Junwei Liang
MeshMimic: Geometry-Aware Humanoid Motion Learning through 3D Scene Reconstruction
Feb 17, 2026Abstract:Humanoid motion control has witnessed significant breakthroughs in recent years, with deep reinforcement learning (RL) emerging as a primary catalyst for achieving complex, human-like behaviors. However, the high dimensionality and intricate dynamics of humanoid robots make manual motion design impractical, leading to a heavy reliance on expensive motion capture (MoCap) data. These datasets are not only costly to acquire but also frequently lack the necessary geometric context of the surrounding physical environment. Consequently, existing motion synthesis frameworks often suffer from a decoupling of motion and scene, resulting in physical inconsistencies such as contact slippage or mesh penetration during terrain-aware tasks. In this work, we present MeshMimic, an innovative framework that bridges 3D scene reconstruction and embodied intelligence to enable humanoid robots to learn coupled "motion-terrain" interactions directly from video. By leveraging state-of-the-art 3D vision models, our framework precisely segments and reconstructs both human trajectories and the underlying 3D geometry of terrains and objects. We introduce an optimization algorithm based on kinematic consistency to extract high-quality motion data from noisy visual reconstructions, alongside a contact-invariant retargeting method that transfers human-environment interaction features to the humanoid agent. Experimental results demonstrate that MeshMimic achieves robust, highly dynamic performance across diverse and challenging terrains. Our approach proves that a low-cost pipeline utilizing only consumer-grade monocular sensors can facilitate the training of complex physical interactions, offering a scalable path toward the autonomous evolution of humanoid robots in unstructured environments.
The RoboSense Challenge: Sense Anything, Navigate Anywhere, Adapt Across Platforms
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Autonomous systems are increasingly deployed in open and dynamic environments -- from city streets to aerial and indoor spaces -- where perception models must remain reliable under sensor noise, environmental variation, and platform shifts. However, even state-of-the-art methods often degrade under unseen conditions, highlighting the need for robust and generalizable robot sensing. The RoboSense 2025 Challenge is designed to advance robustness and adaptability in robot perception across diverse sensing scenarios. It unifies five complementary research tracks spanning language-grounded decision making, socially compliant navigation, sensor configuration generalization, cross-view and cross-modal correspondence, and cross-platform 3D perception. Together, these tasks form a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating real-world sensing reliability under domain shifts, sensor failures, and platform discrepancies. RoboSense 2025 provides standardized datasets, baseline models, and unified evaluation protocols, enabling large-scale and reproducible comparison of robust perception methods. The challenge attracted 143 teams from 85 institutions across 16 countries, reflecting broad community engagement. By consolidating insights from 23 winning solutions, this report highlights emerging methodological trends, shared design principles, and open challenges across all tracks, marking a step toward building robots that can sense reliably, act robustly, and adapt across platforms in real-world environments.
Vision-Language-Action Models for Autonomous Driving: Past, Present, and Future
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving has long relied on modular "Perception-Decision-Action" pipelines, where hand-crafted interfaces and rule-based components often break down in complex or long-tailed scenarios. Their cascaded design further propagates perception errors, degrading downstream planning and control. Vision-Action (VA) models address some limitations by learning direct mappings from visual inputs to actions, but they remain opaque, sensitive to distribution shifts, and lack structured reasoning or instruction-following capabilities. Recent progress in Large Language Models (LLMs) and multimodal learning has motivated the emergence of Vision-Language-Action (VLA) frameworks, which integrate perception with language-grounded decision making. By unifying visual understanding, linguistic reasoning, and actionable outputs, VLAs offer a pathway toward more interpretable, generalizable, and human-aligned driving policies. This work provides a structured characterization of the emerging VLA landscape for autonomous driving. We trace the evolution from early VA approaches to modern VLA frameworks and organize existing methods into two principal paradigms: End-to-End VLA, which integrates perception, reasoning, and planning within a single model, and Dual-System VLA, which separates slow deliberation (via VLMs) from fast, safety-critical execution (via planners). Within these paradigms, we further distinguish subclasses such as textual vs. numerical action generators and explicit vs. implicit guidance mechanisms. We also summarize representative datasets and benchmarks for evaluating VLA-based driving systems and highlight key challenges and open directions, including robustness, interpretability, and instruction fidelity. Overall, this work aims to establish a coherent foundation for advancing human-compatible autonomous driving systems.
From Watch to Imagine: Steering Long-horizon Manipulation via Human Demonstration and Future Envisionment
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Generalizing to long-horizon manipulation tasks in a zero-shot setting remains a central challenge in robotics. Current multimodal foundation based approaches, despite their capabilities, typically fail to decompose high-level commands into executable action sequences from static visual input alone. To address this challenge, we introduce Super-Mimic, a hierarchical framework that enables zero-shot robotic imitation by directly inferring procedural intent from unscripted human demonstration videos. Our framework is composed of two sequential modules. First, a Human Intent Translator (HIT) parses the input video using multimodal reasoning to produce a sequence of language-grounded subtasks. These subtasks then condition a Future Dynamics Predictor (FDP), which employs a generative model that synthesizes a physically plausible video rollout for each step. The resulting visual trajectories are dynamics-aware, explicitly modeling crucial object interactions and contact points to guide the low-level controller. We validate this approach through extensive experiments on a suite of long-horizon manipulation tasks, where Super-Mimic significantly outperforms state-of-the-art zero-shot methods by over 20\%. These results establish that coupling video-driven intent parsing with prospective dynamics modeling is a highly effective strategy for developing general-purpose robotic systems.
End-to-End Humanoid Robot Safe and Comfortable Locomotion Policy
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:The deployment of humanoid robots in unstructured, human-centric environments requires navigation capabilities that extend beyond simple locomotion to include robust perception, provable safety, and socially aware behavior. Current reinforcement learning approaches are often limited by blind controllers that lack environmental awareness or by vision-based systems that fail to perceive complex 3D obstacles. In this work, we present an end-to-end locomotion policy that directly maps raw, spatio-temporal LiDAR point clouds to motor commands, enabling robust navigation in cluttered dynamic scenes. We formulate the control problem as a Constrained Markov Decision Process (CMDP) to formally separate safety from task objectives. Our key contribution is a novel methodology that translates the principles of Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) into costs within the CMDP, allowing a model-free Penalized Proximal Policy Optimization (P3O) to enforce safety constraints during training. Furthermore, we introduce a set of comfort-oriented rewards, grounded in human-robot interaction research, to promote motions that are smooth, predictable, and less intrusive. We demonstrate the efficacy of our framework through a successful sim-to-real transfer to a physical humanoid robot, which exhibits agile and safe navigation around both static and dynamic 3D obstacles.
Stairway to Success: Zero-Shot Floor-Aware Object-Goal Navigation via LLM-Driven Coarse-to-Fine Exploration
May 29, 2025Abstract:Object-Goal Navigation (OGN) remains challenging in real-world, multi-floor environments and under open-vocabulary object descriptions. We observe that most episodes in widely used benchmarks such as HM3D and MP3D involve multi-floor buildings, with many requiring explicit floor transitions. However, existing methods are often limited to single-floor settings or predefined object categories. To address these limitations, we tackle two key challenges: (1) efficient cross-level planning and (2) zero-shot object-goal navigation (ZS-OGN), where agents must interpret novel object descriptions without prior exposure. We propose ASCENT, a framework that combines a Multi-Floor Spatial Abstraction module for hierarchical semantic mapping and a Coarse-to-Fine Frontier Reasoning module leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for context-aware exploration, without requiring additional training on new object semantics or locomotion data. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art ZS-OGN approaches on HM3D and MP3D benchmarks while enabling efficient multi-floor navigation. We further validate its practicality through real-world deployment on a quadruped robot, achieving successful object exploration across unseen floors.
Zero-Shot 3D Visual Grounding from Vision-Language Models
May 28, 2025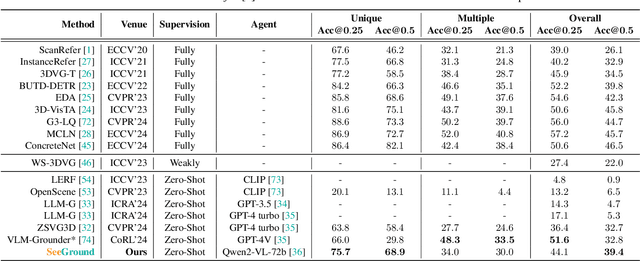
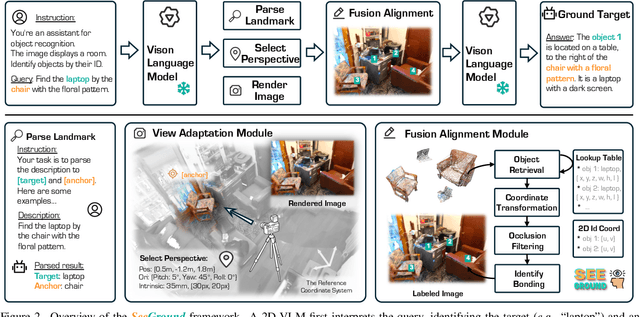
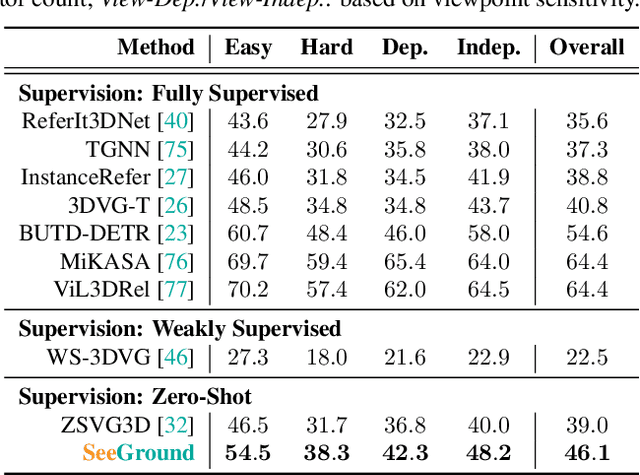
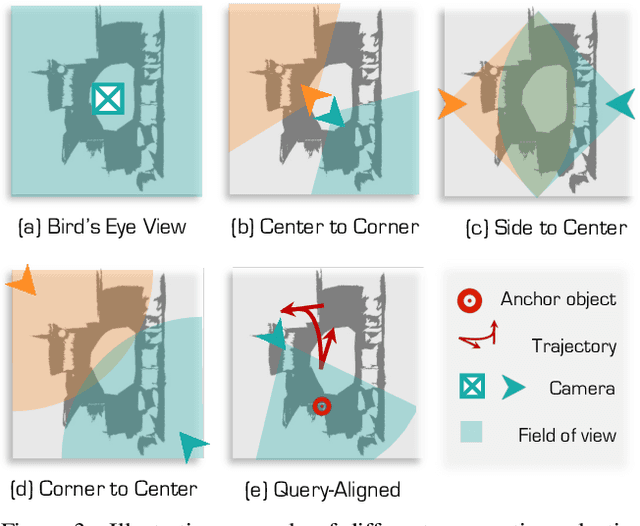
Abstract:3D Visual Grounding (3DVG) seeks to locate target objects in 3D scenes using natural language descriptions, enabling downstream applications such as augmented reality and robotics. Existing approaches typically rely on labeled 3D data and predefined categories, limiting scalability to open-world settings. We present SeeGround, a zero-shot 3DVG framework that leverages 2D Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to bypass the need for 3D-specific training. To bridge the modality gap, we introduce a hybrid input format that pairs query-aligned rendered views with spatially enriched textual descriptions. Our framework incorporates two core components: a Perspective Adaptation Module that dynamically selects optimal viewpoints based on the query, and a Fusion Alignment Module that integrates visual and spatial signals to enhance localization precision. Extensive evaluations on ScanRefer and Nr3D confirm that SeeGround achieves substantial improvements over existing zero-shot baselines -- outperforming them by 7.7% and 7.1%, respectively -- and even rivals fully supervised alternatives, demonstrating strong generalization under challenging conditions.
Omni-Perception: Omnidirectional Collision Avoidance for Legged Locomotion in Dynamic Environments
May 25, 2025Abstract:Agile locomotion in complex 3D environments requires robust spatial awareness to safely avoid diverse obstacles such as aerial clutter, uneven terrain, and dynamic agents. Depth-based perception approaches often struggle with sensor noise, lighting variability, computational overhead from intermediate representations (e.g., elevation maps), and difficulties with non-planar obstacles, limiting performance in unstructured environments. In contrast, direct integration of LiDAR sensing into end-to-end learning for legged locomotion remains underexplored. We propose Omni-Perception, an end-to-end locomotion policy that achieves 3D spatial awareness and omnidirectional collision avoidance by directly processing raw LiDAR point clouds. At its core is PD-RiskNet (Proximal-Distal Risk-Aware Hierarchical Network), a novel perception module that interprets spatio-temporal LiDAR data for environmental risk assessment. To facilitate efficient policy learning, we develop a high-fidelity LiDAR simulation toolkit with realistic noise modeling and fast raycasting, compatible with platforms such as Isaac Gym, Genesis, and MuJoCo, enabling scalable training and effective sim-to-real transfer. Learning reactive control policies directly from raw LiDAR data enables the robot to navigate complex environments with static and dynamic obstacles more robustly than approaches relying on intermediate maps or limited sensing. We validate Omni-Perception through real-world experiments and extensive simulation, demonstrating strong omnidirectional avoidance capabilities and superior locomotion performance in highly dynamic environments. We will open-source our code and models.
SD-OVON: A Semantics-aware Dataset and Benchmark Generation Pipeline for Open-Vocabulary Object Navigation in Dynamic Scenes
May 24, 2025Abstract:We present the Semantics-aware Dataset and Benchmark Generation Pipeline for Open-vocabulary Object Navigation in Dynamic Scenes (SD-OVON). It utilizes pretraining multimodal foundation models to generate infinite unique photo-realistic scene variants that adhere to real-world semantics and daily commonsense for the training and the evaluation of navigation agents, accompanied with a plugin for generating object navigation task episodes compatible to the Habitat simulator. In addition, we offer two pre-generated object navigation task datasets, SD-OVON-3k and SD-OVON-10k, comprising respectively about 3k and 10k episodes of the open-vocabulary object navigation task, derived from the SD-OVON-Scenes dataset with 2.5k photo-realistic scans of real-world environments and the SD-OVON-Objects dataset with 0.9k manually inspected scanned and artist-created manipulatable object models. Unlike prior datasets limited to static environments, SD-OVON covers dynamic scenes and manipulatable objects, facilitating both real-to-sim and sim-to-real robotic applications. This approach enhances the realism of navigation tasks, the training and the evaluation of open-vocabulary object navigation agents in complex settings. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our pipeline and datasets, we propose two baselines and evaluate them along with state-of-the-art baselines on SD-OVON-3k. The datasets, benchmark and source code are publicly available.
Exploring the Limits of Vision-Language-Action Manipulations in Cross-task Generalization
May 21, 2025Abstract:The generalization capabilities of vision-language-action (VLA) models to unseen tasks are crucial to achieving general-purpose robotic manipulation in open-world settings. However, the cross-task generalization capabilities of existing VLA models remain significantly underexplored. To address this gap, we introduce AGNOSTOS, a novel simulation benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate cross-task zero-shot generalization in manipulation. AGNOSTOS comprises 23 unseen manipulation tasks for testing, distinct from common training task distributions, and incorporates two levels of generalization difficulty to assess robustness. Our systematic evaluation reveals that current VLA models, despite being trained on diverse datasets, struggle to generalize effectively to these unseen tasks. To overcome this limitation, we propose Cross-Task In-Context Manipulation (X-ICM), a method that conditions large language models (LLMs) on in-context demonstrations from seen tasks to predict action sequences for unseen tasks. Additionally, we introduce a dynamics-guided sample selection strategy that identifies relevant demonstrations by capturing cross-task dynamics. On AGNOSTOS, X-ICM significantly improves cross-task zero-shot generalization performance over leading VLAs. We believe AGNOSTOS and X-ICM will serve as valuable tools for advancing general-purpose robotic manipulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge