Yufeng Ma
Findings of the WMT 2023 Shared Task on Discourse-Level Literary Translation: A Fresh Orb in the Cosmos of LLMs
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Translating literary works has perennially stood as an elusive dream in machine translation (MT), a journey steeped in intricate challenges. To foster progress in this domain, we hold a new shared task at WMT 2023, the first edition of the Discourse-Level Literary Translation. First, we (Tencent AI Lab and China Literature Ltd.) release a copyrighted and document-level Chinese-English web novel corpus. Furthermore, we put forth an industry-endorsed criteria to guide human evaluation process. This year, we totally received 14 submissions from 7 academia and industry teams. We employ both automatic and human evaluations to measure the performance of the submitted systems. The official ranking of the systems is based on the overall human judgments. In addition, our extensive analysis reveals a series of interesting findings on literary and discourse-aware MT. We release data, system outputs, and leaderboard at http://www2.statmt.org/wmt23/literary-translation-task.html.
THUEE system description for NIST 2020 SRE CTS challenge
Oct 12, 2022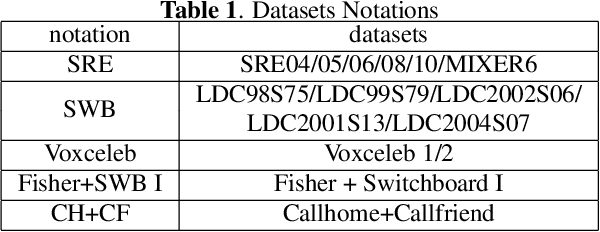
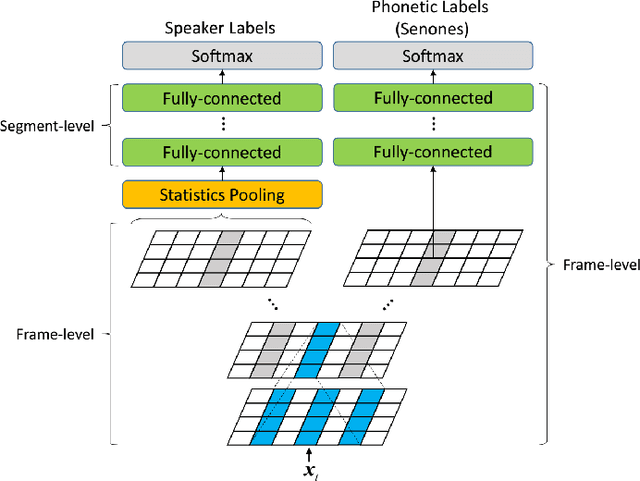
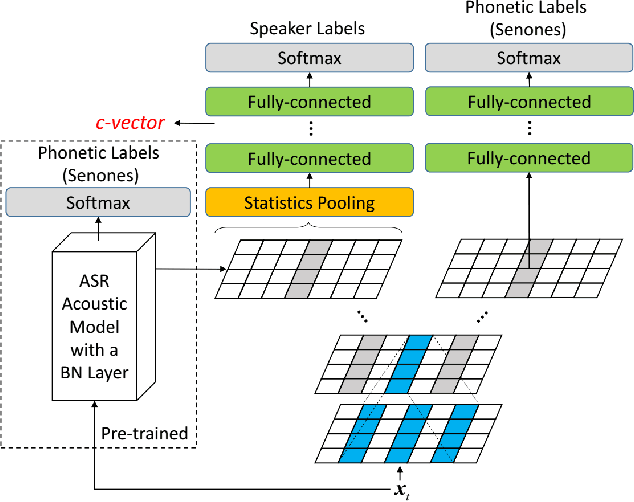
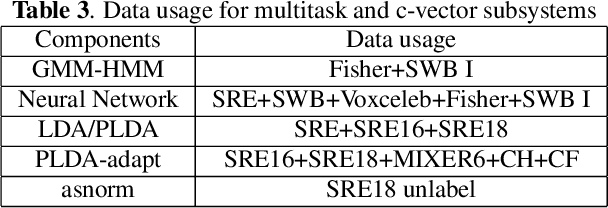
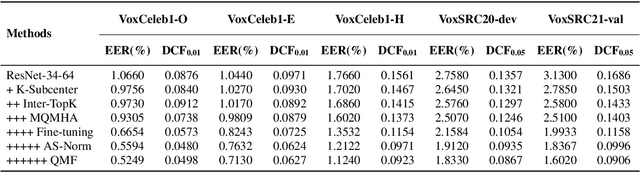
Abstract:This paper presents the system description of the THUEE team for the NIST 2020 Speaker Recognition Evaluation (SRE) conversational telephone speech (CTS) challenge. The subsystems including ResNet74, ResNet152, and RepVGG-B2 are developed as speaker embedding extractors in this evaluation. We used combined AM-Softmax and AAM-Softmax based loss functions, namely CM-Softmax. We adopted a two-staged training strategy to further improve system performance. We fused all individual systems as our final submission. Our approach leads to excellent performance and ranks 1st in the challenge.
Rep Works in Speaker Verification
Oct 19, 2021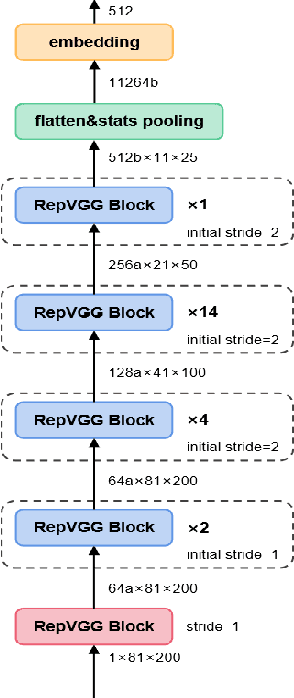
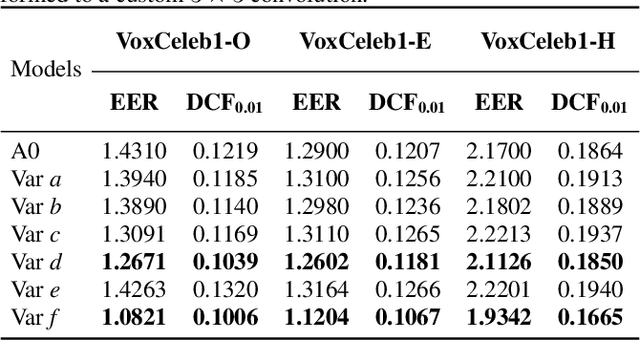
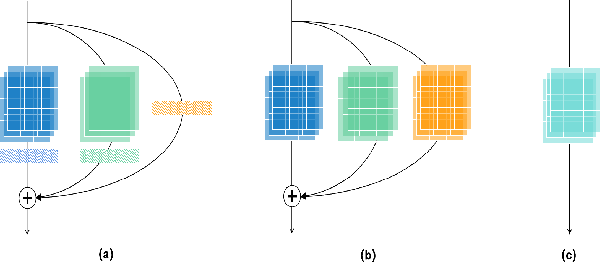
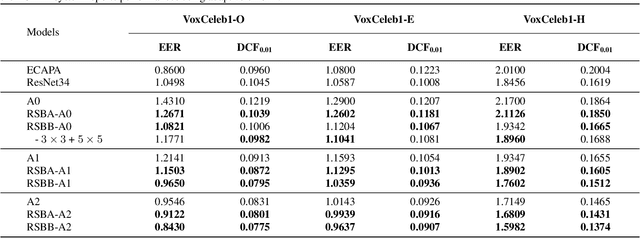
Abstract:Multi-branch convolutional neural network architecture has raised lots of attention in speaker verification since the aggregation of multiple parallel branches can significantly improve performance. However, this design is not efficient enough during the inference time due to the increase of model parameters and extra operations. In this paper, we present a new multi-branch network architecture RepSPKNet that uses a re-parameterization technique. With this technique, our backbone model contains an efficient VGG-like inference state while its training state is a complicated multi-branch structure. We first introduce the specific structure of RepVGG into speaker verification and propose several variants of this structure. The performance is evaluated on VoxCeleb-based test sets. We demonstrate that both the branch diversity and the branch capacity play important roles in RepSPKNet designing. Our RepSPKNet achieves state-of-the-art performance with a 1.5982% EER and a 0.1374 minDCF on VoxCeleb1-H.
Multi-query multi-head attention pooling and Inter-topK penalty for speaker verification
Oct 12, 2021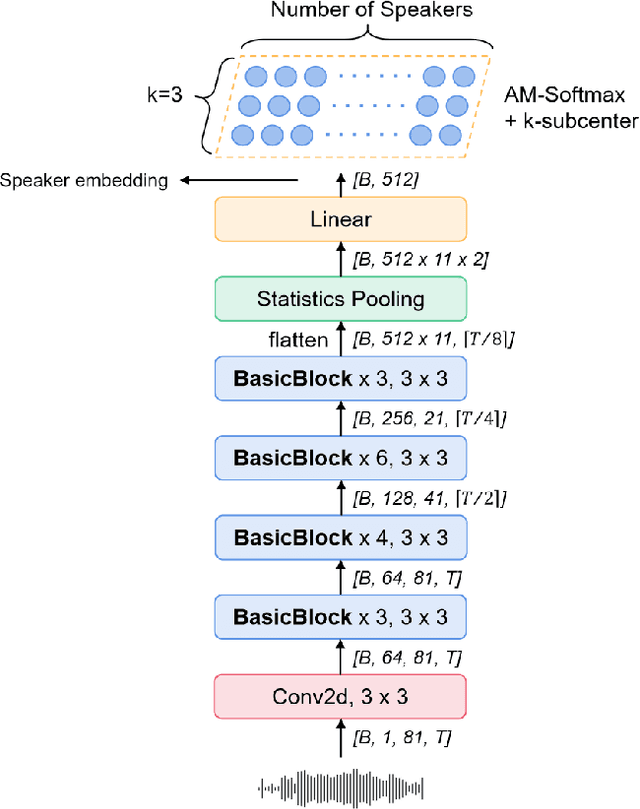
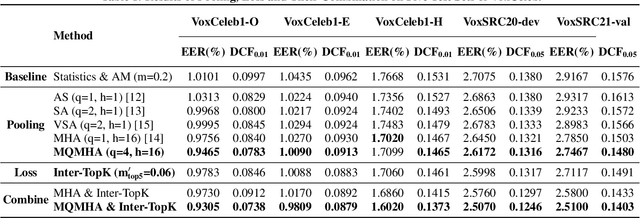
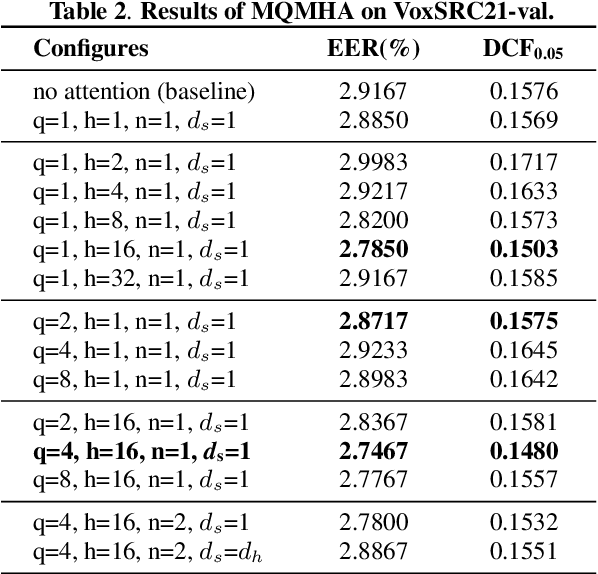
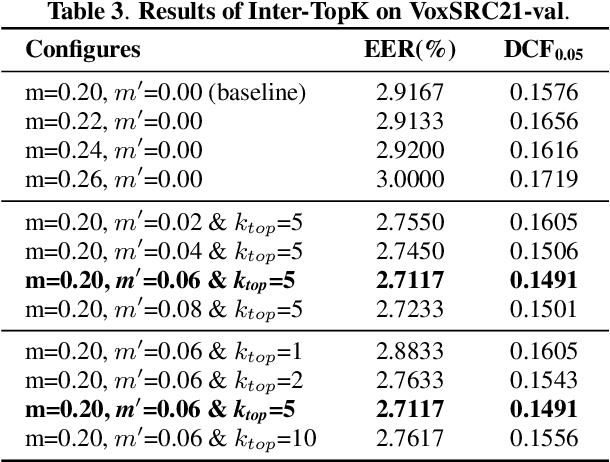
Abstract:This paper describes the multi-query multi-head attention (MQMHA) pooling and inter-topK penalty methods which were first proposed in our submitted system description for VoxCeleb speaker recognition challenge (VoxSRC) 2021. Most multi-head attention pooling mechanisms either attend to the whole feature through multiple heads or attend to several split parts of the whole feature. Our proposed MQMHA combines both these two mechanisms and gain more diversified information. The margin-based softmax loss functions are commonly adopted to obtain discriminative speaker representations. To further enhance the inter-class discriminability, we propose a method that adds an extra inter-topK penalty on some confused speakers. By adopting both the MQMHA and inter-topK penalty, we achieved state-of-the-art performance in all of the public VoxCeleb test sets.
Poformer: A simple pooling transformer for speaker verification
Oct 10, 2021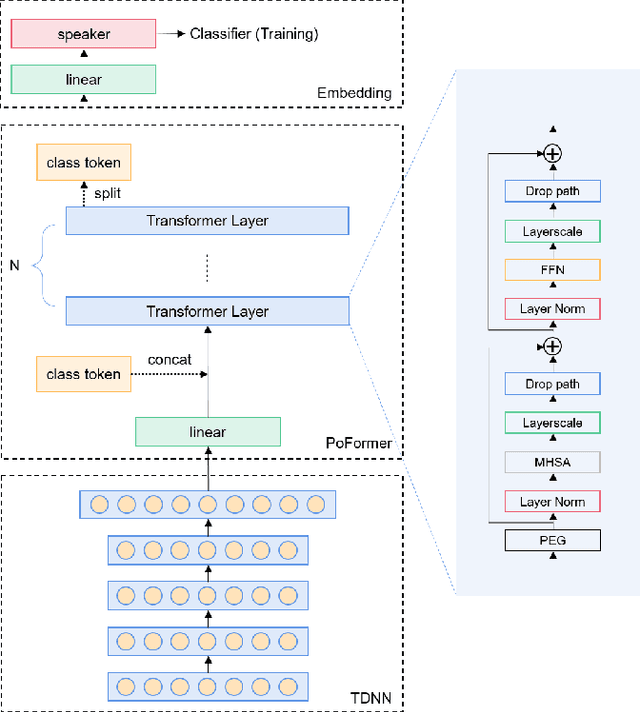
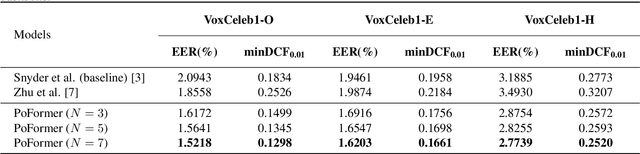
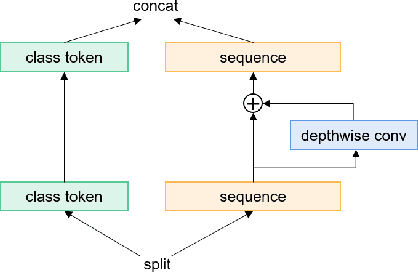
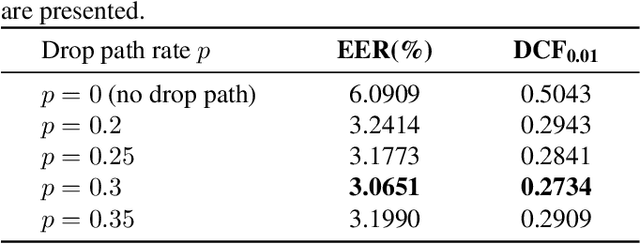
Abstract:Most recent speaker verification systems are based on extracting speaker embeddings using a deep neural network. The pooling layer in the network aims to aggregate frame-level features extracted by the backbone. In this paper, we propose a new transformer based pooling structure called PoFormer to enhance the ability of the pooling layer to capture information along the whole time axis. Different from previous works that apply attention mechanism in a simple way or implement the multi-head mechanism in serial instead of in parallel, PoFormer follows the initial transformer structure with some minor modifications like a positional encoding generator, drop path and LayerScale to make the training procedure more stable and to prevent overfitting. Evaluated on various datasets, PoFormer outperforms the existing pooling system with at least a 13.00% improvement in EER and a 9.12% improvement in minDCF.
The SpeakIn System for VoxCeleb Speaker Recognition Challange 2021
Sep 05, 2021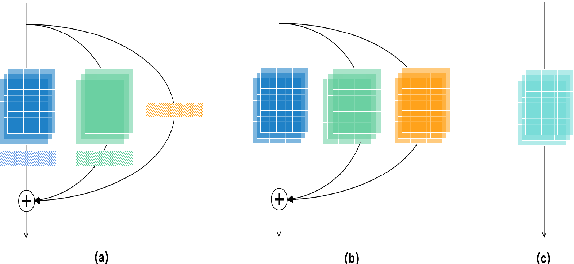
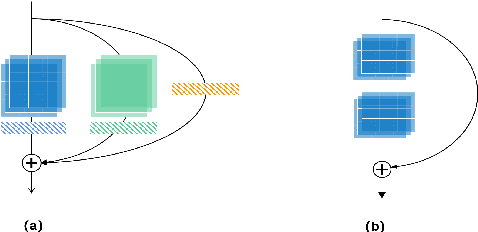
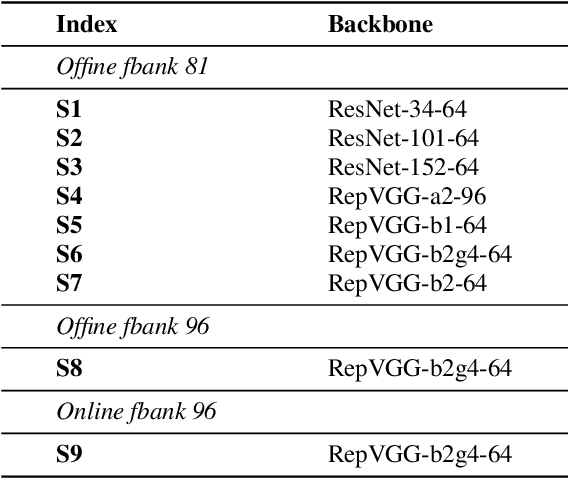
Abstract:This report describes our submission to the track 1 and track 2 of the VoxCeleb Speaker Recognition Challenge 2021 (VoxSRC 2021). Both track 1 and track 2 share the same speaker verification system, which only uses VoxCeleb2-dev as our training set. This report explores several parts, including data augmentation, network structures, domain-based large margin fine-tuning, and back-end refinement. Our system is a fusion of 9 models and achieves first place in these two tracks of VoxSRC 2021. The minDCF of our submission is 0.1034, and the corresponding EER is 1.8460%.
A Surrogate-based Generic Classifier for Chinese TV Series Reviews
Nov 21, 2016


Abstract:With the emerging of various online video platforms like Youtube, Youku and LeTV, online TV series' reviews become more and more important both for viewers and producers. Customers rely heavily on these reviews before selecting TV series, while producers use them to improve the quality. As a result, automatically classifying reviews according to different requirements evolves as a popular research topic and is essential in our daily life. In this paper, we focused on reviews of hot TV series in China and successfully trained generic classifiers based on eight predefined categories. The experimental results showed promising performance and effectiveness of its generalization to different TV series.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge