resulted from active collaboration among researchers across eight research teams - I$^2$R (Singapore), UEF (Finland), VALPT (Italy, Spain), NEC (Japan), THUEE (China), LIA (France), NUS (Singapore), INRIA (France) and TJU (China). The submission was based on the fusion of top performing sub-systems and sub-fusion systems contributed by individual teams. Efforts have been spent on the use of common development and validation sets, submission schedule and milestone, minimizing inconsistency in trial list and score file format across sites.
THUEE system description for NIST 2020 SRE CTS challenge
Oct 12, 2022
Abstract:This paper presents the system description of the THUEE team for the NIST 2020 Speaker Recognition Evaluation (SRE) conversational telephone speech (CTS) challenge. The subsystems including ResNet74, ResNet152, and RepVGG-B2 are developed as speaker embedding extractors in this evaluation. We used combined AM-Softmax and AAM-Softmax based loss functions, namely CM-Softmax. We adopted a two-staged training strategy to further improve system performance. We fused all individual systems as our final submission. Our approach leads to excellent performance and ranks 1st in the challenge.
THUEE system description for NIST 2019 SRE CTS Challenge
Dec 25, 2019



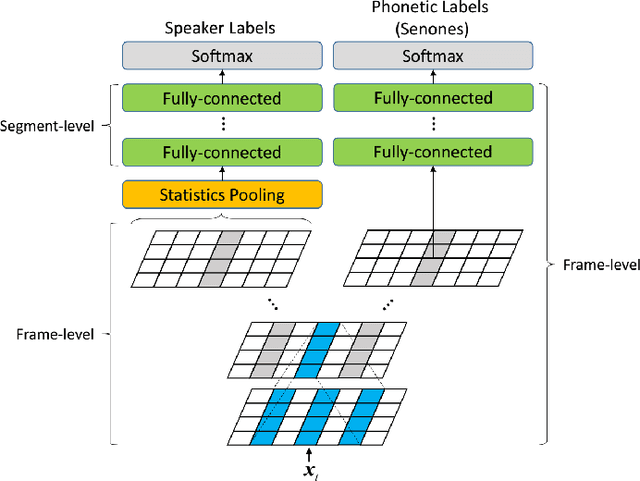
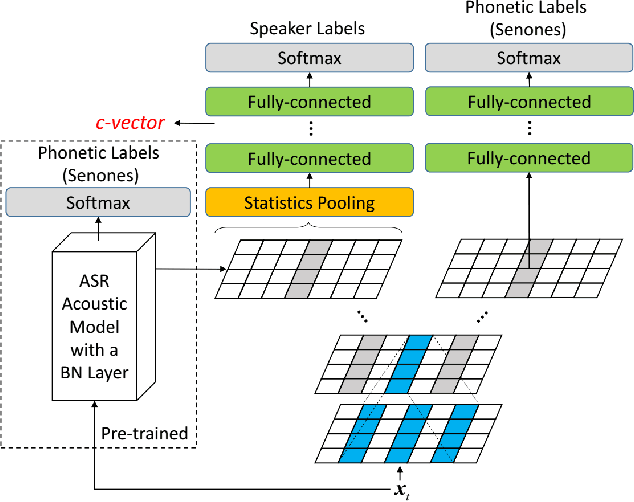
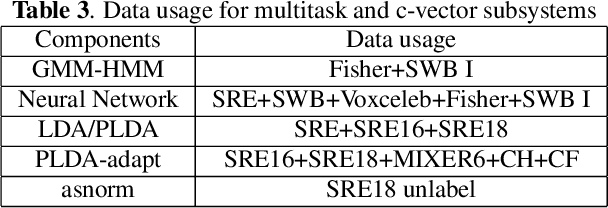
Abstract:This paper describes the systems submitted by the department of electronic engineering, institute of microelectronics of Tsinghua university and TsingMicro Co. Ltd. (THUEE) to the NIST 2019 speaker recognition evaluation CTS challenge. Six subsystems, including etdnn/ams, ftdnn/as, eftdnn/ams, resnet, multitask and c-vector are developed in this evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge