Chong Chen
Panning for Gold: Expanding Domain-Specific Knowledge Graphs with General Knowledge
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Domain-specific knowledge graphs (DKGs) often lack coverage compared to general knowledge graphs (GKGs). To address this, we introduce Domain-specific Knowledge Graph Fusion (DKGF), a novel task that enriches DKGs by integrating relevant facts from GKGs. DKGF faces two key challenges: high ambiguity in domain relevance and misalignment in knowledge granularity across graphs. We propose ExeFuse, a simple yet effective Fact-as-Program paradigm. It treats each GKG fact as a latent semantic program, maps abstract relations to granularity-aware operators, and verifies domain relevance via program executability on the target DKG. This unified probabilistic framework jointly resolves relevance and granularity issues. We construct two benchmarks, DKGF(W-I) and DKGF(Y-I), with 21 evaluation configurations. Extensive experiments validate the task's importance and our model's effectiveness, providing the first standardized testbed for DKGF.
M$^3$Searcher: Modular Multimodal Information Seeking Agency with Retrieval-Oriented Reasoning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in DeepResearch-style agents have demonstrated strong capabilities in autonomous information acquisition and synthesize from real-world web environments. However, existing approaches remain fundamentally limited to text modality. Extending autonomous information-seeking agents to multimodal settings introduces critical challenges: the specialization-generalization trade-off that emerges when training models for multimodal tool-use at scale, and the severe scarcity of training data capturing complex, multi-step multimodal search trajectories. To address these challenges, we propose M$^3$Searcher, a modular multimodal information-seeking agent that explicitly decouples information acquisition from answer derivation. M$^3$Searcher is optimized with a retrieval-oriented multi-objective reward that jointly encourages factual accuracy, reasoning soundness, and retrieval fidelity. In addition, we develop MMSearchVQA, a multimodal multi-hop dataset to support retrieval centric RL training. Experimental results demonstrate that M$^3$Searcher outperforms existing approaches, exhibits strong transfer adaptability and effective reasoning in complex multimodal tasks.
The Best of the Two Worlds: Harmonizing Semantic and Hash IDs for Sequential Recommendation
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Conventional Sequential Recommender Systems (SRS) typically assign unique Hash IDs (HID) to construct item embeddings. These HID embeddings effectively learn collaborative information from historical user-item interactions, making them vulnerable to situations where most items are rarely consumed (the long-tail problem). Recent methods that incorporate auxiliary information often suffer from noisy collaborative sharing caused by co-occurrence signals or semantic homogeneity caused by flat dense embeddings. Semantic IDs (SIDs), with their capability of code sharing and multi-granular semantic modeling, provide a promising alternative. However, the collaborative overwhelming phenomenon hinders the further development of SID-based methods. The quantization mechanisms commonly compromise the uniqueness of identifiers required for modeling head items, creating a performance seesaw between head and tail items. To address this dilemma, we propose \textbf{\name}, a novel framework that harmonizes the SID and HID. Specifically, we devise a dual-branch modeling architecture that enables the model to capture both the multi-granular semantics within SID while preserving the unique collaborative identity of HID. Furthermore, we introduce a dual-level alignment strategy that bridges the two representations, facilitating knowledge transfer and supporting robust preference modeling. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets show that \name~ effectively balances recommendation quality for both head and tail items while surpassing the existing baselines. The implementation code can be found online\footnote{https://github.com/ziwliu8/H2Rec}.
Fracture interactive geodesic active contours for bone segmentation
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:For bone segmentation, the classical geodesic active contour model is usually limited by its indiscriminate feature extraction, and then struggles to handle the phenomena of edge obstruction, edge leakage and bone fracture. Thus, we propose a fracture interactive geodesic active contour algorithm tailored for bone segmentation, which can better capture bone features and perform robustly to the presence of bone fractures and soft tissues. Inspired by orthopedic knowledge, we construct a novel edge-detector function that combines the intensity and gradient norm, which guides the contour towards bone edges without being obstructed by other soft tissues and therefore reduces mis-segmentation. Furthermore, distance information, where fracture prompts can be embedded, is introduced into the contour evolution as an adaptive step size to stabilize the evolution and help the contour stop at bone edges and fractures. This embedding provides a way to interact with bone fractures and improves the accuracy in the fracture regions. Experiments in pelvic and ankle segmentation demonstrate the effectiveness on addressing the aforementioned problems and show an accurate, stable and consistent performance, indicating a broader application in other bone anatomies. Our algorithm also provides insights into combining the domain knowledge and deep neural networks.
M2IO-R1: An Efficient RL-Enhanced Reasoning Framework for Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Multimodal Generation
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Current research on Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (MRAG) enables diverse multimodal inputs but remains limited to single-modality outputs, restricting expressive capacity and practical utility. In contrast, real-world applications often demand both multimodal inputs and multimodal outputs for effective communication and grounded reasoning. Motivated by the recent success of Reinforcement Learning (RL) in complex reasoning tasks for Large Language Models (LLMs), we adopt RL as a principled and effective paradigm to address the multi-step, outcome-driven challenges inherent in multimodal output generation. Here, we introduce M2IO-R1, a novel framework for Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Multimodal Generation (MRAMG) that supports both multimodal inputs and outputs. Central to our framework is an RL-based inserter, Inserter-R1-3B, trained with Group Relative Policy Optimization to guide image selection and placement in a controllable and semantically aligned manner. Empirical results show that our lightweight 3B inserter achieves strong reasoning capabilities with significantly reduced latency, outperforming baselines in both quality and efficiency.
PilotRL: Training Language Model Agents via Global Planning-Guided Progressive Reinforcement Learning
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable advancements in tackling agent-oriented tasks. Despite their potential, existing work faces challenges when deploying LLMs in agent-based environments. The widely adopted agent paradigm ReAct centers on integrating single-step reasoning with immediate action execution, which limits its effectiveness in complex tasks requiring long-term strategic planning. Furthermore, the coordination between the planner and executor during problem-solving is also a critical factor to consider in agent design. Additionally, current approaches predominantly rely on supervised fine-tuning, which often leads models to memorize established task completion trajectories, thereby restricting their generalization ability when confronted with novel problem contexts. To address these challenges, we introduce an adaptive global plan-based agent paradigm AdaPlan, aiming to synergize high-level explicit guidance with execution to support effective long-horizon decision-making. Based on the proposed paradigm, we further put forward PilotRL, a global planning-guided training framework for LLM agents driven by progressive reinforcement learning. We first develop the model's ability to follow explicit guidance from global plans when addressing agent tasks. Subsequently, based on this foundation, we focus on optimizing the quality of generated plans. Finally, we conduct joint optimization of the model's planning and execution coordination. Experiments indicate that PilotRL could achieve state-of-the-art performances, with LLaMA3.1-8B-Instruct + PilotRL surpassing closed-sourced GPT-4o by 3.60%, while showing a more substantial gain of 55.78% comparing to GPT-4o-mini at a comparable parameter scale.
TableRAG: A Retrieval Augmented Generation Framework for Heterogeneous Document Reasoning
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has demonstrated considerable effectiveness in open-domain question answering. However, when applied to heterogeneous documents, comprising both textual and tabular components, existing RAG approaches exhibit critical limitations. The prevailing practice of flattening tables and chunking strategies disrupts the intrinsic tabular structure, leads to information loss, and undermines the reasoning capabilities of LLMs in multi-hop, global queries. To address these challenges, we propose TableRAG, an hybrid framework that unifies textual understanding and complex manipulations over tabular data. TableRAG iteratively operates in four steps: context-sensitive query decomposition, text retrieval, SQL programming and execution, and compositional intermediate answer generation. We also develop HeteQA, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate the multi-hop heterogeneous reasoning capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that TableRAG consistently outperforms existing baselines on both public datasets and our HeteQA, establishing a new state-of-the-art for heterogeneous document question answering. We release TableRAG at https://github.com/yxh-y/TableRAG/tree/main.
Bridge the Domains: Large Language Models Enhanced Cross-domain Sequential Recommendation
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Cross-domain Sequential Recommendation (CDSR) aims to extract the preference from the user's historical interactions across various domains. Despite some progress in CDSR, two problems set the barrier for further advancements, i.e., overlap dilemma and transition complexity. The former means existing CDSR methods severely rely on users who own interactions on all domains to learn cross-domain item relationships, compromising the practicability. The latter refers to the difficulties in learning the complex transition patterns from the mixed behavior sequences. With powerful representation and reasoning abilities, Large Language Models (LLMs) are promising to address these two problems by bridging the items and capturing the user's preferences from a semantic view. Therefore, we propose an LLMs Enhanced Cross-domain Sequential Recommendation model (LLM4CDSR). To obtain the semantic item relationships, we first propose an LLM-based unified representation module to represent items. Then, a trainable adapter with contrastive regularization is designed to adapt the CDSR task. Besides, a hierarchical LLMs profiling module is designed to summarize user cross-domain preferences. Finally, these two modules are integrated into the proposed tri-thread framework to derive recommendations. We have conducted extensive experiments on three public cross-domain datasets, validating the effectiveness of LLM4CDSR. We have released the code online.
MegaSR: Mining Customized Semantics and Expressive Guidance for Image Super-Resolution
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Pioneering text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have ushered in a new era of real-world image super-resolution (Real-ISR), significantly enhancing the visual perception of reconstructed images. However, existing methods typically integrate uniform abstract textual semantics across all blocks, overlooking the distinct semantic requirements at different depths and the fine-grained, concrete semantics inherently present in the images themselves. Moreover, relying solely on a single type of guidance further disrupts the consistency of reconstruction. To address these issues, we propose MegaSR, a novel framework that mines customized block-wise semantics and expressive guidance for diffusion-based ISR. Compared to uniform textual semantics, MegaSR enables flexible adaptation to multi-granularity semantic awareness by dynamically incorporating image attributes at each block. Furthermore, we experimentally identify HED edge maps, depth maps, and segmentation maps as the most expressive guidance, and propose a multi-stage aggregation strategy to modulate them into the T2I models. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of MegaSR in terms of semantic richness and structural consistency.
Chameleon: On the Scene Diversity and Domain Variety of AI-Generated Videos Detection
Mar 09, 2025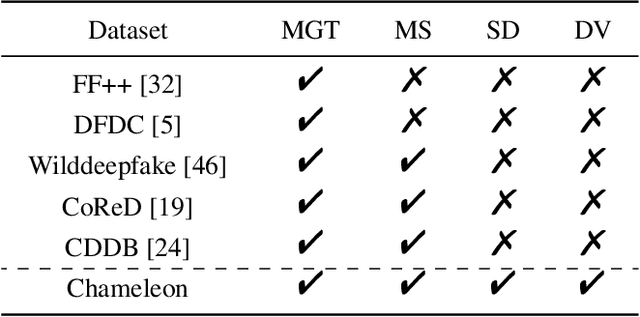

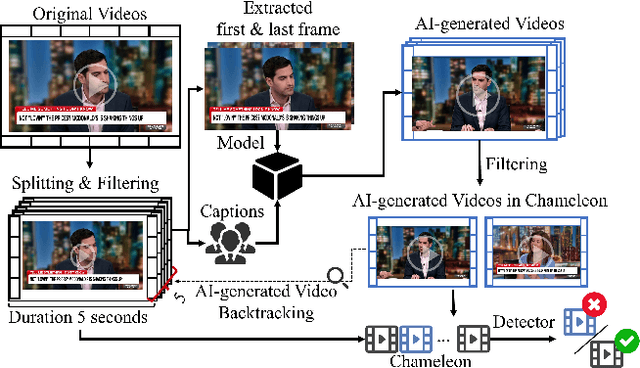
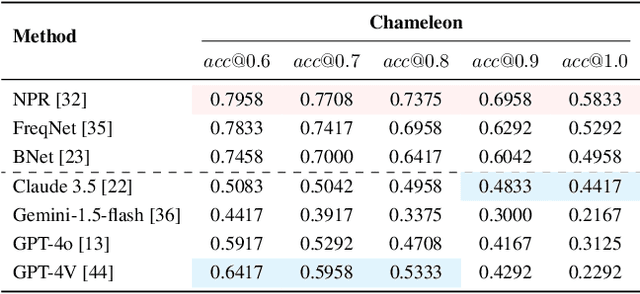
Abstract:Artificial intelligence generated content (AIGC), known as DeepFakes, has emerged as a growing concern because it is being utilized as a tool for spreading disinformation. While much research exists on identifying AI-generated text and images, research on detecting AI-generated videos is limited. Existing datasets for AI-generated videos detection exhibit limitations in terms of diversity, complexity, and realism. To address these issues, this paper focuses on AI-generated videos detection and constructs a diverse dataset named Chameleon. We generate videos through multiple generation tools and various real video sources. At the same time, we preserve the videos' real-world complexity, including scene switches and dynamic perspective changes, and expand beyond face-centered detection to include human actions and environment generation. Our work bridges the gap between AI-generated dataset construction and real-world forensic needs, offering a valuable benchmark to counteract the evolving threats of AI-generated content.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge