Siyu Jiao
ThinkGen: Generalized Thinking for Visual Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrates that Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning enables systematic solutions to complex understanding tasks. However, its extension to generation tasks remains nascent and limited by scenario-specific mechanisms that hinder generalization and adaptation. In this work, we present ThinkGen, the first think-driven visual generation framework that explicitly leverages MLLM's CoT reasoning in various generation scenarios. ThinkGen employs a decoupled architecture comprising a pretrained MLLM and a Diffusion Transformer (DiT), wherein the MLLM generates tailored instructions based on user intent, and DiT produces high-quality images guided by these instructions. We further propose a separable GRPO-based training paradigm (SepGRPO), alternating reinforcement learning between the MLLM and DiT modules. This flexible design enables joint training across diverse datasets, facilitating effective CoT reasoning for a wide range of generative scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ThinkGen achieves robust, state-of-the-art performance across multiple generation benchmarks. Code is available: https://github.com/jiaosiyuu/ThinkGen
M4V: Multi-Modal Mamba for Text-to-Video Generation
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Text-to-video generation has significantly enriched content creation and holds the potential to evolve into powerful world simulators. However, modeling the vast spatiotemporal space remains computationally demanding, particularly when employing Transformers, which incur quadratic complexity in sequence processing and thus limit practical applications. Recent advancements in linear-time sequence modeling, particularly the Mamba architecture, offer a more efficient alternative. Nevertheless, its plain design limits its direct applicability to multi-modal and spatiotemporal video generation tasks. To address these challenges, we introduce M4V, a Multi-Modal Mamba framework for text-to-video generation. Specifically, we propose a multi-modal diffusion Mamba (MM-DiM) block that enables seamless integration of multi-modal information and spatiotemporal modeling through a multi-modal token re-composition design. As a result, the Mamba blocks in M4V reduce FLOPs by 45% compared to the attention-based alternative when generating videos at 768$\times$1280 resolution. Additionally, to mitigate the visual quality degradation in long-context autoregressive generation processes, we introduce a reward learning strategy that further enhances per-frame visual realism. Extensive experiments on text-to-video benchmarks demonstrate M4V's ability to produce high-quality videos while significantly lowering computational costs. Code and models will be publicly available at https://huangjch526.github.io/M4V_project.
SAGE: Exploring the Boundaries of Unsafe Concept Domain with Semantic-Augment Erasing
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models (DMs) have achieved significant progress in text-to-image generation. However, the inevitable inclusion of sensitive information during pre-training poses safety risks, such as unsafe content generation and copyright infringement. Concept erasing finetunes weights to unlearn undesirable concepts, and has emerged as a promising solution. However, existing methods treat unsafe concept as a fixed word and repeatedly erase it, trapping DMs in ``word concept abyss'', which prevents generalized concept-related erasing. To escape this abyss, we introduce semantic-augment erasing which transforms concept word erasure into concept domain erasure by the cyclic self-check and self-erasure. It efficiently explores and unlearns the boundary representation of concept domain through semantic spatial relationships between original and training DMs, without requiring additional preprocessed data. Meanwhile, to mitigate the retention degradation of irrelevant concepts while erasing unsafe concepts, we further propose the global-local collaborative retention mechanism that combines global semantic relationship alignment with local predicted noise preservation, effectively expanding the retentive receptive field for irrelevant concepts. We name our method SAGE, and extensive experiments demonstrate the comprehensive superiority of SAGE compared with other methods in the safe generation of DMs. The code and weights will be open-sourced at https://github.com/KevinLight831/SAGE.
FlexVAR: Flexible Visual Autoregressive Modeling without Residual Prediction
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:This work challenges the residual prediction paradigm in visual autoregressive modeling and presents FlexVAR, a new Flexible Visual AutoRegressive image generation paradigm. FlexVAR facilitates autoregressive learning with ground-truth prediction, enabling each step to independently produce plausible images. This simple, intuitive approach swiftly learns visual distributions and makes the generation process more flexible and adaptable. Trained solely on low-resolution images ($\leq$ 256px), FlexVAR can: (1) Generate images of various resolutions and aspect ratios, even exceeding the resolution of the training images. (2) Support various image-to-image tasks, including image refinement, in/out-painting, and image expansion. (3) Adapt to various autoregressive steps, allowing for faster inference with fewer steps or enhancing image quality with more steps. Our 1.0B model outperforms its VAR counterpart on the ImageNet 256$\times$256 benchmark. Moreover, when zero-shot transfer the image generation process with 13 steps, the performance further improves to 2.08 FID, outperforming state-of-the-art autoregressive models AiM/VAR by 0.25/0.28 FID and popular diffusion models LDM/DiT by 1.52/0.19 FID, respectively. When transferring our 1.0B model to the ImageNet 512$\times$512 benchmark in a zero-shot manner, FlexVAR achieves competitive results compared to the VAR 2.3B model, which is a fully supervised model trained at 512$\times$512 resolution.
CLIP-GS: Unifying Vision-Language Representation with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 26, 2024



Abstract:Recent works in 3D multimodal learning have made remarkable progress. However, typically 3D multimodal models are only capable of handling point clouds. Compared to the emerging 3D representation technique, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), the spatially sparse point cloud cannot depict the texture information of 3D objects, resulting in inferior reconstruction capabilities. This limitation constrains the potential of point cloud-based 3D multimodal representation learning. In this paper, we present CLIP-GS, a novel multimodal representation learning framework grounded in 3DGS. We introduce the GS Tokenizer to generate serialized gaussian tokens, which are then processed through transformer layers pre-initialized with weights from point cloud models, resulting in the 3DGS embeddings. CLIP-GS leverages contrastive loss between 3DGS and the visual-text embeddings of CLIP, and we introduce an image voting loss to guide the directionality and convergence of gradient optimization. Furthermore, we develop an efficient way to generate triplets of 3DGS, images, and text, facilitating CLIP-GS in learning unified multimodal representations. Leveraging the well-aligned multimodal representations, CLIP-GS demonstrates versatility and outperforms point cloud-based models on various 3D tasks, including multimodal retrieval, zero-shot, and few-shot classification.
Collaborative Feature-Logits Contrastive Learning for Open-Set Semi-Supervised Object Detection
Nov 20, 2024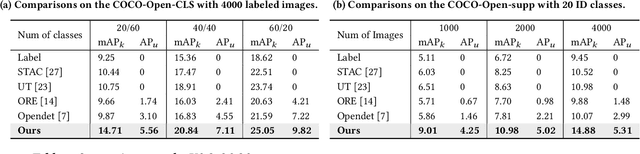
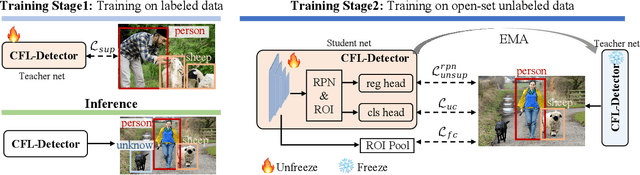
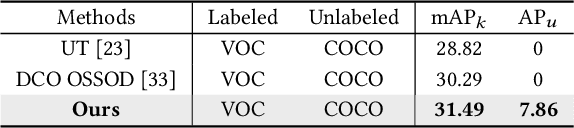
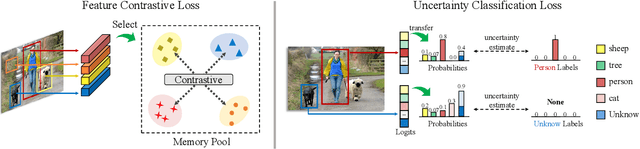
Abstract:Current Semi-Supervised Object Detection (SSOD) methods enhance detector performance by leveraging large amounts of unlabeled data, assuming that both labeled and unlabeled data share the same label space. However, in open-set scenarios, the unlabeled dataset contains both in-distribution (ID) classes and out-of-distribution (OOD) classes. Applying semi-supervised detectors in such settings can lead to misclassifying OOD class as ID classes. To alleviate this issue, we propose a simple yet effective method, termed Collaborative Feature-Logits Detector (CFL-Detector). Specifically, we introduce a feature-level clustering method using contrastive loss to clarify vector boundaries in the feature space and highlight class differences. Additionally, by optimizing the logits-level uncertainty classification loss, the model enhances its ability to effectively distinguish between ID and OOD classes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods.
Collaborative Vision-Text Representation Optimizing for Open-Vocabulary Segmentation
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:Pre-trained vision-language models, e.g. CLIP, have been increasingly used to address the challenging Open-Vocabulary Segmentation (OVS) task, benefiting from their well-aligned vision-text embedding space. Typical solutions involve either freezing CLIP during training to unilaterally maintain its zero-shot capability, or fine-tuning CLIP vision encoder to achieve perceptual sensitivity to local regions. However, few of them incorporate vision-text collaborative optimization. Based on this, we propose the Content-Dependent Transfer to adaptively enhance each text embedding by interacting with the input image, which presents a parameter-efficient way to optimize the text representation. Besides, we additionally introduce a Representation Compensation strategy, reviewing the original CLIP-V representation as compensation to maintain the zero-shot capability of CLIP. In this way, the vision and text representation of CLIP are optimized collaboratively, enhancing the alignment of the vision-text feature space. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to establish the collaborative vision-text optimizing mechanism within the OVS field. Extensive experiments demonstrate our method achieves superior performance on popular OVS benchmarks. In open-vocabulary semantic segmentation, our method outperforms the previous state-of-the-art approaches by +0.5, +2.3, +3.4, +0.4 and +1.1 mIoU, respectively on A-847, A-150, PC-459, PC-59 and PAS-20. Furthermore, in a panoptic setting on ADE20K, we achieve the performance of 27.1 PQ, 73.5 SQ, and 32.9 RQ. Code will be available at https://github.com/jiaosiyu1999/MAFT-Plus.git .
Learning Mask-aware CLIP Representations for Zero-Shot Segmentation
Sep 30, 2023



Abstract:Recently, pre-trained vision-language models have been increasingly used to tackle the challenging zero-shot segmentation task. Typical solutions follow the paradigm of first generating mask proposals and then adopting CLIP to classify them. To maintain the CLIP's zero-shot transferability, previous practices favour to freeze CLIP during training. However, in the paper, we reveal that CLIP is insensitive to different mask proposals and tends to produce similar predictions for various mask proposals of the same image. This insensitivity results in numerous false positives when classifying mask proposals. This issue mainly relates to the fact that CLIP is trained with image-level supervision. To alleviate this issue, we propose a simple yet effective method, named Mask-aware Fine-tuning (MAFT). Specifically, Image-Proposals CLIP Encoder (IP-CLIP Encoder) is proposed to handle arbitrary numbers of image and mask proposals simultaneously. Then, mask-aware loss and self-distillation loss are designed to fine-tune IP-CLIP Encoder, ensuring CLIP is responsive to different mask proposals while not sacrificing transferability. In this way, mask-aware representations can be easily learned to make the true positives stand out. Notably, our solution can seamlessly plug into most existing methods without introducing any new parameters during the fine-tuning process. We conduct extensive experiments on the popular zero-shot benchmarks. With MAFT, the performance of the state-of-the-art methods is promoted by a large margin: 50.4% (+ 8.2%) on COCO, 81.8% (+ 3.2%) on Pascal-VOC, and 8.7% (+4.3%) on ADE20K in terms of mIoU for unseen classes. The code is available at https://github.com/jiaosiyu1999/MAFT.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge