Sebastian Möller
Content Leakage in LibriSpeech and Its Impact on the Privacy Evaluation of Speaker Anonymization
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Speaker anonymization aims to conceal a speaker's identity, without considering the linguistic content. In this study, we reveal a weakness of Librispeech, the dataset that is commonly used to evaluate anonymizers: the books read by the Librispeech speakers are so distinct, that speakers can be identified by their vocabularies. Even perfect anonymizers cannot prevent this identity leakage. The EdAcc dataset is better in this regard: only a few speakers can be identified through their vocabularies, encouraging the attacker to look elsewhere for the identities of the anonymized speakers. EdAcc also comprises spontaneous speech and more diverse speakers, complementing Librispeech and giving more insights into how anonymizers work.
Order in the Evaluation Court: A Critical Analysis of NLG Evaluation Trends
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Despite advances in Natural Language Generation (NLG), evaluation remains challenging. Although various new metrics and LLM-as-a-judge (LaaJ) methods are proposed, human judgment persists as the gold standard. To systematically review how NLG evaluation has evolved, we employ an automatic information extraction scheme to gather key information from NLG papers, focusing on different evaluation methods (metrics, LaaJ and human evaluation). With extracted metadata from 14,171 papers across four major conferences (ACL, EMNLP, NAACL, and INLG) over the past six years, we reveal several critical findings: (1) Task Divergence: While Dialogue Generation demonstrates a rapid shift toward LaaJ (>40% in 2025), Machine Translation remains locked into n-gram metrics, and Question Answering exhibits a substantial decline in the proportion of studies conducting human evaluation. (2) Metric Inertia: Despite the development of semantic metrics, general-purpose metrics (e.g., BLEU, ROUGE) continue to be widely used across tasks without empirical justification, often lacking the discriminative power to distinguish between specific quality criteria. (3) Human-LaaJ Divergence: Our association analysis challenges the assumption that LLMs act as mere proxies for humans; LaaJ and human evaluations prioritize very different signals, and explicit validation is scarce (<8% of papers comparing the two), with only moderate to low correlation. Based on these observations, we derive practical recommendations to improve the rigor of future NLG evaluation.
Parallel Universes, Parallel Languages: A Comprehensive Study on LLM-based Multilingual Counterfactual Example Generation
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Counterfactuals refer to minimally edited inputs that cause a model's prediction to change, serving as a promising approach to explaining the model's behavior. Large language models (LLMs) excel at generating English counterfactuals and demonstrate multilingual proficiency. However, their effectiveness in generating multilingual counterfactuals remains unclear. To this end, we conduct a comprehensive study on multilingual counterfactuals. We first conduct automatic evaluations on both directly generated counterfactuals in the target languages and those derived via English translation across six languages. Although translation-based counterfactuals offer higher validity than their directly generated counterparts, they demand substantially more modifications and still fall short of matching the quality of the original English counterfactuals. Second, we find the patterns of edits applied to high-resource European-language counterfactuals to be remarkably similar, suggesting that cross-lingual perturbations follow common strategic principles. Third, we identify and categorize four main types of errors that consistently appear in the generated counterfactuals across languages. Finally, we reveal that multilingual counterfactual data augmentation (CDA) yields larger model performance improvements than cross-lingual CDA, especially for lower-resource languages. Yet, the imperfections of the generated counterfactuals limit gains in model performance and robustness.
Can Large Language Models Still Explain Themselves? Investigating the Impact of Quantization on Self-Explanations
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Quantization is widely used to accelerate inference and streamline the deployment of large language models (LLMs), yet its effects on self-explanations (SEs) remain unexplored. SEs, generated by LLMs to justify their own outputs, require reasoning about the model's own decision-making process, a capability that may exhibit particular sensitivity to quantization. As SEs are increasingly relied upon for transparency in high-stakes applications, understanding whether and to what extent quantization degrades SE quality and faithfulness is critical. To address this gap, we examine two types of SEs: natural language explanations (NLEs) and counterfactual examples, generated by LLMs quantized using three common techniques at distinct bit widths. Our findings indicate that quantization typically leads to moderate declines in both SE quality (up to 4.4\%) and faithfulness (up to 2.38\%). The user study further demonstrates that quantization diminishes both the coherence and trustworthiness of SEs (up to 8.5\%). Compared to smaller models, larger models show limited resilience to quantization in terms of SE quality but better maintain faithfulness. Moreover, no quantization technique consistently excels across task accuracy, SE quality, and faithfulness. Given that quantization's impact varies by context, we recommend validating SE quality for specific use cases, especially for NLEs, which show greater sensitivity. Nonetheless, the relatively minor deterioration in SE quality and faithfulness does not undermine quantization's effectiveness as a model compression technique.
Multilingual Datasets for Custom Input Extraction and Explanation Requests Parsing in Conversational XAI Systems
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Conversational explainable artificial intelligence (ConvXAI) systems based on large language models (LLMs) have garnered considerable attention for their ability to enhance user comprehension through dialogue-based explanations. Current ConvXAI systems often are based on intent recognition to accurately identify the user's desired intention and map it to an explainability method. While such methods offer great precision and reliability in discerning users' underlying intentions for English, a significant challenge in the scarcity of training data persists, which impedes multilingual generalization. Besides, the support for free-form custom inputs, which are user-defined data distinct from pre-configured dataset instances, remains largely limited. To bridge these gaps, we first introduce MultiCoXQL, a multilingual extension of the CoXQL dataset spanning five typologically diverse languages, including one low-resource language. Subsequently, we propose a new parsing approach aimed at enhancing multilingual parsing performance, and evaluate three LLMs on MultiCoXQL using various parsing strategies. Furthermore, we present Compass, a new multilingual dataset designed for custom input extraction in ConvXAI systems, encompassing 11 intents across the same five languages as MultiCoXQL. We conduct monolingual, cross-lingual, and multilingual evaluations on Compass, employing three LLMs of varying sizes alongside BERT-type models.
Evaluation of a Sign Language Avatar on Comprehensibility, User Experience \& Acceptability
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an investigation into the impact of adding adjustment features to an existing sign language (SL) avatar on a Microsoft Hololens 2 device. Through a detailed analysis of interactions of expert German Sign Language (DGS) users with both adjustable and non-adjustable avatars in a specific use case, this study identifies the key factors influencing the comprehensibility, the user experience (UX), and the acceptability of such a system. Despite user preference for adjustable settings, no significant improvements in UX or comprehensibility were observed, which remained at low levels, amid missing SL elements (mouthings and facial expressions) and implementation issues (indistinct hand shapes, lack of feedback and menu positioning). Hedonic quality was rated higher than pragmatic quality, indicating that users found the system more emotionally or aesthetically pleasing than functionally useful. Stress levels were higher for the adjustable avatar, reflecting lower performance, greater effort and more frustration. Additionally, concerns were raised about whether the Hololens adjustment gestures are intuitive and easy to familiarise oneself with. While acceptability of the concept of adjustability was generally positive, it was strongly dependent on usability and animation quality. This study highlights that personalisation alone is insufficient, and that SL avatars must be comprehensible by default. Key recommendations include enhancing mouthing and facial animation, improving interaction interfaces, and applying participatory design.
The TUB Sign Language Corpus Collection
Aug 07, 2025
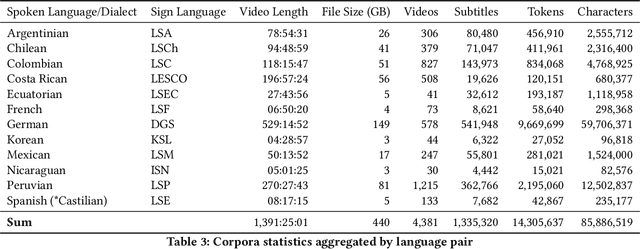
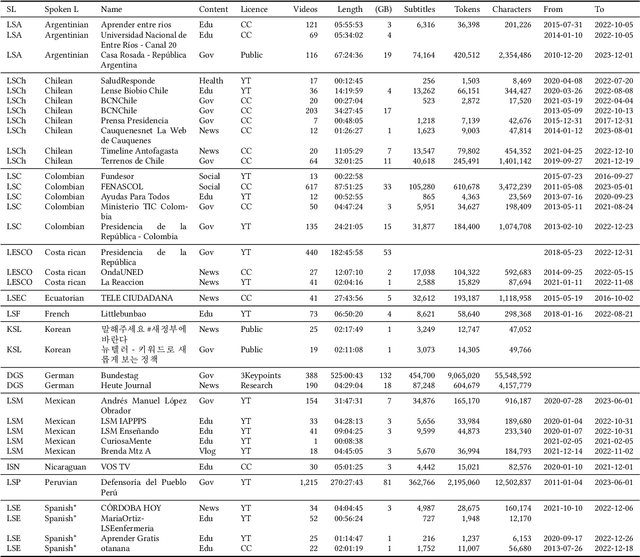
Abstract:We present a collection of parallel corpora of 12 sign languages in video format, together with subtitles in the dominant spoken languages of the corresponding countries. The entire collection includes more than 1,300 hours in 4,381 video files, accompanied by 1,3~M subtitles containing 14~M tokens. Most notably, it includes the first consistent parallel corpora for 8 Latin American sign languages, whereas the size of the German Sign Language corpora is ten times the size of the previously available corpora. The collection was created by collecting and processing videos of multiple sign languages from various online sources, mainly broadcast material of news shows, governmental bodies and educational channels. The preparation involved several stages, including data collection, informing the content creators and seeking usage approvals, scraping, and cropping. The paper provides statistics on the collection and an overview of the methods used to collect the data.
Two Views, One Truth: Spectral and Self-Supervised Features Fusion for Robust Speech Deepfake Detection
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in synthetic speech have made audio deepfakes increasingly realistic, posing significant security risks. Existing detection methods that rely on a single modality, either raw waveform embeddings or spectral based features, are vulnerable to non spoof disturbances and often overfit to known forgery algorithms, resulting in poor generalization to unseen attacks. To address these shortcomings, we investigate hybrid fusion frameworks that integrate self supervised learning (SSL) based representations with handcrafted spectral descriptors (MFCC , LFCC, CQCC). By aligning and combining complementary information across modalities, these fusion approaches capture subtle artifacts that single feature approaches typically overlook. We explore several fusion strategies, including simple concatenation, cross attention, mutual cross attention, and a learnable gating mechanism, to optimally blend SSL features with fine grained spectral cues. We evaluate our approach on four challenging public benchmarks and report generalization performance. All fusion variants consistently outperform an SSL only baseline, with the cross attention strategy achieving the best generalization with a 38% relative reduction in equal error rate (EER). These results confirm that joint modeling of waveform and spectral views produces robust, domain agnostic representations for audio deepfake detection.
One Size Fits None: Rethinking Fairness in Medical AI
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Machine learning (ML) models are increasingly used to support clinical decision-making. However, real-world medical datasets are often noisy, incomplete, and imbalanced, leading to performance disparities across patient subgroups. These differences raise fairness concerns, particularly when they reinforce existing disadvantages for marginalized groups. In this work, we analyze several medical prediction tasks and demonstrate how model performance varies with patient characteristics. While ML models may demonstrate good overall performance, we argue that subgroup-level evaluation is essential before integrating them into clinical workflows. By conducting a performance analysis at the subgroup level, differences can be clearly identified-allowing, on the one hand, for performance disparities to be considered in clinical practice, and on the other hand, for these insights to inform the responsible development of more effective models. Thereby, our work contributes to a practical discussion around the subgroup-sensitive development and deployment of medical ML models and the interconnectedness of fairness and transparency.
Private kNN-VC: Interpretable Anonymization of Converted Speech
May 23, 2025Abstract:Speaker anonymization seeks to conceal a speaker's identity while preserving the utility of their speech. The achieved privacy is commonly evaluated with a speaker recognition model trained on anonymized speech. Although this represents a strong attack, it is unclear which aspects of speech are exploited to identify the speakers. Our research sets out to unveil these aspects. It starts with kNN-VC, a powerful voice conversion model that performs poorly as an anonymization system, presumably because of prosody leakage. To test this hypothesis, we extend kNN-VC with two interpretable components that anonymize the duration and variation of phones. These components increase privacy significantly, proving that the studied prosodic factors encode speaker identity and are exploited by the privacy attack. Additionally, we show that changes in the target selection algorithm considerably influence the outcome of the privacy attack.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge