Tieke He
Tabular Foundation Models are Strong Graph Anomaly Detectors
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Graph anomaly detection (GAD), which aims to identify abnormal nodes that deviate from the majority, has become increasingly important in high-stakes Web domains. However, existing GAD methods follow a "one model per dataset" paradigm, leading to high computational costs, substantial data demands, and poor generalization when transferred to new datasets. This calls for a foundation model that enables a "one-for-all" GAD solution capable of detecting anomalies across diverse graphs without retraining. Yet, achieving this is challenging due to the large structural and feature heterogeneity across domains. In this paper, we propose TFM4GAD, a simple yet effective framework that adapts tabular foundation models (TFMs) for graph anomaly detection. Our key insight is that the core challenges of foundation GAD, handling heterogeneous features, generalizing across domains, and operating with scarce labels, are the exact problems that modern TFMs are designed to solve via synthetic pre-training and powerful in-context learning. The primary challenge thus becomes structural: TFMs are agnostic to graph topology. TFM4GAD bridges this gap by "flattening" the graph, constructing an augmented feature table that enriches raw node features with Laplacian embeddings, local and global structural characteristics, and anomaly-sensitive neighborhood aggregations. This augmented table is processed by a TFM in a fully in-context regime. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets with various TFM backbones reveal that TFM4GAD surprisingly achieves significant performance gains over specialized GAD models trained from scratch. Our work offers a new perspective and a practical paradigm for leveraging TFMs as powerful, generalist graph anomaly detectors.
A Pre-Training and Adaptive Fine-Tuning Framework for Graph Anomaly Detection
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Graph anomaly detection (GAD) has garnered increasing attention in recent years, yet it remains challenging due to the scarcity of abnormal nodes and the high cost of label annotations. Graph pre-training, the two-stage learning paradigm, has emerged as an effective approach for label-efficient learning, largely benefiting from expressive neighborhood aggregation under the assumption of strong homophily. However, in GAD, anomalies typically exhibit high local heterophily, while normal nodes retain strong homophily, resulting in a complex homophily-heterophily mixture. To understand the impact of this mixed pattern on graph pre-training, we analyze it through the lens of spectral filtering and reveal that relying solely on a global low-pass filter is insufficient for GAD. We further provide a theoretical justification for the necessity of selectively applying appropriate filters to individual nodes. Building upon this insight, we propose PAF, a Pre-Training and Adaptive Fine-tuning framework specifically designed for GAD. In particular, we introduce joint training with low- and high-pass filters in the pre-training phase to capture the full spectrum of frequency information in node features. During fine-tuning, we devise a gated fusion network that adaptively combines node representations generated by both filters. Extensive experiments across ten benchmark datasets consistently demonstrate the effectiveness of PAF.
Learning Accurate, Efficient, and Interpretable MLPs on Multiplex Graphs via Node-wise Multi-View Ensemble Distillation
Feb 09, 2025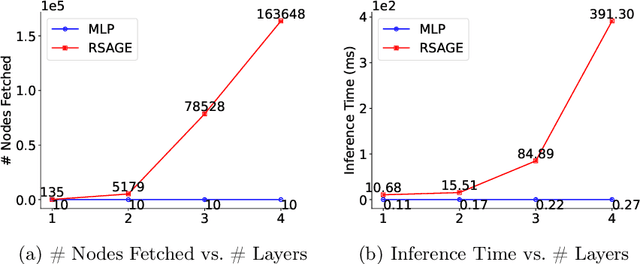
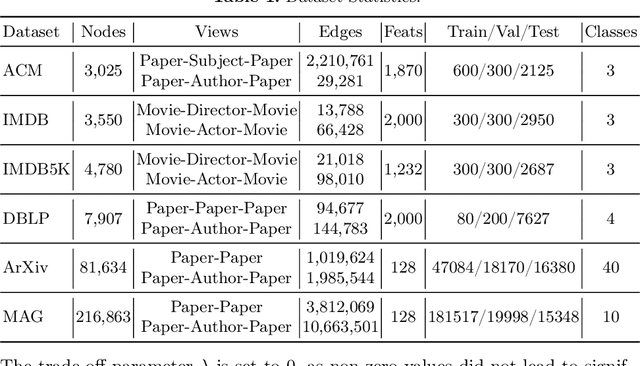
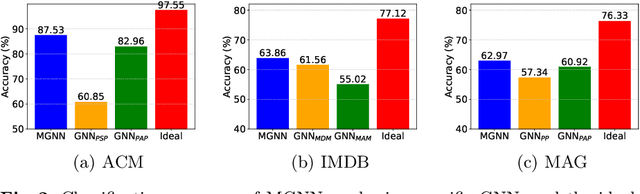
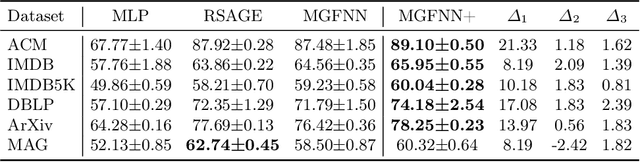
Abstract:Multiplex graphs, with multiple edge types (graph views) among common nodes, provide richer structural semantics and better modeling capabilities. Multiplex Graph Neural Networks (MGNNs), typically comprising view-specific GNNs and a multi-view integration layer, have achieved advanced performance in various downstream tasks. However, their reliance on neighborhood aggregation poses challenges for deployment in latency-sensitive applications. Motivated by recent GNN-to-MLP knowledge distillation frameworks, we propose Multiplex Graph-Free Neural Networks (MGFNN and MGFNN+) to combine MGNNs' superior performance and MLPs' efficient inference via knowledge distillation. MGFNN directly trains student MLPs with node features as input and soft labels from teacher MGNNs as targets. MGFNN+ further employs a low-rank approximation-based reparameterization to learn node-wise coefficients, enabling adaptive knowledge ensemble from each view-specific GNN. This node-wise multi-view ensemble distillation strategy allows student MLPs to learn more informative multiplex semantic knowledge for different nodes. Experiments show that MGFNNs achieve average accuracy improvements of about 10% over vanilla MLPs and perform comparably or even better to teacher MGNNs (accurate); MGFNNs achieve a 35.40$\times$-89.14$\times$ speedup in inference over MGNNs (efficient); MGFNN+ adaptively assigns different coefficients for multi-view ensemble distillation regarding different nodes (interpretable).
Norm Augmented Graph AutoEncoders for Link Prediction
Feb 09, 2025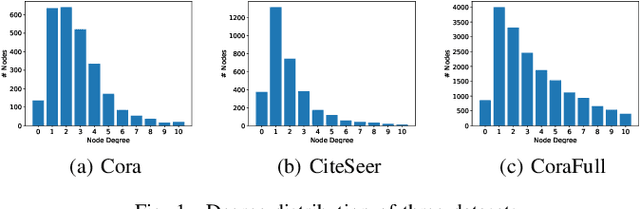
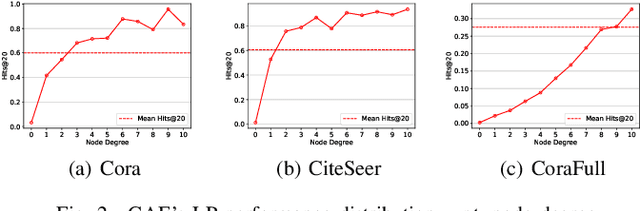
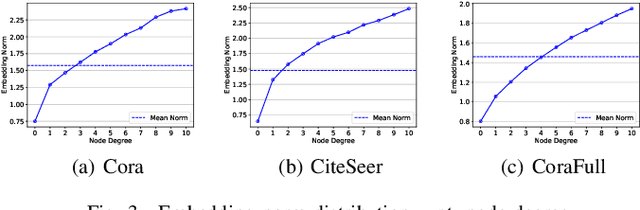
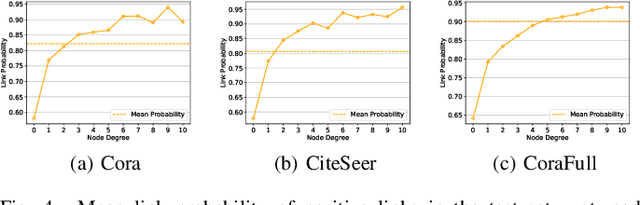
Abstract:Link Prediction (LP) is a crucial problem in graph-structured data. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have gained prominence in LP, with Graph AutoEncoders (GAEs) being a notable representation. However, our empirical findings reveal that GAEs' LP performance suffers heavily from the long-tailed node degree distribution, i.e., low-degree nodes tend to exhibit inferior LP performance compared to high-degree nodes. \emph{What causes this degree-related bias, and how can it be mitigated?} In this study, we demonstrate that the norm of node embeddings learned by GAEs exhibits variation among nodes with different degrees, underscoring its central significance in influencing the final performance of LP. Specifically, embeddings with larger norms tend to guide the decoder towards predicting higher scores for positive links and lower scores for negative links, thereby contributing to superior performance. This observation motivates us to improve GAEs' LP performance on low-degree nodes by increasing their embedding norms, which can be implemented simply yet effectively by introducing additional self-loops into the training objective for low-degree nodes. This norm augmentation strategy can be seamlessly integrated into existing GAE methods with light computational cost. Extensive experiments on various datasets and GAE methods show the superior performance of norm-augmented GAEs.
Multi-Scale Heterogeneous Text-Attributed Graph Datasets From Diverse Domains
Dec 12, 2024
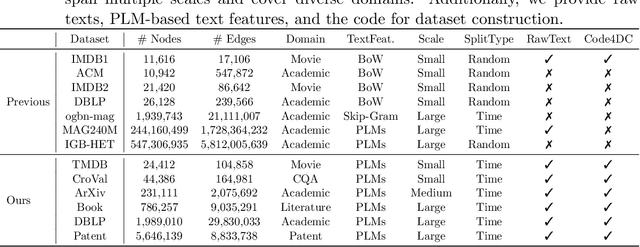
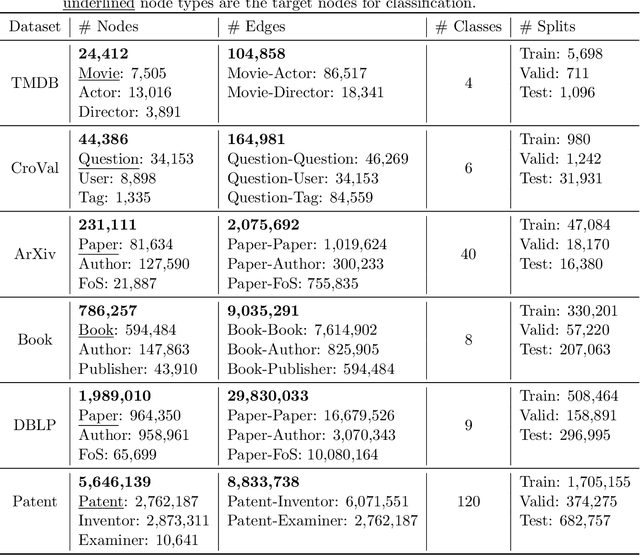
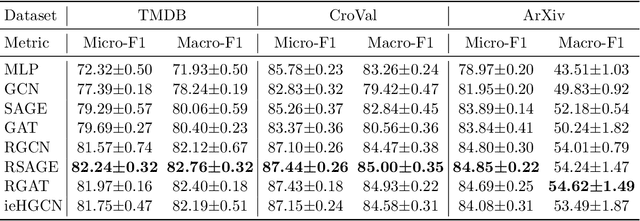
Abstract:Heterogeneous Text-Attributed Graphs (HTAGs), where different types of entities are not only associated with texts but also connected by diverse relationships, have gained widespread popularity and application across various domains. However, current research on text-attributed graph learning predominantly focuses on homogeneous graphs, which feature a single node and edge type, thus leaving a gap in understanding how methods perform on HTAGs. One crucial reason is the lack of comprehensive HTAG datasets that offer original textual content and span multiple domains of varying sizes. To this end, we introduce a collection of challenging and diverse benchmark datasets for realistic and reproducible evaluation of machine learning models on HTAGs. Our HTAG datasets are multi-scale, span years in duration, and cover a wide range of domains, including movie, community question answering, academic, literature, and patent networks. We further conduct benchmark experiments on these datasets with various graph neural networks. All source data, dataset construction codes, processed HTAGs, data loaders, benchmark codes, and evaluation setup are publicly available at GitHub and Hugging Face.
Teaching MLPs to Master Heterogeneous Graph-Structured Knowledge for Efficient and Accurate Inference
Nov 21, 2024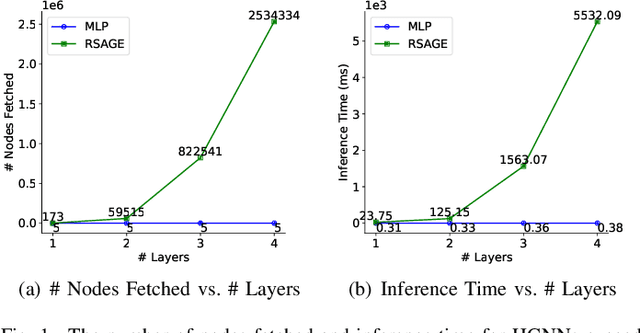
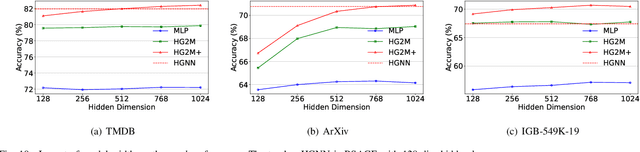
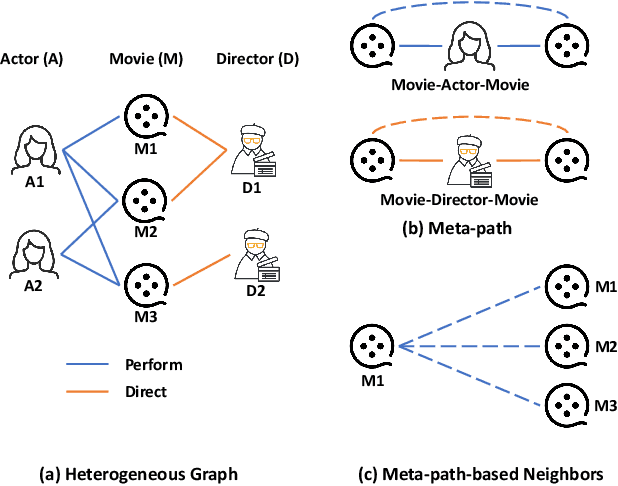
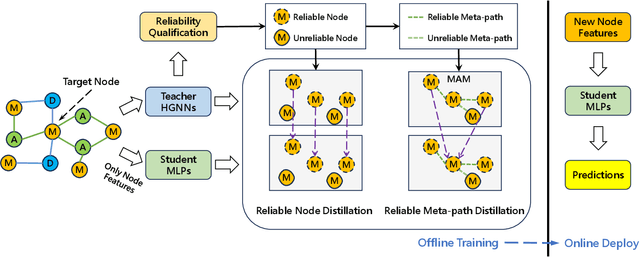
Abstract:Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks (HGNNs) have achieved promising results in various heterogeneous graph learning tasks, owing to their superiority in capturing the intricate relationships and diverse relational semantics inherent in heterogeneous graph structures. However, the neighborhood-fetching latency incurred by structure dependency in HGNNs makes it challenging to deploy for latency-constrained applications that require fast inference. Inspired by recent GNN-to-MLP knowledge distillation frameworks, we introduce HG2M and HG2M+ to combine both HGNN's superior performance and MLP's efficient inference. HG2M directly trains student MLPs with node features as input and soft labels from teacher HGNNs as targets, and HG2M+ further distills reliable and heterogeneous semantic knowledge into student MLPs through reliable node distillation and reliable meta-path distillation. Experiments conducted on six heterogeneous graph datasets show that despite lacking structural dependencies, HG2Ms can still achieve competitive or even better performance than HGNNs and significantly outperform vanilla MLPs. Moreover, HG2Ms demonstrate a 379.24$\times$ speedup in inference over HGNNs on the large-scale IGB-3M-19 dataset, showcasing their ability for latency-sensitive deployments.
Negative-Free Self-Supervised Gaussian Embedding of Graphs
Nov 02, 2024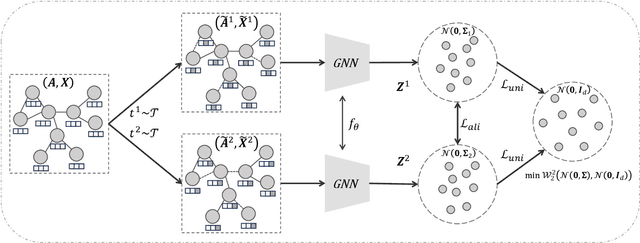
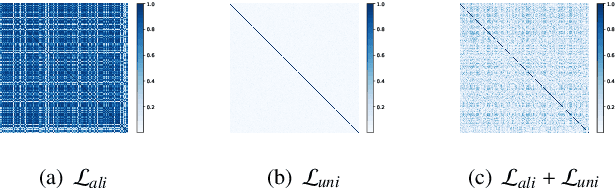
Abstract:Graph Contrastive Learning (GCL) has recently emerged as a promising graph self-supervised learning framework for learning discriminative node representations without labels. The widely adopted objective function of GCL benefits from two key properties: \emph{alignment} and \emph{uniformity}, which align representations of positive node pairs while uniformly distributing all representations on the hypersphere. The uniformity property plays a critical role in preventing representation collapse and is achieved by pushing apart augmented views of different nodes (negative pairs). As such, existing GCL methods inherently rely on increasing the quantity and quality of negative samples, resulting in heavy computational demands, memory overhead, and potential class collision issues. In this study, we propose a negative-free objective to achieve uniformity, inspired by the fact that points distributed according to a normalized isotropic Gaussian are uniformly spread across the unit hypersphere. Therefore, we can minimize the distance between the distribution of learned representations and the isotropic Gaussian distribution to promote the uniformity of node representations. Our method also distinguishes itself from other approaches by eliminating the need for a parameterized mutual information estimator, an additional projector, asymmetric structures, and, crucially, negative samples. Extensive experiments over seven graph benchmarks demonstrate that our proposal achieves competitive performance with fewer parameters, shorter training times, and lower memory consumption compared to existing GCL methods.
Scalable and Adaptive Spectral Embedding for Attributed Graph Clustering
Aug 11, 2024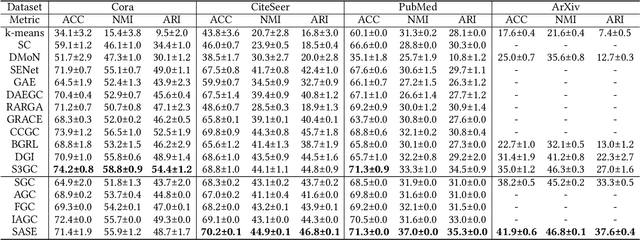
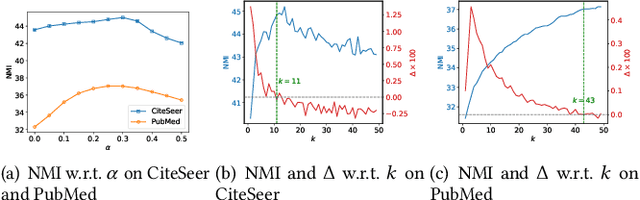
Abstract:Attributed graph clustering, which aims to group the nodes of an attributed graph into disjoint clusters, has made promising advancements in recent years. However, most existing methods face challenges when applied to large graphs due to the expensive computational cost and high memory usage. In this paper, we introduce Scalable and Adaptive Spectral Embedding (SASE), a simple attributed graph clustering method devoid of parameter learning. SASE comprises three main components: node features smoothing via $k$-order simple graph convolution, scalable spectral clustering using random Fourier features, and adaptive order selection. With these designs, SASE not only effectively captures global cluster structures but also exhibits linear time and space complexity relative to the graph size. Empirical results demonstrate the superiority of SASE. For example, on the ArXiv dataset with 169K nodes and 1.17M edges, SASE achieves a 6.9\% improvement in ACC and a $5.87\times$ speedup compared to the runner-up, S3GC.
Bootstrap Latents of Nodes and Neighbors for Graph Self-Supervised Learning
Aug 09, 2024Abstract:Contrastive learning is a significant paradigm in graph self-supervised learning. However, it requires negative samples to prevent model collapse and learn discriminative representations. These negative samples inevitably lead to heavy computation, memory overhead and class collision, compromising the representation learning. Recent studies present that methods obviating negative samples can attain competitive performance and scalability enhancements, exemplified by bootstrapped graph latents (BGRL). However, BGRL neglects the inherent graph homophily, which provides valuable insights into underlying positive pairs. Our motivation arises from the observation that subtly introducing a few ground-truth positive pairs significantly improves BGRL. Although we can't obtain ground-truth positive pairs without labels under the self-supervised setting, edges in the graph can reflect noisy positive pairs, i.e., neighboring nodes often share the same label. Therefore, we propose to expand the positive pair set with node-neighbor pairs. Subsequently, we introduce a cross-attention module to predict the supportiveness score of a neighbor with respect to the anchor node. This score quantifies the positive support from each neighboring node, and is encoded into the training objective. Consequently, our method mitigates class collision from negative and noisy positive samples, concurrently enhancing intra-class compactness. Extensive experiments are conducted on five benchmark datasets and three downstream task node classification, node clustering, and node similarity search. The results demonstrate that our method generates node representations with enhanced intra-class compactness and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Reliable Node Similarity Matrix Guided Contrastive Graph Clustering
Aug 07, 2024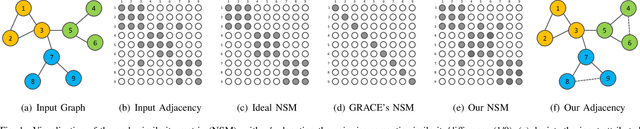
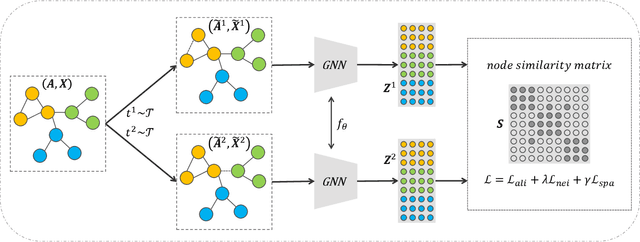
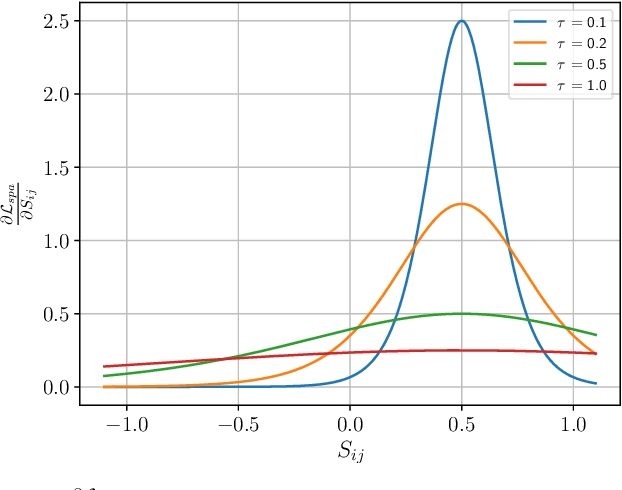
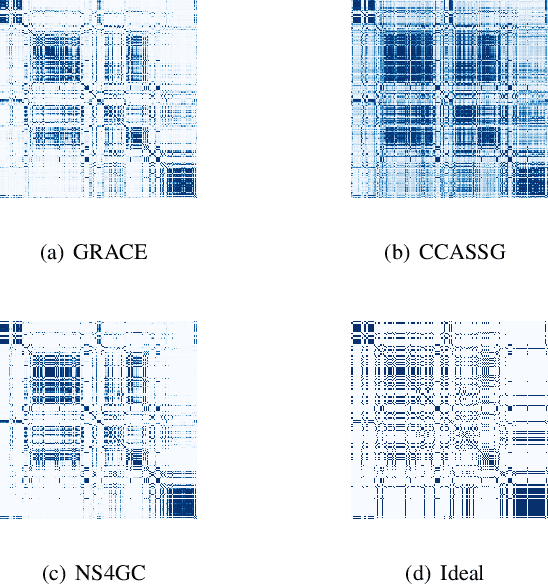
Abstract:Graph clustering, which involves the partitioning of nodes within a graph into disjoint clusters, holds significant importance for numerous subsequent applications. Recently, contrastive learning, known for utilizing supervisory information, has demonstrated encouraging results in deep graph clustering. This methodology facilitates the learning of favorable node representations for clustering by attracting positively correlated node pairs and distancing negatively correlated pairs within the representation space. Nevertheless, a significant limitation of existing methods is their inadequacy in thoroughly exploring node-wise similarity. For instance, some hypothesize that the node similarity matrix within the representation space is identical, ignoring the inherent semantic relationships among nodes. Given the fundamental role of instance similarity in clustering, our research investigates contrastive graph clustering from the perspective of the node similarity matrix. We argue that an ideal node similarity matrix within the representation space should accurately reflect the inherent semantic relationships among nodes, ensuring the preservation of semantic similarities in the learned representations. In response to this, we introduce a new framework, Reliable Node Similarity Matrix Guided Contrastive Graph Clustering (NS4GC), which estimates an approximately ideal node similarity matrix within the representation space to guide representation learning. Our method introduces node-neighbor alignment and semantic-aware sparsification, ensuring the node similarity matrix is both accurate and efficiently sparse. Comprehensive experiments conducted on $8$ real-world datasets affirm the efficacy of learning the node similarity matrix and the superior performance of NS4GC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge