Linfeng Yu
Text-aware Speech Separation for Multi-talker Keyword Spotting
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:For noisy environments, ensuring the robustness of keyword spotting (KWS) systems is essential. While much research has focused on noisy KWS, less attention has been paid to multi-talker mixed speech scenarios. Unlike the usual cocktail party problem where multi-talker speech is separated using speaker clues, the key challenge here is to extract the target speech for KWS based on text clues. To address it, this paper proposes a novel Text-aware Permutation Determinization Training method for multi-talker KWS with a clue-based Speech Separation front-end (TPDT-SS). Our research highlights the critical role of SS front-ends and shows that incorporating keyword-specific clues into these models can greatly enhance the effectiveness. TPDT-SS shows remarkable success in addressing permutation problems in mixed keyword speech, thereby greatly boosting the performance of the backend. Additionally, fine-tuning our system on unseen mixed speech results in further performance improvement.
Tokensome: Towards a Genetic Vision-Language GPT for Explainable and Cognitive Karyotyping
Mar 17, 2024



Abstract:Automatic karyotype analysis is often defined as a visual perception task focused solely on chromosomal object-level modeling. This definition has led most existing methods to overlook componential and holistic information, significantly constraining model performance. Moreover, the lack of interpretability in current technologies hinders clinical adoption. In this paper, we introduce Tokensome, a novel vision-language model based on chromosome tokenization for explainable and cognitive karyotyping. Tokensome elevates the method from the conventional visual perception layer to the cognitive decision-making layer. This elevation enables the integration of domain knowledge and cognitive reasoning via knowledge graphs and LLMs, markedly enhancing model's explainability and facilitating abnormality detection.
Diffusion Conditional Expectation Model for Efficient and Robust Target Speech Extraction
Sep 25, 2023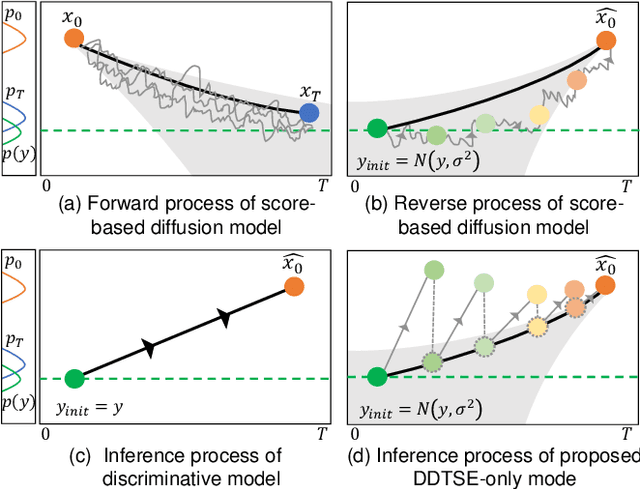
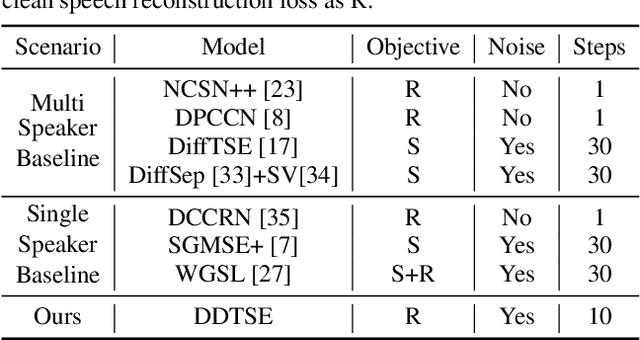
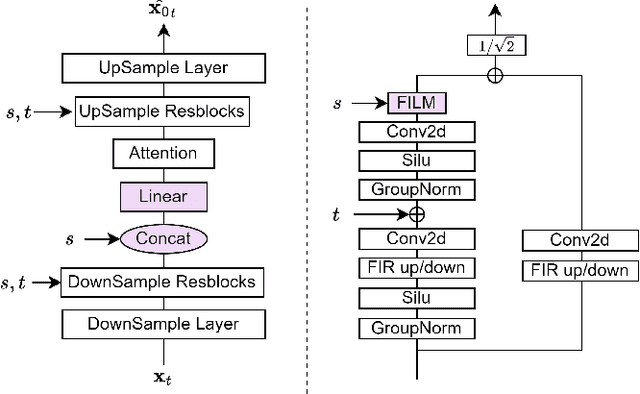
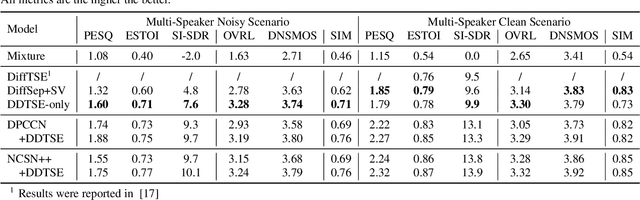
Abstract:Target Speech Extraction (TSE) is a crucial task in speech processing that focuses on isolating the clean speech of a specific speaker from complex mixtures. While discriminative methods are commonly used for TSE, they can introduce distortion in terms of speech perception quality. On the other hand, generative approaches, particularly diffusion-based methods, can enhance speech quality perceptually but suffer from slower inference speed. We propose an efficient generative approach named Diffusion Conditional Expectation Model (DCEM) for TSE. It can handle multi- and single-speaker scenarios in both noisy and clean conditions. Additionally, we introduce Regenerate-DCEM (R-DCEM) that can regenerate and optimize speech quality based on pre-processed speech from a discriminative model. Our method outperforms conventional methods in terms of both intrusive and non-intrusive metrics and demonstrates notable strengths in inference efficiency and robustness to unseen tasks. Audio examples are available online (https://vivian556123.github.io/dcem).
GMAIR: Unsupervised Object Detection Based on Spatial Attention and Gaussian Mixture
Jun 03, 2021



Abstract:Recent studies on unsupervised object detection based on spatial attention have achieved promising results. Models, such as AIR and SPAIR, output "what" and "where" latent variables that represent the attributes and locations of objects in a scene, respectively. Most of the previous studies concentrate on the "where" localization performance; however, we claim that acquiring "what" object attributes is also essential for representation learning. This paper presents a framework, GMAIR, for unsupervised object detection. It incorporates spatial attention and a Gaussian mixture in a unified deep generative model. GMAIR can locate objects in a scene and simultaneously cluster them without supervision. Furthermore, we analyze the "what" latent variables and clustering process. Finally, we evaluate our model on MultiMNIST and Fruit2D datasets and show that GMAIR achieves competitive results on localization and clustering compared to state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge