Leying Zhang
DeepASMR: LLM-Based Zero-Shot ASMR Speech Generation for Anyone of Any Voice
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:While modern Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems achieve high fidelity for read-style speech, they struggle to generate Autonomous Sensory Meridian Response (ASMR), a specialized, low-intensity speech style essential for relaxation. The inherent challenges include ASMR's subtle, often unvoiced characteristics and the demand for zero-shot speaker adaptation. In this paper, we introduce DeepASMR, the first framework designed for zero-shot ASMR generation. We demonstrate that a single short snippet of a speaker's ordinary, read-style speech is sufficient to synthesize high-fidelity ASMR in their voice, eliminating the need for whispered training data from the target speaker. Methodologically, we first identify that discrete speech tokens provide a soft factorization of ASMR style from speaker timbre. Leveraging this insight, we propose a two-stage pipeline incorporating a Large Language Model (LLM) for content-style encoding and a flow-matching acoustic decoder for timbre reconstruction. Furthermore, we contribute DeepASMR-DB, a comprehensive 670-hour English-Chinese multi-speaker ASMR speech corpus, and introduce a novel evaluation protocol integrating objective metrics, human listening tests, LLM-based scoring and unvoiced speech analysis. Extensive experiments confirm that DeepASMR achieves state-of-the-art naturalness and style fidelity in ASMR generation for anyone of any voice, while maintaining competitive performance on normal speech synthesis.
Stairway to Success: Zero-Shot Floor-Aware Object-Goal Navigation via LLM-Driven Coarse-to-Fine Exploration
May 29, 2025Abstract:Object-Goal Navigation (OGN) remains challenging in real-world, multi-floor environments and under open-vocabulary object descriptions. We observe that most episodes in widely used benchmarks such as HM3D and MP3D involve multi-floor buildings, with many requiring explicit floor transitions. However, existing methods are often limited to single-floor settings or predefined object categories. To address these limitations, we tackle two key challenges: (1) efficient cross-level planning and (2) zero-shot object-goal navigation (ZS-OGN), where agents must interpret novel object descriptions without prior exposure. We propose ASCENT, a framework that combines a Multi-Floor Spatial Abstraction module for hierarchical semantic mapping and a Coarse-to-Fine Frontier Reasoning module leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for context-aware exploration, without requiring additional training on new object semantics or locomotion data. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art ZS-OGN approaches on HM3D and MP3D benchmarks while enabling efficient multi-floor navigation. We further validate its practicality through real-world deployment on a quadruped robot, achieving successful object exploration across unseen floors.
Advanced Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech for Background Removal and Preservation with Controllable Masked Speech Prediction
Feb 11, 2025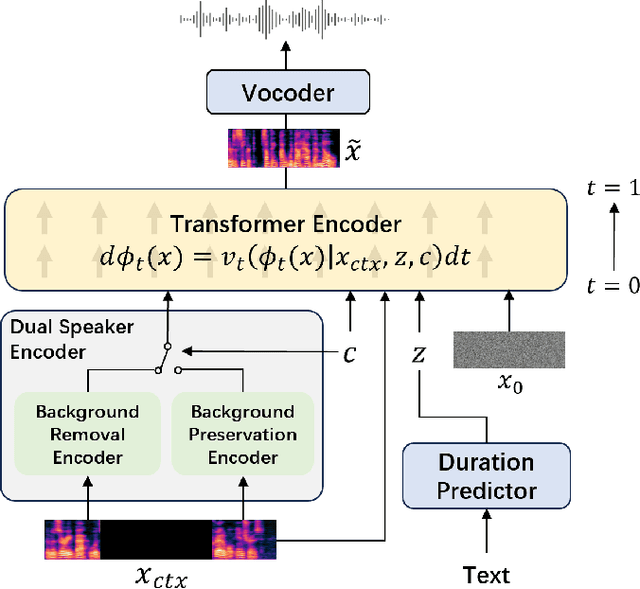
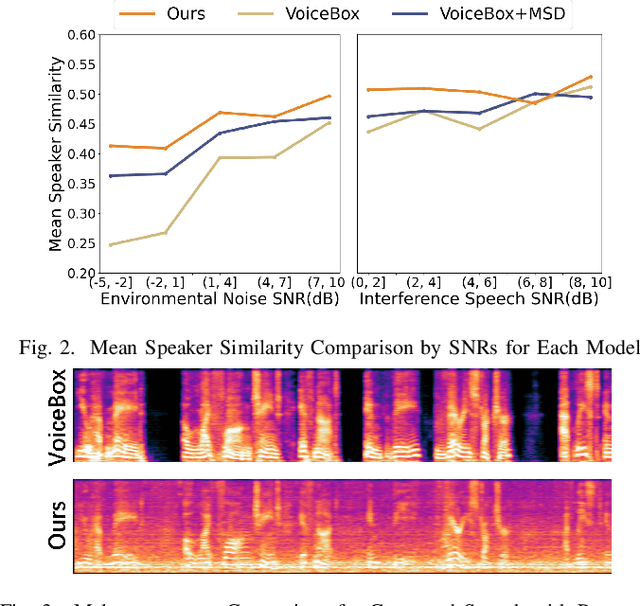
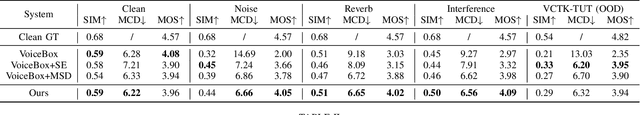
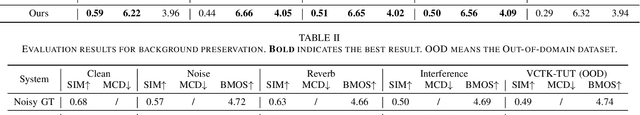
Abstract:The acoustic background plays a crucial role in natural conversation. It provides context and helps listeners understand the environment, but a strong background makes it difficult for listeners to understand spoken words. The appropriate handling of these backgrounds is situation-dependent: Although it may be necessary to remove background to ensure speech clarity, preserving the background is sometimes crucial to maintaining the contextual integrity of the speech. Despite recent advancements in zero-shot Text-to-Speech technologies, current systems often struggle with speech prompts containing backgrounds. To address these challenges, we propose a Controllable Masked Speech Prediction strategy coupled with a dual-speaker encoder, utilizing a task-related control signal to guide the prediction of dual background removal and preservation targets. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach enables precise control over the removal or preservation of background across various acoustic conditions and exhibits strong generalization capabilities in unseen scenarios.
SLIDE: Integrating Speech Language Model with LLM for Spontaneous Spoken Dialogue Generation
Jan 01, 2025



Abstract:Recently, ``textless" speech language models (SLMs) based on speech units have made huge progress in generating naturalistic speech, including non-verbal vocalizations. However, the generated speech samples often lack semantic coherence. In this paper, we propose SLM and LLM Integration for spontaneous spoken Dialogue gEneration (SLIDE). Specifically, we first utilize an LLM to generate the textual content of spoken dialogue. Next, we convert the textual dialogues into phoneme sequences and use a two-tower transformer-based duration predictor to predict the duration of each phoneme. Finally, an SLM conditioned on the spoken phoneme sequences is used to vocalize the textual dialogue. Experimental results on the Fisher dataset demonstrate that our system can generate naturalistic spoken dialogue while maintaining high semantic coherence.
Scale This, Not That: Investigating Key Dataset Attributes for Efficient Speech Enhancement Scaling
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Recent speech enhancement models have shown impressive performance gains by scaling up model complexity and training data. However, the impact of dataset variability (e.g. text, language, speaker, and noise) has been underexplored. Analyzing each attribute individually is often challenging, as multiple attributes are usually entangled in commonly used datasets, posing a significant obstacle in understanding the distinct contributions of each attribute to the model's performance. To address this challenge, we propose a generation-training-evaluation framework that leverages zero-shot text-to-speech systems to investigate the impact of controlled attribute variations on speech enhancement performance. It enables us to synthesize training datasets in a scalable manner while carefully altering each attribute. Based on the proposed framework, we analyze the scaling effects of various dataset attributes on the performance of both discriminative and generative SE models. Extensive experiments on multi-domain corpora imply that acoustic attributes (e.g., speaker and noise) are much more important to current speech enhancement models than semantic attributes (e.g., language and text), offering new insights for future research.
CoVoMix: Advancing Zero-Shot Speech Generation for Human-like Multi-talker Conversations
Apr 10, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) modeling have led to significant strides in generating high-fidelity and diverse speech. However, dialogue generation, along with achieving human-like naturalness in speech, continues to be a challenge in the field. In this paper, we introduce CoVoMix: Conversational Voice Mixture Generation, a novel model for zero-shot, human-like, multi-speaker, multi-round dialogue speech generation. CoVoMix is capable of first converting dialogue text into multiple streams of discrete tokens, with each token stream representing semantic information for individual talkers. These token streams are then fed into a flow-matching based acoustic model to generate mixed mel-spectrograms. Finally, the speech waveforms are produced using a HiFi-GAN model. Furthermore, we devise a comprehensive set of metrics for measuring the effectiveness of dialogue modeling and generation. Our experimental results show that CoVoMix can generate dialogues that are not only human-like in their naturalness and coherence but also involve multiple talkers engaging in multiple rounds of conversation. These dialogues, generated within a single channel, are characterized by seamless speech transitions, including overlapping speech, and appropriate paralinguistic behaviors such as laughter. Audio samples are available at https://aka.ms/covomix.
Diffusion Conditional Expectation Model for Efficient and Robust Target Speech Extraction
Sep 25, 2023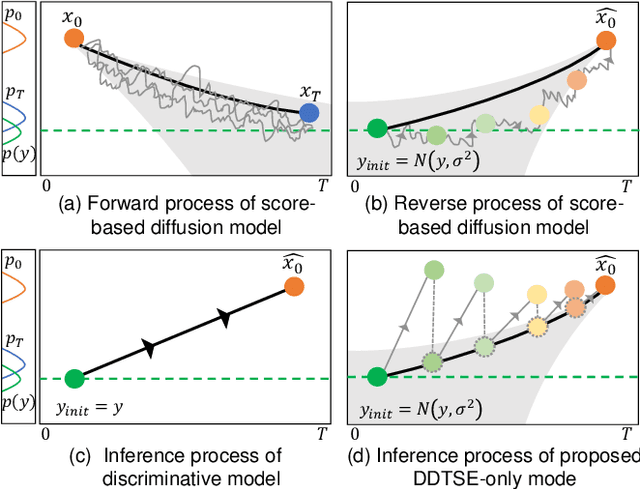
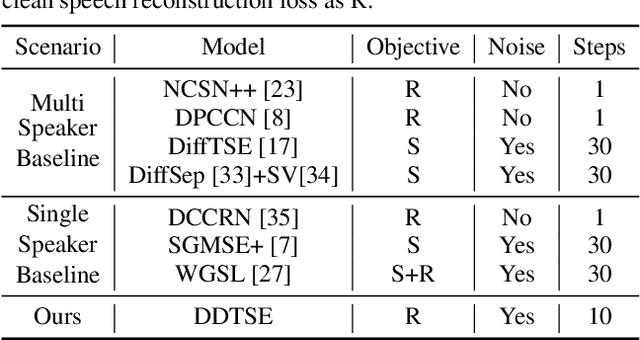
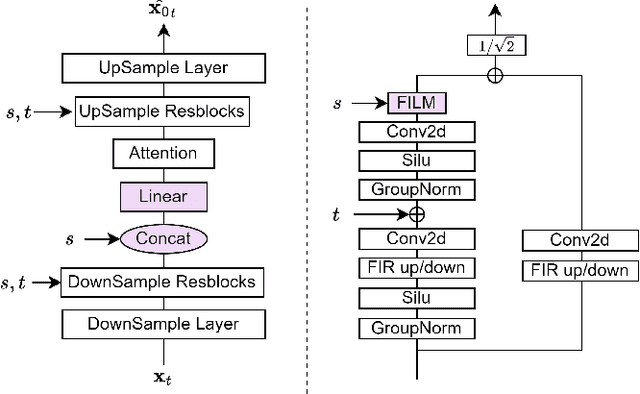
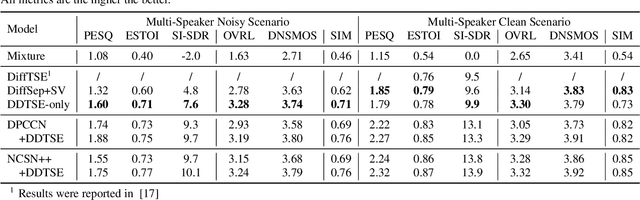
Abstract:Target Speech Extraction (TSE) is a crucial task in speech processing that focuses on isolating the clean speech of a specific speaker from complex mixtures. While discriminative methods are commonly used for TSE, they can introduce distortion in terms of speech perception quality. On the other hand, generative approaches, particularly diffusion-based methods, can enhance speech quality perceptually but suffer from slower inference speed. We propose an efficient generative approach named Diffusion Conditional Expectation Model (DCEM) for TSE. It can handle multi- and single-speaker scenarios in both noisy and clean conditions. Additionally, we introduce Regenerate-DCEM (R-DCEM) that can regenerate and optimize speech quality based on pre-processed speech from a discriminative model. Our method outperforms conventional methods in terms of both intrusive and non-intrusive metrics and demonstrates notable strengths in inference efficiency and robustness to unseen tasks. Audio examples are available online (https://vivian556123.github.io/dcem).
PromptTTS 2: Describing and Generating Voices with Text Prompt
Sep 05, 2023



Abstract:Speech conveys more information than just text, as the same word can be uttered in various voices to convey diverse information. Compared to traditional text-to-speech (TTS) methods relying on speech prompts (reference speech) for voice variability, using text prompts (descriptions) is more user-friendly since speech prompts can be hard to find or may not exist at all. TTS approaches based on the text prompt face two challenges: 1) the one-to-many problem, where not all details about voice variability can be described in the text prompt, and 2) the limited availability of text prompt datasets, where vendors and large cost of data labeling are required to write text prompt for speech. In this work, we introduce PromptTTS 2 to address these challenges with a variation network to provide variability information of voice not captured by text prompts, and a prompt generation pipeline to utilize the large language models (LLM) to compose high quality text prompts. Specifically, the variation network predicts the representation extracted from the reference speech (which contains full information about voice) based on the text prompt representation. For the prompt generation pipeline, it generates text prompts for speech with a speech understanding model to recognize voice attributes (e.g., gender, speed) from speech and a large language model to formulate text prompt based on the recognition results. Experiments on a large-scale (44K hours) speech dataset demonstrate that compared to the previous works, PromptTTS 2 generates voices more consistent with text prompts and supports the sampling of diverse voice variability, thereby offering users more choices on voice generation. Additionally, the prompt generation pipeline produces high-quality prompts, eliminating the large labeling cost. The demo page of PromptTTS 2 is available online\footnote{https://speechresearch.github.io/prompttts2}.
The SJTU X-LANCE Lab System for CNSRC 2022
Jun 23, 2022



Abstract:This technical report describes the SJTU X-LANCE Lab system for the three tracks in CNSRC 2022. In this challenge, we explored the speaker embedding modeling ability of deep ResNet (Deeper r-vector). All the systems are only trained on the Cnceleb training set and we use the same systems for the three tracks in CNSRC 2022. In this challenge, our system ranks the first place in the fixed track of speaker verification task. Our best single system and fusion system achieve 0.3164 and 0.2975 minDCF respectively. Besides, we submit the result of ResNet221 to the speaker retrieval track and achieve 0.4626 mAP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge