Scalable and Adaptive Spectral Embedding for Attributed Graph Clustering
Paper and Code
Aug 11, 2024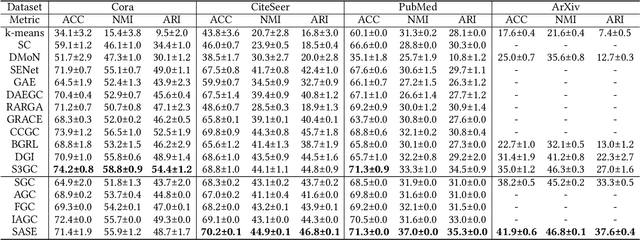
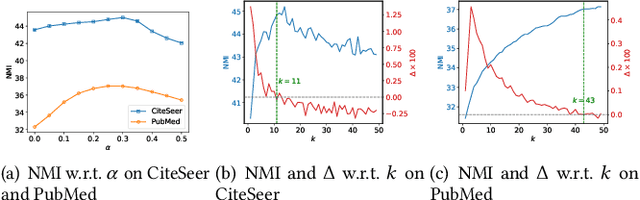
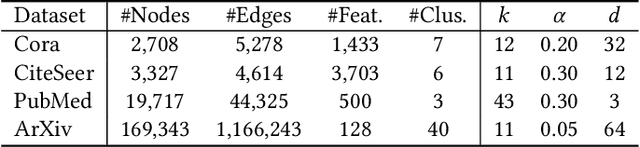
Attributed graph clustering, which aims to group the nodes of an attributed graph into disjoint clusters, has made promising advancements in recent years. However, most existing methods face challenges when applied to large graphs due to the expensive computational cost and high memory usage. In this paper, we introduce Scalable and Adaptive Spectral Embedding (SASE), a simple attributed graph clustering method devoid of parameter learning. SASE comprises three main components: node features smoothing via $k$-order simple graph convolution, scalable spectral clustering using random Fourier features, and adaptive order selection. With these designs, SASE not only effectively captures global cluster structures but also exhibits linear time and space complexity relative to the graph size. Empirical results demonstrate the superiority of SASE. For example, on the ArXiv dataset with 169K nodes and 1.17M edges, SASE achieves a 6.9\% improvement in ACC and a $5.87\times$ speedup compared to the runner-up, S3GC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge