Md Sahidullah
MULTISPEECH
MK-SGC-SC: Multiple Kernel Guided Sparse Graph Construction in Spectral Clustering for Unsupervised Speaker Diarization
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Speaker diarization aims to segment audio recordings into regions corresponding to individual speakers. Although unsupervised speaker diarization is inherently challenging, the prospect of identifying speaker regions without pretraining or weak supervision motivates research on clustering techniques. In this work, we share the notable observation that measuring multiple kernel similarities of speaker embeddings to thereafter craft a sparse graph for spectral clustering in a principled manner is sufficient to achieve state-of-the-art performances in a fully unsupervised setting. Specifically, we consider four polynomial kernels and a degree one arccosine kernel to measure similarities in speaker embeddings, using which sparse graphs are constructed in a principled manner to emphasize local similarities. Experiments show the proposed approach excels in unsupervised speaker diarization over a variety of challenging environments in the DIHARD-III, AMI, and VoxConverse corpora. To encourage further research, our implementations are available at https://github.com/nikhilraghav29/MK-SGC-SC.
Shortcut Learning in Binary Classifier Black Boxes: Applications to Voice Anti-Spoofing and Biometrics
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:The widespread adoption of deep-learning models in data-driven applications has drawn attention to the potential risks associated with biased datasets and models. Neglected or hidden biases within datasets and models can lead to unexpected results. This study addresses the challenges of dataset bias and explores ``shortcut learning'' or ``Clever Hans effect'' in binary classifiers. We propose a novel framework for analyzing the black-box classifiers and for examining the impact of both training and test data on classifier scores. Our framework incorporates intervention and observational perspectives, employing a linear mixed-effects model for post-hoc analysis. By evaluating classifier performance beyond error rates, we aim to provide insights into biased datasets and offer a comprehensive understanding of their influence on classifier behavior. The effectiveness of our approach is demonstrated through experiments on audio anti-spoofing and speaker verification tasks using both statistical models and deep neural networks. The insights gained from this study have broader implications for tackling biases in other domains and advancing the field of explainable artificial intelligence.
ASVspoof 5: Evaluation of Spoofing, Deepfake, and Adversarial Attack Detection Using Crowdsourced Speech
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake detection solutions. A significant change from previous challenge editions is a new crowdsourced database collected from a substantially greater number of speakers under diverse recording conditions, and a mix of cutting-edge and legacy generative speech technology. With the new database described elsewhere, we provide in this paper an overview of the ASVspoof 5 challenge results for the submissions of 53 participating teams. While many solutions perform well, performance degrades under adversarial attacks and the application of neural encoding/compression schemes. Together with a review of post-challenge results, we also report a study of calibration in addition to other principal challenges and outline a road-map for the future of ASVspoof.
ASVspoof 5: Design, Collection and Validation of Resources for Spoofing, Deepfake, and Adversarial Attack Detection Using Crowdsourced Speech
Feb 13, 2025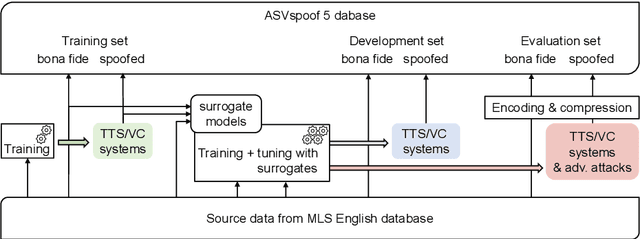

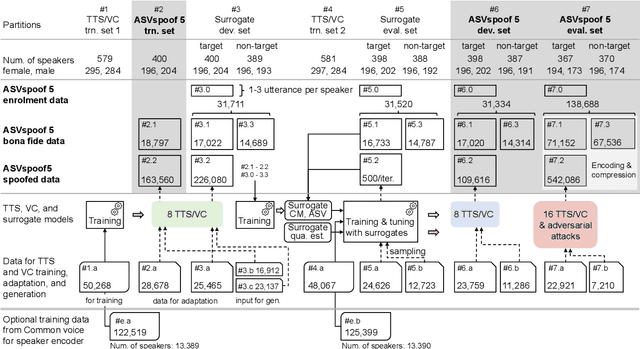
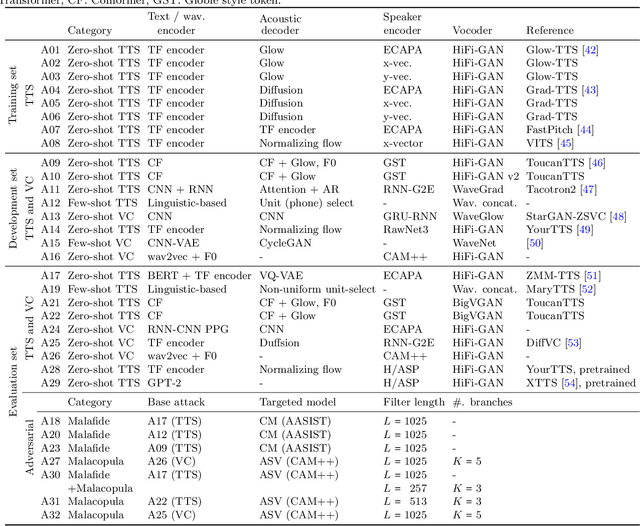
Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake attacks as well as the design of detection solutions. We introduce the ASVspoof 5 database which is generated in crowdsourced fashion from data collected in diverse acoustic conditions (cf. studio-quality data for earlier ASVspoof databases) and from ~2,000 speakers (cf. ~100 earlier). The database contains attacks generated with 32 different algorithms, also crowdsourced, and optimised to varying degrees using new surrogate detection models. Among them are attacks generated with a mix of legacy and contemporary text-to-speech synthesis and voice conversion models, in addition to adversarial attacks which are incorporated for the first time. ASVspoof 5 protocols comprise seven speaker-disjoint partitions. They include two distinct partitions for the training of different sets of attack models, two more for the development and evaluation of surrogate detection models, and then three additional partitions which comprise the ASVspoof 5 training, development and evaluation sets. An auxiliary set of data collected from an additional 30k speakers can also be used to train speaker encoders for the implementation of attack algorithms. Also described herein is an experimental validation of the new ASVspoof 5 database using a set of automatic speaker verification and spoof/deepfake baseline detectors. With the exception of protocols and tools for the generation of spoofed/deepfake speech, the resources described in this paper, already used by participants of the ASVspoof 5 challenge in 2024, are now all freely available to the community.
IITKGP-ABSP Submission to LRE22: Language Recognition in Low-Resource Settings
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:This is the detailed system description of the IITKGP-ABSP lab's submission to the NIST language recognition evaluation (LRE) 2022. The objective of this LRE (LRE22) is focused on recognizing 14 low-resourced African languages. Even though NIST has provided additional training and development data, we develop our systems with additional constraints of extreme low-resource. Our primary fixed-set submission ensures the usage of only the LRE 22 development data that contains the utterances of 14 target languages. We further restrict our system from using any pre-trained models for feature extraction or classifier fine-tuning. To address the issue of low-resource, our system relies on diverse audio augmentations followed by classifier fusions. Abiding by all the constraints, the proposed methods achieve an EER of 11.43% and cost metric of 0.41 in the LRE22 development set. For users with limited computational resources or limited storage/network capabilities, the proposed system will help achieve efficient LID performance.
Explaining Speaker and Spoof Embeddings via Probing
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:This study investigates the explainability of embedding representations, specifically those used in modern audio spoofing detection systems based on deep neural networks, known as spoof embeddings. Building on established work in speaker embedding explainability, we examine how well these spoof embeddings capture speaker-related information. We train simple neural classifiers using either speaker or spoof embeddings as input, with speaker-related attributes as target labels. These attributes are categorized into two groups: metadata-based traits (e.g., gender, age) and acoustic traits (e.g., fundamental frequency, speaking rate). Our experiments on the ASVspoof 2019 LA evaluation set demonstrate that spoof embeddings preserve several key traits, including gender, speaking rate, F0, and duration. Further analysis of gender and speaking rate indicates that the spoofing detector partially preserves these traits, potentially to ensure the decision process remains robust against them.
ASVspoof 5: Crowdsourced Speech Data, Deepfakes, and Adversarial Attacks at Scale
Aug 16, 2024



Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges that promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake attacks, and the design of detection solutions. Compared to previous challenges, the ASVspoof 5 database is built from crowdsourced data collected from a vastly greater number of speakers in diverse acoustic conditions. Attacks, also crowdsourced, are generated and tested using surrogate detection models, while adversarial attacks are incorporated for the first time. New metrics support the evaluation of spoofing-robust automatic speaker verification (SASV) as well as stand-alone detection solutions, i.e., countermeasures without ASV. We describe the two challenge tracks, the new database, the evaluation metrics, baselines, and the evaluation platform, and present a summary of the results. Attacks significantly compromise the baseline systems, while submissions bring substantial improvements.
Beyond Silence: Bias Analysis through Loss and Asymmetric Approach in Audio Anti-Spoofing
Jun 25, 2024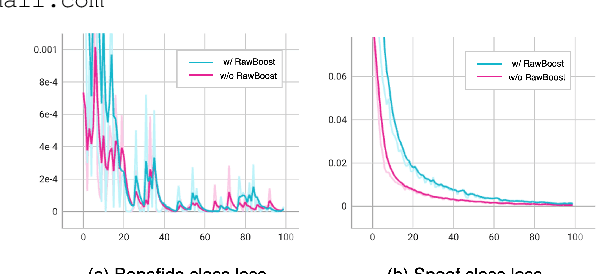
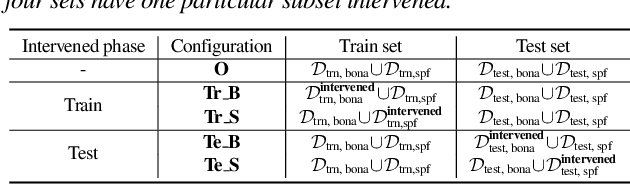
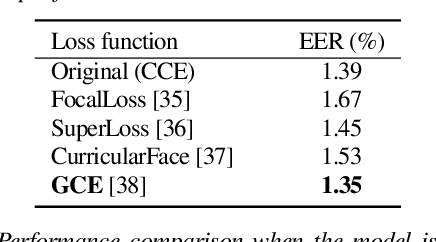
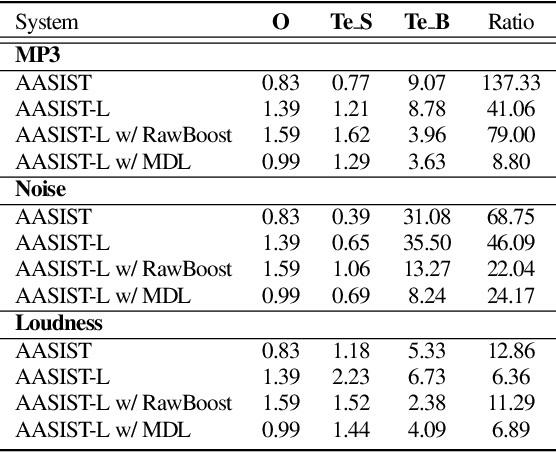
Abstract:Current trends in audio anti-spoofing detection research strive to improve models' ability to generalize across unseen attacks by learning to identify a variety of spoofing artifacts. This emphasis has primarily focused on the spoof class. Recently, several studies have noted that the distribution of silence differs between the two classes, which can serve as a shortcut. In this paper, we extend class-wise interpretations beyond silence. We employ loss analysis and asymmetric methodologies to move away from traditional attack-focused and result-oriented evaluations towards a deeper examination of model behaviors. Our investigations highlight the significant differences in training dynamics between the two classes, emphasizing the need for future research to focus on robust modeling of the bonafide class.
Assessing the Robustness of Spectral Clustering for Deep Speaker Diarization
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:Clustering speaker embeddings is crucial in speaker diarization but hasn't received as much focus as other components. Moreover, the robustness of speaker diarization across various datasets hasn't been explored when the development and evaluation data are from different domains. To bridge this gap, this study thoroughly examines spectral clustering for both same-domain and cross-domain speaker diarization. Our extensive experiments on two widely used corpora, AMI and DIHARD, reveal the performance trend of speaker diarization in the presence of domain mismatch. We observe that the performance difference between two different domain conditions can be attributed to the role of spectral clustering. In particular, keeping other modules unchanged, we show that differences in optimal tuning parameters as well as speaker count estimation originates due to the mismatch. This study opens several future directions for speaker diarization research.
Exploring Green AI for Audio Deepfake Detection
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:The state-of-the-art audio deepfake detectors leveraging deep neural networks exhibit impressive recognition performance. Nonetheless, this advantage is accompanied by a significant carbon footprint. This is mainly due to the use of high-performance computing with accelerators and high training time. Studies show that average deep NLP model produces around 626k lbs of CO\textsubscript{2} which is equivalent to five times of average US car emission at its lifetime. This is certainly a massive threat to the environment. To tackle this challenge, this study presents a novel framework for audio deepfake detection that can be seamlessly trained using standard CPU resources. Our proposed framework utilizes off-the-shelve self-supervised learning (SSL) based models which are pre-trained and available in public repositories. In contrast to existing methods that fine-tune SSL models and employ additional deep neural networks for downstream tasks, we exploit classical machine learning algorithms such as logistic regression and shallow neural networks using the SSL embeddings extracted using the pre-trained model. Our approach shows competitive results compared to the commonly used high-carbon footprint approaches. In experiments with the ASVspoof 2019 LA dataset, we achieve a 0.90\% equal error rate (EER) with less than 1k trainable model parameters. To encourage further research in this direction and support reproducible results, the Python code will be made publicly accessible following acceptance. Github: https://github.com/sahasubhajit/Speech-Spoofing-
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge