Jianlong Wu
StructAlign: Structured Cross-Modal Alignment for Continual Text-to-Video Retrieval
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Continual Text-to-Video Retrieval (CTVR) is a challenging multimodal continual learning setting, where models must incrementally learn new semantic categories while maintaining accurate text-video alignment for previously learned ones, thus making it particularly prone to catastrophic forgetting. A key challenge in CTVR is feature drift, which manifests in two forms: intra-modal feature drift caused by continual learning within each modality, and non-cooperative feature drift across modalities that leads to modality misalignment. To mitigate these issues, we propose StructAlign, a structured cross-modal alignment method for CTVR. First, StructAlign introduces a simplex Equiangular Tight Frame (ETF) geometry as a unified geometric prior to mitigate modality misalignment. Building upon this geometric prior, we design a cross-modal ETF alignment loss that aligns text and video features with category-level ETF prototypes, encouraging the learned representations to form an approximate simplex ETF geometry. In addition, to suppress intra-modal feature drift, we design a Cross-modal Relation Preserving loss, which leverages complementary modalities to preserve cross-modal similarity relations, providing stable relational supervision for feature updates. By jointly addressing non-cooperative feature drift across modalities and intra-modal feature drift, StructAlign effectively alleviates catastrophic forgetting in CTVR. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art continual retrieval approaches.
AdaReTaKe: Adaptive Redundancy Reduction to Perceive Longer for Video-language Understanding
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have revolutionized video understanding, yet are still limited by context length when processing long videos. Recent methods compress videos by leveraging visual redundancy uniformly, yielding promising results. Nevertheless, our quantitative analysis shows that redundancy varies significantly across time and model layers, necessitating a more flexible compression strategy. We propose AdaReTaKe, a training-free method that flexibly reduces visual redundancy by allocating compression ratios among time and layers with theoretical guarantees. Integrated into state-of-the-art MLLMs, AdaReTaKe improves processing capacity from 256 to 2048 frames while preserving critical information. Experiments on VideoMME, MLVU, LongVideoBench, and LVBench datasets demonstrate that AdaReTaKe outperforms existing methods by 2.3% and 2.8% for 7B and 72B models, respectively, with even greater improvements of 5.9% and 6.0% on the longest LVBench. Our code is available at https://github.com/SCZwangxiao/video-FlexReduc.git.
MegaSR: Mining Customized Semantics and Expressive Guidance for Image Super-Resolution
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Pioneering text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have ushered in a new era of real-world image super-resolution (Real-ISR), significantly enhancing the visual perception of reconstructed images. However, existing methods typically integrate uniform abstract textual semantics across all blocks, overlooking the distinct semantic requirements at different depths and the fine-grained, concrete semantics inherently present in the images themselves. Moreover, relying solely on a single type of guidance further disrupts the consistency of reconstruction. To address these issues, we propose MegaSR, a novel framework that mines customized block-wise semantics and expressive guidance for diffusion-based ISR. Compared to uniform textual semantics, MegaSR enables flexible adaptation to multi-granularity semantic awareness by dynamically incorporating image attributes at each block. Furthermore, we experimentally identify HED edge maps, depth maps, and segmentation maps as the most expressive guidance, and propose a multi-stage aggregation strategy to modulate them into the T2I models. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of MegaSR in terms of semantic richness and structural consistency.
HAIC: Improving Human Action Understanding and Generation with Better Captions for Multi-modal Large Language Models
Feb 28, 2025


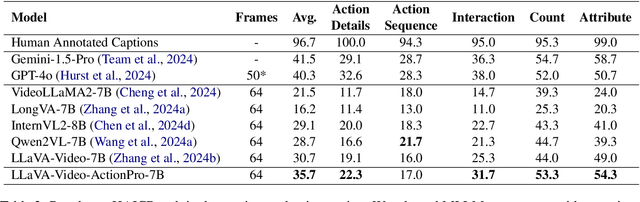
Abstract:Recent Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have made great progress in video understanding. However, their performance on videos involving human actions is still limited by the lack of high-quality data. To address this, we introduce a two-stage data annotation pipeline. First, we design strategies to accumulate videos featuring clear human actions from the Internet. Second, videos are annotated in a standardized caption format that uses human attributes to distinguish individuals and chronologically details their actions and interactions. Through this pipeline, we curate two datasets, namely HAICTrain and HAICBench. \textbf{HAICTrain} comprises 126K video-caption pairs generated by Gemini-Pro and verified for training purposes. Meanwhile, \textbf{HAICBench} includes 500 manually annotated video-caption pairs and 1,400 QA pairs, for a comprehensive evaluation of human action understanding. Experimental results demonstrate that training with HAICTrain not only significantly enhances human understanding abilities across 4 benchmarks, but can also improve text-to-video generation results. Both the HAICTrain and HAICBench are released at https://huggingface.co/datasets/KuaishouHAIC/HAIC.
Continuous Knowledge-Preserving Decomposition for Few-Shot Continual Learning
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) involves learning new classes from limited data while retaining prior knowledge, and often results in catastrophic forgetting. Existing methods either freeze backbone networks to preserve knowledge, which limits adaptability, or rely on additional modules or prompts, introducing inference overhead. To this end, we propose Continuous Knowledge-Preserving Decomposition for FSCIL (CKPD-FSCIL), a framework that decomposes a model's weights into two parts: one that compacts existing knowledge (knowledge-sensitive components) and another that carries redundant capacity to accommodate new abilities (redundant-capacity components). The decomposition is guided by a covariance matrix from replay samples, ensuring principal components align with classification abilities. During adaptation, we freeze the knowledge-sensitive components and only adapt the redundant-capacity components, fostering plasticity while minimizing interference without changing the architecture or increasing overhead. Additionally, CKPD introduces an adaptive layer selection strategy to identify layers with redundant capacity, dynamically allocating adapters. Experiments on multiple benchmarks show that CKPD-FSCIL outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
LipGen: Viseme-Guided Lip Video Generation for Enhancing Visual Speech Recognition
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Visual speech recognition (VSR), commonly known as lip reading, has garnered significant attention due to its wide-ranging practical applications. The advent of deep learning techniques and advancements in hardware capabilities have significantly enhanced the performance of lip reading models. Despite these advancements, existing datasets predominantly feature stable video recordings with limited variability in lip movements. This limitation results in models that are highly sensitive to variations encountered in real-world scenarios. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework, LipGen, which aims to improve model robustness by leveraging speech-driven synthetic visual data, thereby mitigating the constraints of current datasets. Additionally, we introduce an auxiliary task that incorporates viseme classification alongside attention mechanisms. This approach facilitates the efficient integration of temporal information, directing the model's focus toward the relevant segments of speech, thereby enhancing discriminative capabilities. Our method demonstrates superior performance compared to the current state-of-the-art on the lip reading in the wild (LRW) dataset and exhibits even more pronounced advantages under challenging conditions.
ReTaKe: Reducing Temporal and Knowledge Redundancy for Long Video Understanding
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:Video Large Language Models (VideoLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in video understanding. However, existing VideoLLMs often inherit the limitations of their backbone LLMs in handling long sequences, leading to challenges for long video understanding. Common solutions either simply uniformly sample videos' frames or compress visual tokens, which focus primarily on low-level temporal visual redundancy, overlooking high-level knowledge redundancy. This limits the achievable compression rate with minimal loss. To this end. we introduce a training-free method, $\textbf{ReTaKe}$, containing two novel modules DPSelect and PivotKV, to jointly model and reduce both temporal visual redundancy and knowledge redundancy for long video understanding. Specifically, DPSelect identifies keyframes with local maximum peak distance based on their visual features, which are closely aligned with human video perception. PivotKV employs the obtained keyframes as pivots and conducts KV-Cache compression for the non-pivot tokens with low attention scores, which are derived from the learned prior knowledge of LLMs. Experiments on benchmarks VideoMME, MLVU, and LVBench, show that ReTaKe can support 4x longer video sequences with minimal performance loss (<1%) and outperform all similar-size VideoLLMs with 3%-5%, even surpassing or on par with much larger ones. Our code is available at https://github.com/SCZwangxiao/video-ReTaKe
Efficient Dataset Distillation via Diffusion-Driven Patch Selection for Improved Generalization
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Dataset distillation offers an efficient way to reduce memory and computational costs by optimizing a smaller dataset with performance comparable to the full-scale original. However, for large datasets and complex deep networks (e.g., ImageNet-1K with ResNet-101), the extensive optimization space limits performance, reducing its practicality. Recent approaches employ pre-trained diffusion models to generate informative images directly, avoiding pixel-level optimization and achieving notable results. However, these methods often face challenges due to distribution shifts between pre-trained models and target datasets, along with the need for multiple distillation steps across varying settings. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework orthogonal to existing diffusion-based distillation methods, leveraging diffusion models for selection rather than generation. Our method starts by predicting noise generated by the diffusion model based on input images and text prompts (with or without label text), then calculates the corresponding loss for each pair. With the loss differences, we identify distinctive regions of the original images. Additionally, we perform intra-class clustering and ranking on selected patches to maintain diversity constraints. This streamlined framework enables a single-step distillation process, and extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods across various metrics.
RA-BLIP: Multimodal Adaptive Retrieval-Augmented Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training
Oct 18, 2024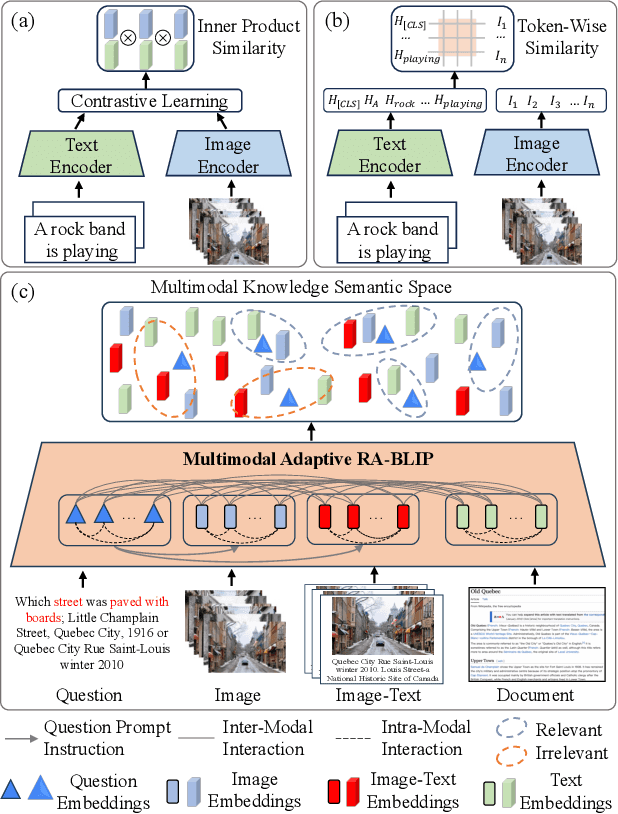
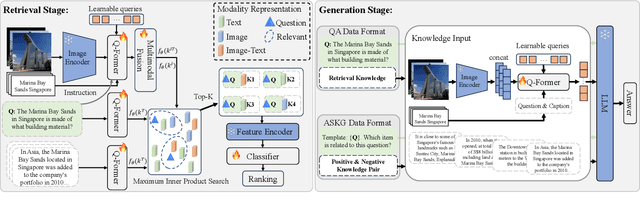
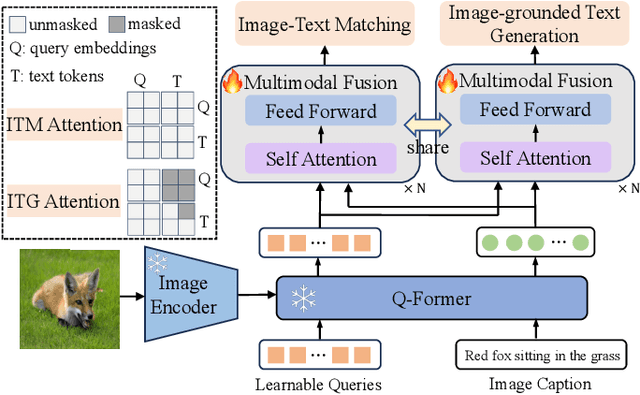
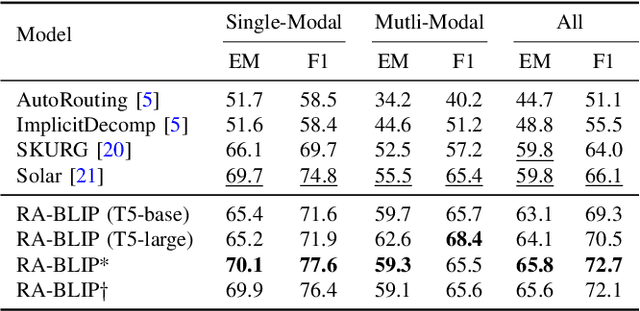
Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have recently received substantial interest, which shows their emerging potential as general-purpose models for various vision-language tasks. MLLMs involve significant external knowledge within their parameters; however, it is challenging to continually update these models with the latest knowledge, which involves huge computational costs and poor interpretability. Retrieval augmentation techniques have proven to be effective plugins for both LLMs and MLLMs. In this study, we propose multimodal adaptive Retrieval-Augmented Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training (RA-BLIP), a novel retrieval-augmented framework for various MLLMs. Considering the redundant information within vision modality, we first leverage the question to instruct the extraction of visual information through interactions with one set of learnable queries, minimizing irrelevant interference during retrieval and generation. Besides, we introduce a pre-trained multimodal adaptive fusion module to achieve question text-to-multimodal retrieval and integration of multimodal knowledge by projecting visual and language modalities into a unified semantic space. Furthermore, we present an Adaptive Selection Knowledge Generation (ASKG) strategy to train the generator to autonomously discern the relevance of retrieved knowledge, which realizes excellent denoising performance. Extensive experiments on open multimodal question-answering datasets demonstrate that RA-BLIP achieves significant performance and surpasses the state-of-the-art retrieval-augmented models.
Preview-based Category Contrastive Learning for Knowledge Distillation
Oct 18, 2024Abstract:Knowledge distillation is a mainstream algorithm in model compression by transferring knowledge from the larger model (teacher) to the smaller model (student) to improve the performance of student. Despite many efforts, existing methods mainly investigate the consistency between instance-level feature representation or prediction, which neglects the category-level information and the difficulty of each sample, leading to undesirable performance. To address these issues, we propose a novel preview-based category contrastive learning method for knowledge distillation (PCKD). It first distills the structural knowledge of both instance-level feature correspondence and the relation between instance features and category centers in a contrastive learning fashion, which can explicitly optimize the category representation and explore the distinct correlation between representations of instances and categories, contributing to discriminative category centers and better classification results. Besides, we introduce a novel preview strategy to dynamically determine how much the student should learn from each sample according to their difficulty. Different from existing methods that treat all samples equally and curriculum learning that simply filters out hard samples, our method assigns a small weight for hard instances as a preview to better guide the student training. Extensive experiments on several challenging datasets, including CIFAR-100 and ImageNet, demonstrate the superiority over state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge