Shijie Li
DV-VLN: Dual Verification for Reliable LLM-Based Vision-and-Language Navigation
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) requires an embodied agent to navigate in a complex 3D environment according to natural language instructions. Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) has enabled language-driven navigation with improved interpretability. However, most LLM-based agents still rely on single-shot action decisions, where the model must choose one option from noisy, textualized multi-perspective observations. Due to local mismatches and imperfect intermediate reasoning, such decisions can easily deviate from the correct path, leading to error accumulation and reduced reliability in unseen environments. In this paper, we propose DV-VLN, a new VLN framework that follows a generate-then-verify paradigm. DV-VLN first performs parameter-efficient in-domain adaptation of an open-source LLaMA-2 backbone to produce a structured navigational chain-of-thought, and then verifies candidate actions with two complementary channels: True-False Verification (TFV) and Masked-Entity Verification (MEV). DV-VLN selects actions by aggregating verification successes across multiple samples, yielding interpretable scores for reranking. Experiments on R2R, RxR (English subset), and REVERIE show that DV-VLN consistently improves over direct prediction and sampling-only baselines, achieving competitive performance among language-only VLN agents and promising results compared with several cross-modal systems.Code is available at https://github.com/PlumJun/DV-VLN.
VidLaDA: Bidirectional Diffusion Large Language Models for Efficient Video Understanding
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Standard Autoregressive Video LLMs inevitably suffer from causal masking biases that hinder global spatiotemporal modeling, leading to suboptimal understanding efficiency. We propose VidLaDA, a Video LLM based on Diffusion Language Model utilizing bidirectional attention to capture bidirectional dependencies. To further tackle the inference bottleneck of diffusion decoding on massive video tokens, we introduce MARS-Cache. This framework accelerates inference by combining asynchronous visual cache refreshing with frame-wise chunk attention, effectively pruning redundancy while preserving global connectivity via anchor tokens. Extensive experiments show VidLaDA outperforms diffusion baselines and rivals state-of-the-art autoregressive models (e.g., Qwen2.5-VL and LLaVA-Video), with MARS-Cache delivering over 12x speedup without compromising reasoning accuracy. Code and checkpoints are open-sourced at https://github.com/ziHoHe/VidLaDA.
Patch-as-Decodable-Token: Towards Unified Multi-Modal Vision Tasks in MLLMs
Oct 02, 2025
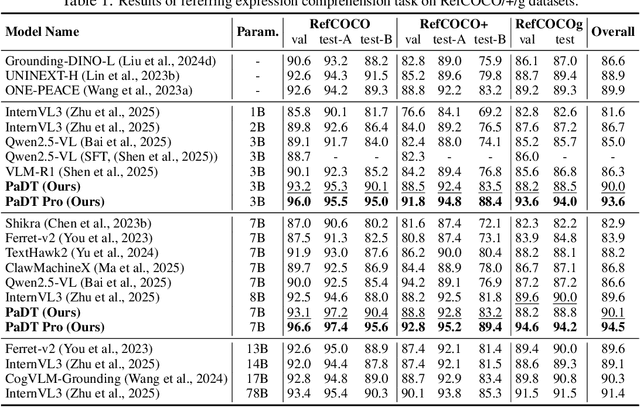
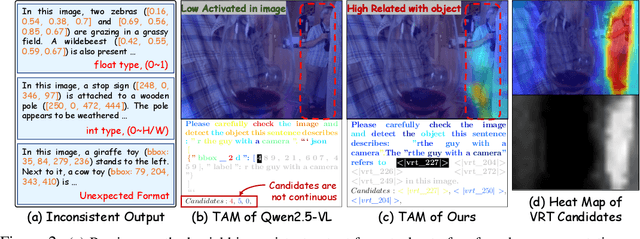
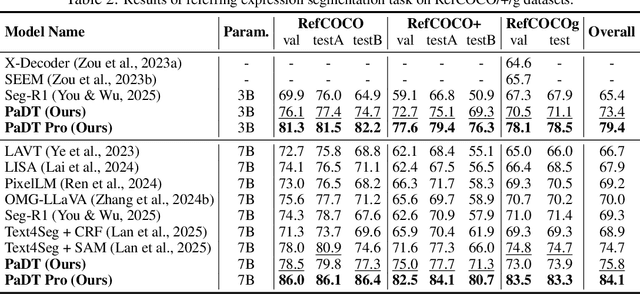
Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have advanced rapidly in recent years. However, existing approaches for vision tasks often rely on indirect representations, such as generating coordinates as text for detection, which limits performance and prevents dense prediction tasks like segmentation. To overcome these challenges, we introduce Patch-as-Decodable Token (PaDT), a unified paradigm that enables MLLMs to directly generate both textual and diverse visual outputs. Central to PaDT are Visual Reference Tokens (VRTs), derived from visual patch embeddings of query images and interleaved seamlessly with LLM's output textual tokens. A lightweight decoder then transforms LLM's outputs into detection, segmentation, and grounding predictions. Unlike prior methods, PaDT processes VRTs independently at each forward pass and dynamically expands the embedding table, thus improving localization and differentiation among similar objects. We further tailor a training strategy for PaDT by randomly selecting VRTs for supervised fine-tuning and introducing a robust per-token cross-entropy loss. Our empirical studies across four visual perception and understanding tasks suggest PaDT consistently achieving state-of-the-art performance, even compared with significantly larger MLLM models. The code is available at https://github.com/Gorilla-Lab-SCUT/PaDT.
GLM-4.5: Agentic, Reasoning, and Coding (ARC) Foundation Models
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:We present GLM-4.5, an open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 355B total parameters and 32B activated parameters, featuring a hybrid reasoning method that supports both thinking and direct response modes. Through multi-stage training on 23T tokens and comprehensive post-training with expert model iteration and reinforcement learning, GLM-4.5 achieves strong performance across agentic, reasoning, and coding (ARC) tasks, scoring 70.1% on TAU-Bench, 91.0% on AIME 24, and 64.2% on SWE-bench Verified. With much fewer parameters than several competitors, GLM-4.5 ranks 3rd overall among all evaluated models and 2nd on agentic benchmarks. We release both GLM-4.5 (355B parameters) and a compact version, GLM-4.5-Air (106B parameters), to advance research in reasoning and agentic AI systems. Code, models, and more information are available at https://github.com/zai-org/GLM-4.5.
CogStream: Context-guided Streaming Video Question Answering
Jun 12, 2025



Abstract:Despite advancements in Video Large Language Models (Vid-LLMs) improving multimodal understanding, challenges persist in streaming video reasoning due to its reliance on contextual information. Existing paradigms feed all available historical contextual information into Vid-LLMs, resulting in a significant computational burden for visual data processing. Furthermore, the inclusion of irrelevant context distracts models from key details. This paper introduces a challenging task called Context-guided Streaming Video Reasoning (CogStream), which simulates real-world streaming video scenarios, requiring models to identify the most relevant historical contextual information to deduce answers for questions about the current stream. To support CogStream, we present a densely annotated dataset featuring extensive and hierarchical question-answer pairs, generated by a semi-automatic pipeline. Additionally, we present CogReasoner as a baseline model. It efficiently tackles this task by leveraging visual stream compression and historical dialogue retrieval. Extensive experiments prove the effectiveness of this method. Code will be released soon.
Zero-Shot 3D Visual Grounding from Vision-Language Models
May 28, 2025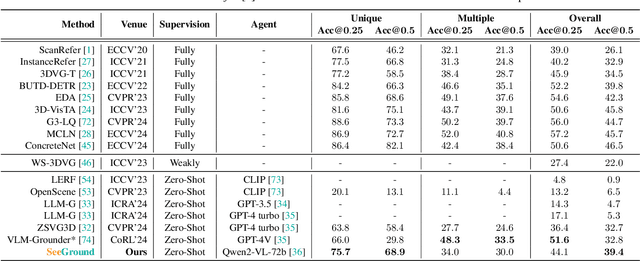
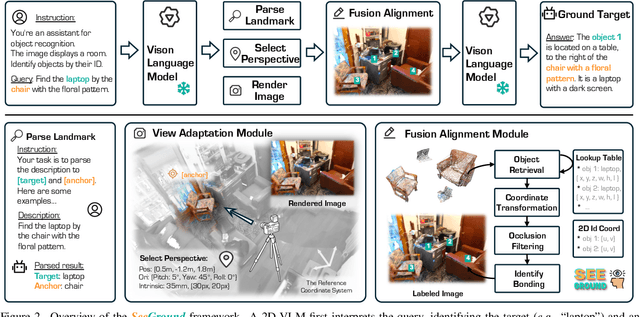
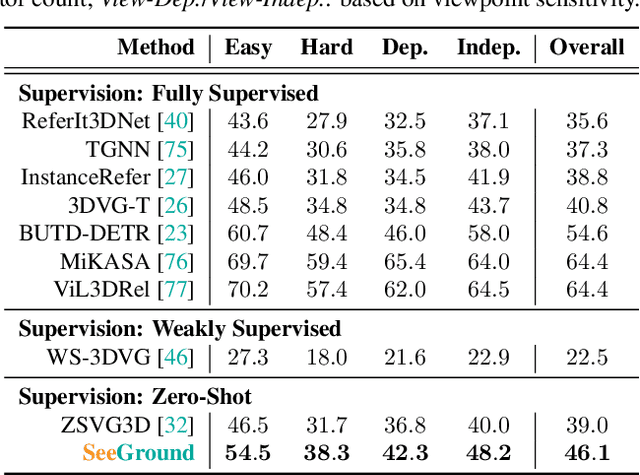
Abstract:3D Visual Grounding (3DVG) seeks to locate target objects in 3D scenes using natural language descriptions, enabling downstream applications such as augmented reality and robotics. Existing approaches typically rely on labeled 3D data and predefined categories, limiting scalability to open-world settings. We present SeeGround, a zero-shot 3DVG framework that leverages 2D Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to bypass the need for 3D-specific training. To bridge the modality gap, we introduce a hybrid input format that pairs query-aligned rendered views with spatially enriched textual descriptions. Our framework incorporates two core components: a Perspective Adaptation Module that dynamically selects optimal viewpoints based on the query, and a Fusion Alignment Module that integrates visual and spatial signals to enhance localization precision. Extensive evaluations on ScanRefer and Nr3D confirm that SeeGround achieves substantial improvements over existing zero-shot baselines -- outperforming them by 7.7% and 7.1%, respectively -- and even rivals fully supervised alternatives, demonstrating strong generalization under challenging conditions.
Multi-View Industrial Anomaly Detection with Epipolar Constrained Cross-View Fusion
Mar 14, 2025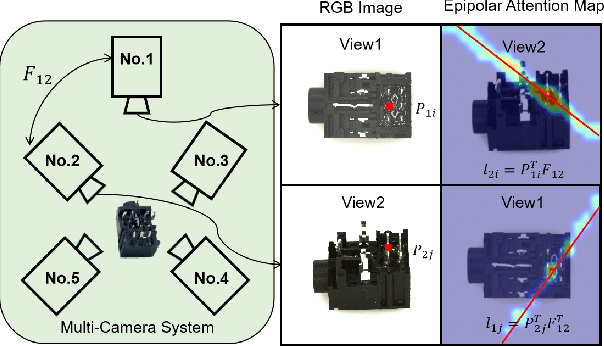
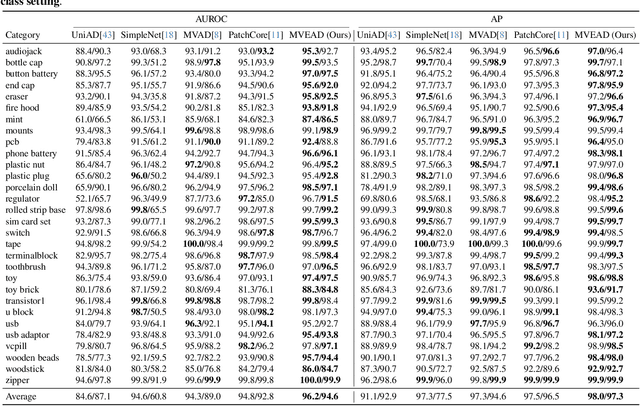
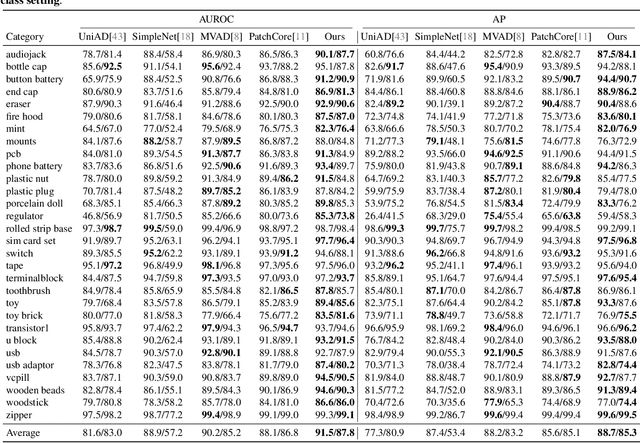
Abstract:Multi-camera systems provide richer contextual information for industrial anomaly detection. However, traditional methods process each view independently, disregarding the complementary information across viewpoints. Existing multi-view anomaly detection approaches typically employ data-driven cross-view attention for feature fusion but fail to leverage the unique geometric properties of multi-camera setups. In this work, we introduce an epipolar geometry-constrained attention module to guide cross-view fusion, ensuring more effective information aggregation. To further enhance the potential of cross-view attention, we propose a pretraining strategy inspired by memory bank-based anomaly detection. This approach encourages normal feature representations to form multiple local clusters and incorporate multi-view aware negative sample synthesis to regularize pretraining. We demonstrate that our epipolar guided multi-view anomaly detection framework outperforms existing methods on the state-of-the-art multi-view anomaly detection dataset.
Global-Aware Monocular Semantic Scene Completion with State Space Models
Mar 09, 2025



Abstract:Monocular Semantic Scene Completion (MonoSSC) reconstructs and interprets 3D environments from a single image, enabling diverse real-world applications. However, existing methods are often constrained by the local receptive field of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), making it challenging to handle the non-uniform distribution of projected points (Fig. \ref{fig:perspective}) and effectively reconstruct missing information caused by the 3D-to-2D projection. In this work, we introduce GA-MonoSSC, a hybrid architecture for MonoSSC that effectively captures global context in both the 2D image domain and 3D space. Specifically, we propose a Dual-Head Multi-Modality Encoder, which leverages a Transformer architecture to capture spatial relationships across all features in the 2D image domain, enabling more comprehensive 2D feature extraction. Additionally, we introduce the Frustum Mamba Decoder, built on the State Space Model (SSM), to efficiently capture long-range dependencies in 3D space. Furthermore, we propose a frustum reordering strategy within the Frustum Mamba Decoder to mitigate feature discontinuities in the reordered voxel sequence, ensuring better alignment with the scan mechanism of the State Space Model (SSM) for improved 3D representation learning. We conduct extensive experiments on the widely used Occ-ScanNet and NYUv2 datasets, demonstrating that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance, validating its effectiveness. The code will be released upon acceptance.
Future-Aware Interaction Network For Motion Forecasting
Mar 09, 2025



Abstract:Motion forecasting is a crucial component of autonomous driving systems, enabling the generation of accurate and smooth future trajectories to ensure safe navigation to the destination. In previous methods, potential future trajectories are often absent in the scene encoding stage, which may lead to suboptimal outcomes. Additionally, prior approaches typically employ transformer architectures for spatiotemporal modeling of trajectories and map information, which suffer from the quadratic scaling complexity of the transformer architecture. In this work, we propose an interaction-based method, named Future-Aware Interaction Network, that introduces potential future trajectories into scene encoding for a comprehensive traffic representation. Furthermore, a State Space Model (SSM), specifically Mamba, is introduced for both spatial and temporal modeling. To adapt Mamba for spatial interaction modeling, we propose an adaptive reordering strategy that transforms unordered data into a structured sequence. Additionally, Mamba is employed to refine generated future trajectories temporally, ensuring more consistent predictions. These enhancements not only improve model efficiency but also enhance the accuracy and diversity of predictions. We conduct comprehensive experiments on the widely used Argoverse 1 and Argoverse 2 datasets, demonstrating that the proposed method achieves superior performance compared to previous approaches in a more efficient way. The code will be released according to the acceptance.
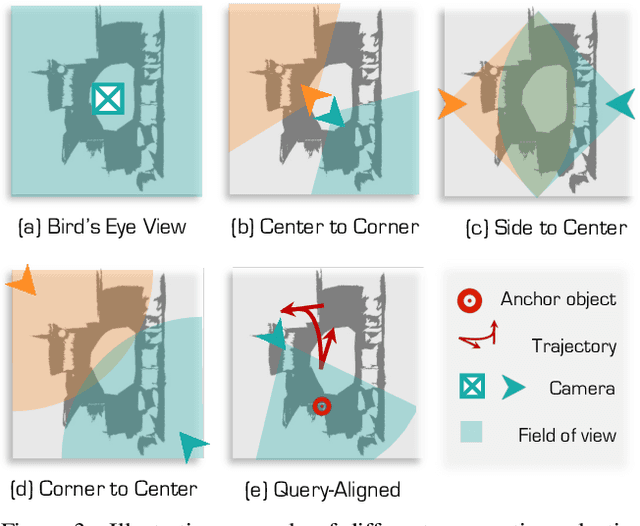
SeeGround: See and Ground for Zero-Shot Open-Vocabulary 3D Visual Grounding
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:3D Visual Grounding (3DVG) aims to locate objects in 3D scenes based on textual descriptions, which is essential for applications like augmented reality and robotics. Traditional 3DVG approaches rely on annotated 3D datasets and predefined object categories, limiting scalability and adaptability. To overcome these limitations, we introduce SeeGround, a zero-shot 3DVG framework leveraging 2D Vision-Language Models (VLMs) trained on large-scale 2D data. We propose to represent 3D scenes as a hybrid of query-aligned rendered images and spatially enriched text descriptions, bridging the gap between 3D data and 2D-VLMs input formats. We propose two modules: the Perspective Adaptation Module, which dynamically selects viewpoints for query-relevant image rendering, and the Fusion Alignment Module, which integrates 2D images with 3D spatial descriptions to enhance object localization. Extensive experiments on ScanRefer and Nr3D demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing zero-shot methods by large margins. Notably, we exceed weakly supervised methods and rival some fully supervised ones, outperforming previous SOTA by 7.7% on ScanRefer and 7.1% on Nr3D, showcasing its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge