Xinhao Zhong
Differential Vector Erasure: Unified Training-Free Concept Erasure for Flow Matching Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating high-quality images, yet their tendency to reproduce undesirable concepts, such as NSFW content, copyrighted styles, or specific objects, poses growing concerns for safe and controllable deployment. While existing concept erasure approaches primarily focus on DDPM-based diffusion models and rely on costly fine-tuning, the recent emergence of flow matching models introduces a fundamentally different generative paradigm for which prior methods are not directly applicable. In this paper, we propose Differential Vector Erasure (DVE), a training-free concept erasure method specifically designed for flow matching models. Our key insight is that semantic concepts are implicitly encoded in the directional structure of the velocity field governing the generative flow. Leveraging this observation, we construct a differential vector field that characterizes the directional discrepancy between a target concept and a carefully chosen anchor concept. During inference, DVE selectively removes concept-specific components by projecting the velocity field onto the differential direction, enabling precise concept suppression without affecting irrelevant semantics. Extensive experiments on FLUX demonstrate that DVE consistently outperforms existing baselines on a wide range of concept erasure tasks, including NSFW suppression, artistic style removal, and object erasure, while preserving image quality and diversity.
ActErase: A Training-Free Paradigm for Precise Concept Erasure via Activation Patching
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable generation capabilities, yet they raise significant concerns regarding safety, copyright, and ethical implications. Existing concept erasure methods address these risks by removing sensitive concepts from pre-trained models, but most of them rely on data-intensive and computationally expensive fine-tuning, which poses a critical limitation. To overcome these challenges, inspired by the observation that the model's activations are predominantly composed of generic concepts, with only a minimal component can represent the target concept, we propose a novel training-free method (ActErase) for efficient concept erasure. Specifically, the proposed method operates by identifying activation difference regions via prompt-pair analysis, extracting target activations and dynamically replacing input activations during forward passes. Comprehensive evaluations across three critical erasure tasks (nudity, artistic style, and object removal) demonstrates that our training-free method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) erasure performance, while effectively preserving the model's overall generative capability. Our approach also exhibits strong robustness against adversarial attacks, establishing a new plug-and-play paradigm for lightweight yet effective concept manipulation in diffusion models.
Closing the Safety Gap: Surgical Concept Erasure in Visual Autoregressive Models
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress of visual autoregressive (VAR) models has brought new opportunities for text-to-image generation, but also heightened safety concerns. Existing concept erasure techniques, primarily designed for diffusion models, fail to generalize to VARs due to their next-scale token prediction paradigm. In this paper, we first propose a novel VAR Erasure framework VARE that enables stable concept erasure in VAR models by leveraging auxiliary visual tokens to reduce fine-tuning intensity. Building upon this, we introduce S-VARE, a novel and effective concept erasure method designed for VAR, which incorporates a filtered cross entropy loss to precisely identify and minimally adjust unsafe visual tokens, along with a preservation loss to maintain semantic fidelity, addressing the issues such as language drift and reduced diversity introduce by na\"ive fine-tuning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves surgical concept erasure while preserving generation quality, thereby closing the safety gap in autoregressive text-to-image generation by earlier methods.
Temporal Saliency-Guided Distillation: A Scalable Framework for Distilling Video Datasets
May 27, 2025Abstract:Dataset distillation (DD) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for dataset compression, enabling the synthesis of compact surrogate datasets that approximate the training utility of large-scale ones. While significant progress has been achieved in distilling image datasets, extending DD to the video domain remains challenging due to the high dimensionality and temporal complexity inherent in video data. Existing video distillation (VD) methods often suffer from excessive computational costs and struggle to preserve temporal dynamics, as na\"ive extensions of image-based approaches typically lead to degraded performance. In this paper, we propose a novel uni-level video dataset distillation framework that directly optimizes synthetic videos with respect to a pre-trained model. To address temporal redundancy and enhance motion preservation, we introduce a temporal saliency-guided filtering mechanism that leverages inter-frame differences to guide the distillation process, encouraging the retention of informative temporal cues while suppressing frame-level redundancy. Extensive experiments on standard video benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, bridging the gap between real and distilled video data and offering a scalable solution for video dataset compression.
DD-Ranking: Rethinking the Evaluation of Dataset Distillation
May 19, 2025



Abstract:In recent years, dataset distillation has provided a reliable solution for data compression, where models trained on the resulting smaller synthetic datasets achieve performance comparable to those trained on the original datasets. To further improve the performance of synthetic datasets, various training pipelines and optimization objectives have been proposed, greatly advancing the field of dataset distillation. Recent decoupled dataset distillation methods introduce soft labels and stronger data augmentation during the post-evaluation phase and scale dataset distillation up to larger datasets (e.g., ImageNet-1K). However, this raises a question: Is accuracy still a reliable metric to fairly evaluate dataset distillation methods? Our empirical findings suggest that the performance improvements of these methods often stem from additional techniques rather than the inherent quality of the images themselves, with even randomly sampled images achieving superior results. Such misaligned evaluation settings severely hinder the development of DD. Therefore, we propose DD-Ranking, a unified evaluation framework, along with new general evaluation metrics to uncover the true performance improvements achieved by different methods. By refocusing on the actual information enhancement of distilled datasets, DD-Ranking provides a more comprehensive and fair evaluation standard for future research advancements.
Going Beyond Feature Similarity: Effective Dataset distillation based on Class-aware Conditional Mutual Information
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Dataset distillation (DD) aims to minimize the time and memory consumption needed for training deep neural networks on large datasets, by creating a smaller synthetic dataset that has similar performance to that of the full real dataset. However, current dataset distillation methods often result in synthetic datasets that are excessively difficult for networks to learn from, due to the compression of a substantial amount of information from the original data through metrics measuring feature similarity, e,g., distribution matching (DM). In this work, we introduce conditional mutual information (CMI) to assess the class-aware complexity of a dataset and propose a novel method by minimizing CMI. Specifically, we minimize the distillation loss while constraining the class-aware complexity of the synthetic dataset by minimizing its empirical CMI from the feature space of pre-trained networks, simultaneously. Conducting on a thorough set of experiments, we show that our method can serve as a general regularization method to existing DD methods and improve the performance and training efficiency.
Efficient Dataset Distillation via Diffusion-Driven Patch Selection for Improved Generalization
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Dataset distillation offers an efficient way to reduce memory and computational costs by optimizing a smaller dataset with performance comparable to the full-scale original. However, for large datasets and complex deep networks (e.g., ImageNet-1K with ResNet-101), the extensive optimization space limits performance, reducing its practicality. Recent approaches employ pre-trained diffusion models to generate informative images directly, avoiding pixel-level optimization and achieving notable results. However, these methods often face challenges due to distribution shifts between pre-trained models and target datasets, along with the need for multiple distillation steps across varying settings. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework orthogonal to existing diffusion-based distillation methods, leveraging diffusion models for selection rather than generation. Our method starts by predicting noise generated by the diffusion model based on input images and text prompts (with or without label text), then calculates the corresponding loss for each pair. With the loss differences, we identify distinctive regions of the original images. Additionally, we perform intra-class clustering and ranking on selected patches to maintain diversity constraints. This streamlined framework enables a single-step distillation process, and extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods across various metrics.
Collaborative Feature-Logits Contrastive Learning for Open-Set Semi-Supervised Object Detection
Nov 20, 2024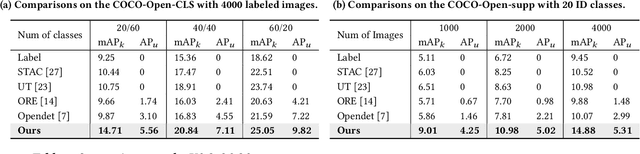
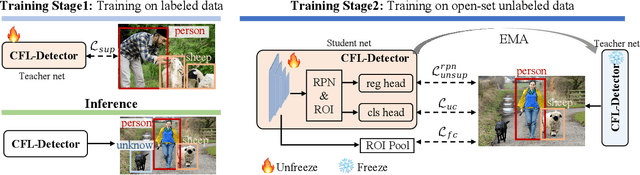
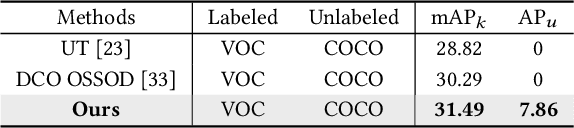
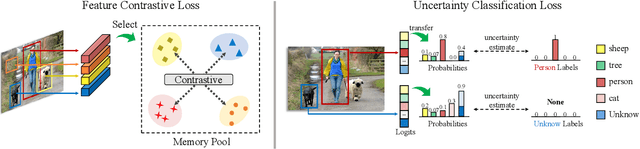
Abstract:Current Semi-Supervised Object Detection (SSOD) methods enhance detector performance by leveraging large amounts of unlabeled data, assuming that both labeled and unlabeled data share the same label space. However, in open-set scenarios, the unlabeled dataset contains both in-distribution (ID) classes and out-of-distribution (OOD) classes. Applying semi-supervised detectors in such settings can lead to misclassifying OOD class as ID classes. To alleviate this issue, we propose a simple yet effective method, termed Collaborative Feature-Logits Detector (CFL-Detector). Specifically, we introduce a feature-level clustering method using contrastive loss to clarify vector boundaries in the feature space and highlight class differences. Additionally, by optimizing the logits-level uncertainty classification loss, the model enhances its ability to effectively distinguish between ID and OOD classes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods.
Hierarchical Features Matter: A Deep Exploration of GAN Priors for Improved Dataset Distillation
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Dataset distillation is an emerging dataset reduction method, which condenses large-scale datasets while maintaining task accuracy. Current methods have integrated parameterization techniques to boost synthetic dataset performance by shifting the optimization space from pixel to another informative feature domain. However, they limit themselves to a fixed optimization space for distillation, neglecting the diverse guidance across different informative latent spaces. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel parameterization method dubbed Hierarchical Generative Latent Distillation (H-GLaD), to systematically explore hierarchical layers within the generative adversarial networks (GANs). This allows us to progressively span from the initial latent space to the final pixel space. In addition, we introduce a novel class-relevant feature distance metric to alleviate the computational burden associated with synthetic dataset evaluation, bridging the gap between synthetic and original datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed H-GLaD achieves a significant improvement in both same-architecture and cross-architecture performance with equivalent time consumption.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge