Xinyi Gao
Relational Database Distillation: From Structured Tables to Condensed Graph Data
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Relational databases (RDBs) underpin the majority of global data management systems, where information is structured into multiple interdependent tables. To effectively use the knowledge within RDBs for predictive tasks, recent advances leverage graph representation learning to capture complex inter-table relations as multi-hop dependencies. Despite achieving state-of-the-art performance, these methods remain hindered by the prohibitive storage overhead and excessive training time, due to the massive scale of the database and the computational burden of intensive message passing across interconnected tables. To alleviate these concerns, we propose and study the problem of Relational Database Distillation (RDD). Specifically, we aim to distill large-scale RDBs into compact heterogeneous graphs while retaining the predictive power (i.e., utility) required for training graph-based models. Multi-modal column information is preserved through node features, and primary-foreign key relations are encoded via heterogeneous edges, thereby maintaining both data fidelity and relational structure. To ensure adaptability across diverse downstream tasks without engaging the traditional, inefficient bi-level distillation framework, we further design a kernel ridge regression-guided objective with pseudo-labels, which produces quality features for the distilled graph. Extensive experiments on multiple real-world RDBs demonstrate that our solution substantially reduces the data size while maintaining competitive performance on classification and regression tasks, creating an effective pathway for scalable learning with RDBs.
A Hierarchical Probabilistic Framework for Incremental Knowledge Tracing in Classroom Settings
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Knowledge tracing (KT) aims to estimate a student's evolving knowledge state and predict their performance on new exercises based on performance history. Many realistic classroom settings for KT are typically low-resource in data and require online updates as students' exercise history grows, which creates significant challenges for existing KT approaches. To restore strong performance under low-resource conditions, we revisit the hierarchical knowledge concept (KC) information, which is typically available in many classroom settings and can provide strong prior when data are sparse. We therefore propose Knowledge-Tree-based Knowledge Tracing (KT$^2$), a probabilistic KT framework that models student understanding over a tree-structured hierarchy of knowledge concepts using a Hidden Markov Tree Model. KT$^2$ estimates student mastery via an EM algorithm and supports personalized prediction through an incremental update mechanism as new responses arrive. Our experiments show that KT$^2$ consistently outperforms strong baselines in realistic online, low-resource settings.
A Comprehensive Survey on Imbalanced Data Learning
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:With the expansion of data availability, machine learning (ML) has achieved remarkable breakthroughs in both academia and industry. However, imbalanced data distributions are prevalent in various types of raw data and severely hinder the performance of ML by biasing the decision-making processes. To deepen the understanding of imbalanced data and facilitate the related research and applications, this survey systematically analyzing various real-world data formats and concludes existing researches for different data formats into four distinct categories: data re-balancing, feature representation, training strategy, and ensemble learning. This structured analysis help researchers comprehensively understand the pervasive nature of imbalance across diverse data format, thereby paving a clearer path toward achieving specific research goals. we provide an overview of relevant open-source libraries, spotlight current challenges, and offer novel insights aimed at fostering future advancements in this critical area of study.
Norm Augmented Graph AutoEncoders for Link Prediction
Feb 09, 2025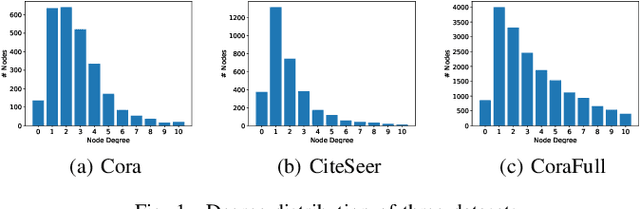
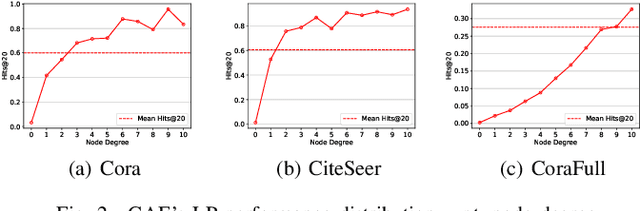
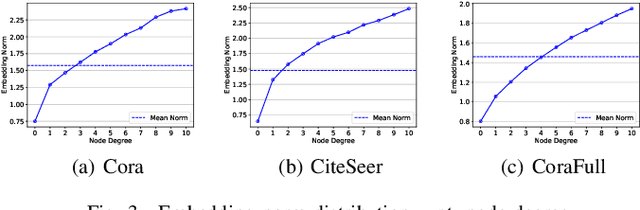
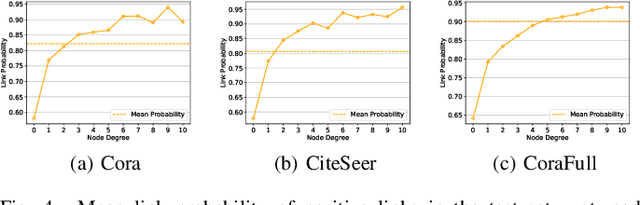
Abstract:Link Prediction (LP) is a crucial problem in graph-structured data. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have gained prominence in LP, with Graph AutoEncoders (GAEs) being a notable representation. However, our empirical findings reveal that GAEs' LP performance suffers heavily from the long-tailed node degree distribution, i.e., low-degree nodes tend to exhibit inferior LP performance compared to high-degree nodes. \emph{What causes this degree-related bias, and how can it be mitigated?} In this study, we demonstrate that the norm of node embeddings learned by GAEs exhibits variation among nodes with different degrees, underscoring its central significance in influencing the final performance of LP. Specifically, embeddings with larger norms tend to guide the decoder towards predicting higher scores for positive links and lower scores for negative links, thereby contributing to superior performance. This observation motivates us to improve GAEs' LP performance on low-degree nodes by increasing their embedding norms, which can be implemented simply yet effectively by introducing additional self-loops into the training objective for low-degree nodes. This norm augmentation strategy can be seamlessly integrated into existing GAE methods with light computational cost. Extensive experiments on various datasets and GAE methods show the superior performance of norm-augmented GAEs.
FedVCK: Non-IID Robust and Communication-Efficient Federated Learning via Valuable Condensed Knowledge for Medical Image Analysis
Dec 24, 2024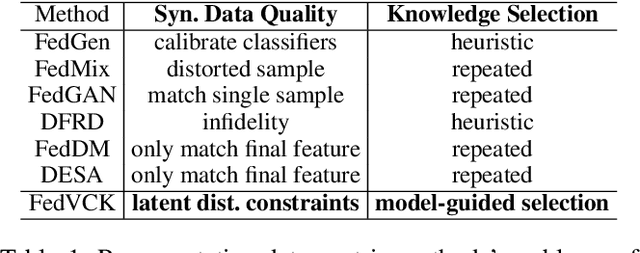
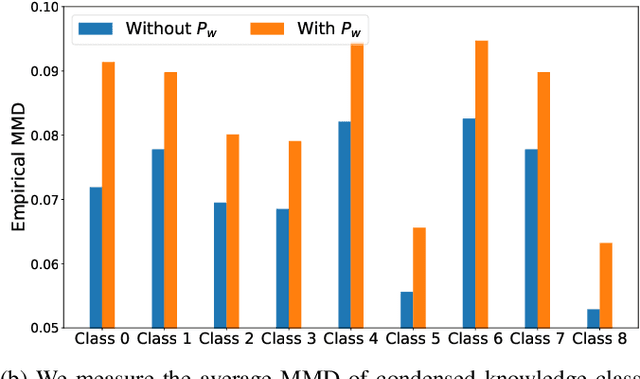
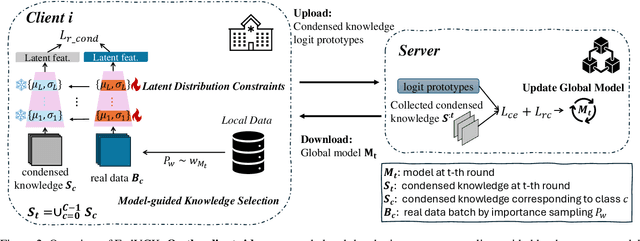
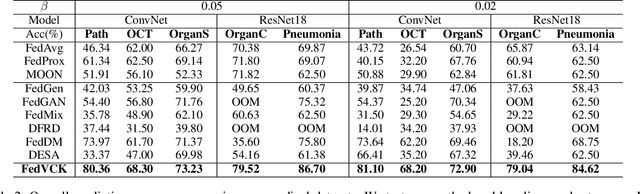
Abstract:Federated learning has become a promising solution for collaboration among medical institutions. However, data owned by each institution would be highly heterogeneous and the distribution is always non-independent and identical distribution (non-IID), resulting in client drift and unsatisfactory performance. Despite existing federated learning methods attempting to solve the non-IID problems, they still show marginal advantages but rely on frequent communication which would incur high costs and privacy concerns. In this paper, we propose a novel federated learning method: \textbf{Fed}erated learning via \textbf{V}aluable \textbf{C}ondensed \textbf{K}nowledge (FedVCK). We enhance the quality of condensed knowledge and select the most necessary knowledge guided by models, to tackle the non-IID problem within limited communication budgets effectively. Specifically, on the client side, we condense the knowledge of each client into a small dataset and further enhance the condensation procedure with latent distribution constraints, facilitating the effective capture of high-quality knowledge. During each round, we specifically target and condense knowledge that has not been assimilated by the current model, thereby preventing unnecessary repetition of homogeneous knowledge and minimizing the frequency of communications required. On the server side, we propose relational supervised contrastive learning to provide more supervision signals to aid the global model updating. Comprehensive experiments across various medical tasks show that FedVCK can outperform state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating that it's non-IID robust and communication-efficient.
Training-free Heterogeneous Graph Condensation via Data Selection
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Efficient training of large-scale heterogeneous graphs is of paramount importance in real-world applications. However, existing approaches typically explore simplified models to mitigate resource and time overhead, neglecting the crucial aspect of simplifying large-scale heterogeneous graphs from the data-centric perspective. Addressing this gap, HGCond introduces graph condensation (GC) in heterogeneous graphs and generates a small condensed graph for efficient model training. Despite its efficacy in graph generation, HGCond encounters two significant limitations. The first is low effectiveness, HGCond excessively relies on the simplest relay model for the condensation procedure, which restricts the ability to exert powerful Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks (HGNNs) with flexible condensation ratio and limits the generalization ability. The second is low efficiency, HGCond follows the existing GC methods designed for homogeneous graphs and leverages the sophisticated optimization paradigm, resulting in a time-consuming condensing procedure. In light of these challenges, we present the first Training \underline{Free} Heterogeneous Graph Condensation method, termed FreeHGC, facilitating both efficient and high-quality generation of heterogeneous condensed graphs. Specifically, we reformulate the heterogeneous graph condensation problem as a data selection issue, offering a new perspective for assessing and condensing representative nodes and edges in the heterogeneous graphs. By leveraging rich meta-paths, we introduce a new, high-quality heterogeneous data selection criterion to select target-type nodes. Furthermore, two training-free condensation strategies for heterogeneous graphs are designed to condense and synthesize other-types nodes effectively.
Contrastive Graph Condensation: Advancing Data Versatility through Self-Supervised Learning
Nov 26, 2024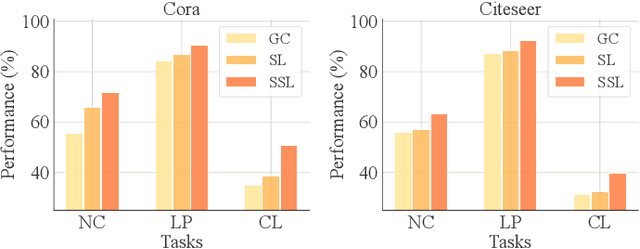
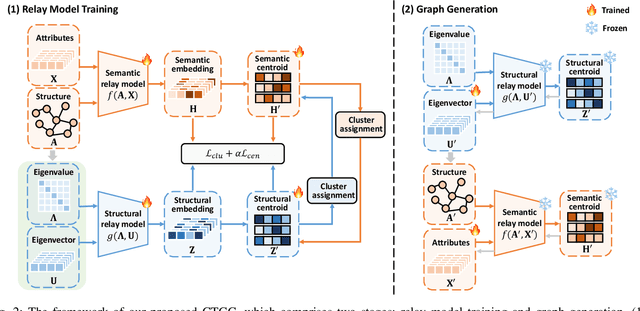
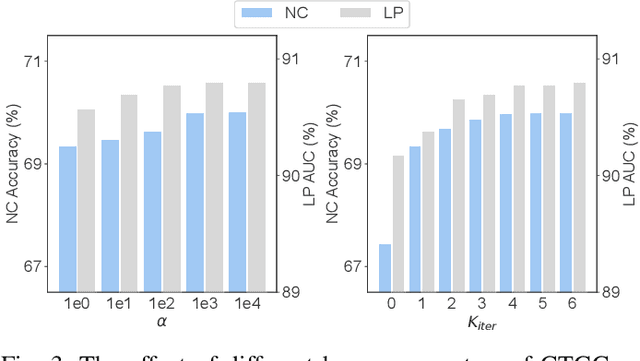
Abstract:With the increasing computation of training graph neural networks (GNNs) on large-scale graphs, graph condensation (GC) has emerged as a promising solution to synthesize a compact, substitute graph of the large-scale original graph for efficient GNN training. However, existing GC methods predominantly employ classification as the surrogate task for optimization, thus excessively relying on node labels and constraining their utility in label-sparsity scenarios. More critically, this surrogate task tends to overfit class-specific information within the condensed graph, consequently restricting the generalization capabilities of GC for other downstream tasks. To address these challenges, we introduce Contrastive Graph Condensation (CTGC), which adopts a self-supervised surrogate task to extract critical, causal information from the original graph and enhance the cross-task generalizability of the condensed graph. Specifically, CTGC employs a dual-branch framework to disentangle the generation of the node attributes and graph structures, where a dedicated structural branch is designed to explicitly encode geometric information through nodes' positional embeddings. By implementing an alternating optimization scheme with contrastive loss terms, CTGC promotes the mutual enhancement of both branches and facilitates high-quality graph generation through the model inversion technique. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CTGC excels in handling various downstream tasks with a limited number of labels, consistently outperforming state-of-the-art GC methods.
Teaching MLPs to Master Heterogeneous Graph-Structured Knowledge for Efficient and Accurate Inference
Nov 21, 2024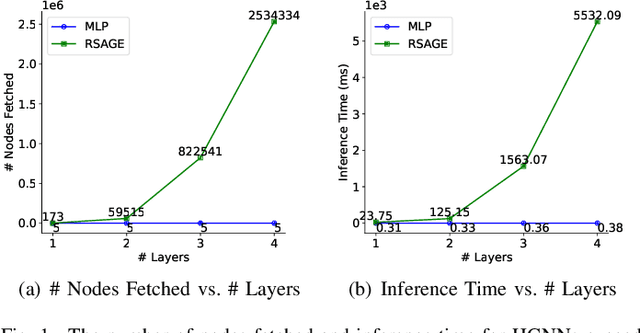
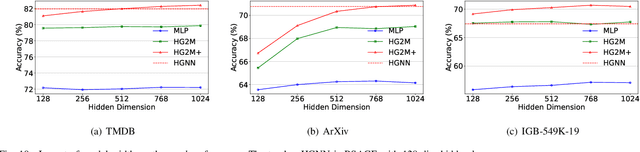
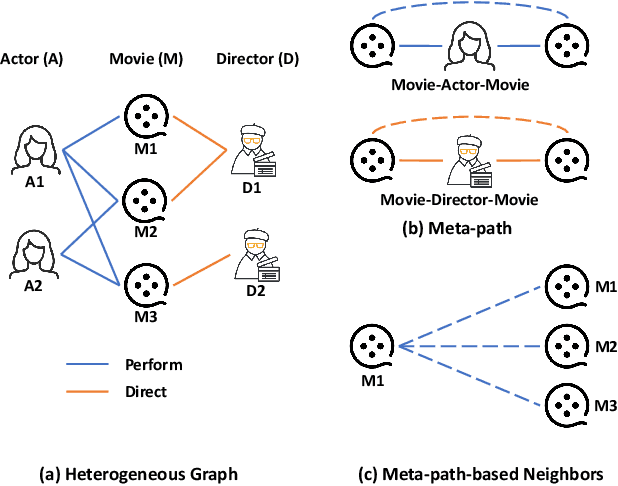
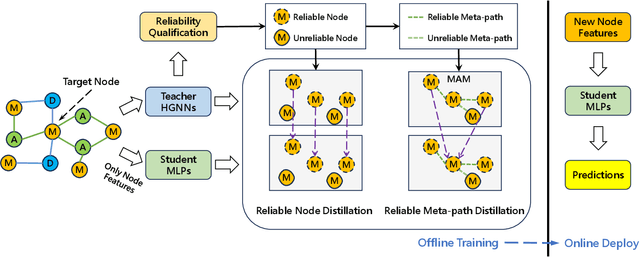
Abstract:Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks (HGNNs) have achieved promising results in various heterogeneous graph learning tasks, owing to their superiority in capturing the intricate relationships and diverse relational semantics inherent in heterogeneous graph structures. However, the neighborhood-fetching latency incurred by structure dependency in HGNNs makes it challenging to deploy for latency-constrained applications that require fast inference. Inspired by recent GNN-to-MLP knowledge distillation frameworks, we introduce HG2M and HG2M+ to combine both HGNN's superior performance and MLP's efficient inference. HG2M directly trains student MLPs with node features as input and soft labels from teacher HGNNs as targets, and HG2M+ further distills reliable and heterogeneous semantic knowledge into student MLPs through reliable node distillation and reliable meta-path distillation. Experiments conducted on six heterogeneous graph datasets show that despite lacking structural dependencies, HG2Ms can still achieve competitive or even better performance than HGNNs and significantly outperform vanilla MLPs. Moreover, HG2Ms demonstrate a 379.24$\times$ speedup in inference over HGNNs on the large-scale IGB-3M-19 dataset, showcasing their ability for latency-sensitive deployments.
Epidemiology-informed Network for Robust Rumor Detection
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:The rapid spread of rumors on social media has posed significant challenges to maintaining public trust and information integrity. Since an information cascade process is essentially a propagation tree, recent rumor detection models leverage graph neural networks to additionally capture information propagation patterns, thus outperforming text-only solutions. Given the variations in topics and social impact of the root node, different source information naturally has distinct outreach capabilities, resulting in different heights of propagation trees. This variation, however, impedes the data-driven design of existing graph-based rumor detectors. Given a shallow propagation tree with limited interactions, it is unlikely for graph-based approaches to capture sufficient cascading patterns, questioning their ability to handle less popular news or early detection needs. In contrast, a deep propagation tree is prone to noisy user responses, and this can in turn obfuscate the predictions. In this paper, we propose a novel Epidemiology-informed Network (EIN) that integrates epidemiological knowledge to enhance performance by overcoming data-driven methods sensitivity to data quality. Meanwhile, to adapt epidemiology theory to rumor detection, it is expected that each users stance toward the source information will be annotated. To bypass the costly and time-consuming human labeling process, we take advantage of large language models to generate stance labels, facilitating optimization objectives for learning epidemiology-informed representations. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed EIN not only outperforms state-of-the-art methods on real-world datasets but also exhibits enhanced robustness across varying tree depths.
Adaptive Paradigm Synergy: Can a Cross-Paradigm Objective Enhance Long-Tailed Learning?
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) has achieved impressive results across several computer vision tasks, even rivaling supervised methods. However, its performance degrades on real-world datasets with long-tailed distributions due to difficulties in capturing inherent class imbalances. Although supervised long-tailed learning offers significant insights, the absence of labels in SSL prevents direct transfer of these strategies.To bridge this gap, we introduce Adaptive Paradigm Synergy (APS), a cross-paradigm objective that seeks to unify the strengths of both paradigms. Our approach reexamines contrastive learning from a spatial structure perspective, dynamically adjusting the uniformity of latent space structure through adaptive temperature tuning. Furthermore, we draw on a re-weighting strategy from supervised learning to compensate for the shortcomings of temperature adjustment in explicit quantity perception.Extensive experiments on commonly used long-tailed datasets demonstrate that APS improves performance effectively and efficiently. Our findings reveal the potential for deeper integration between supervised and self-supervised learning, paving the way for robust models that handle real-world class imbalance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge