Peng Di
From One-to-One to Many-to-Many: Dynamic Cross-Layer Injection for Deep Vision-Language Fusion
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) create a severe visual feature bottleneck by using a crude, asymmetric connection that links only the output of the vision encoder to the input of the large language model (LLM). This static architecture fundamentally limits the ability of LLMs to achieve comprehensive alignment with hierarchical visual knowledge, compromising their capacity to accurately integrate local details with global semantics into coherent reasoning. To resolve this, we introduce Cross-Layer Injection (CLI), a novel and lightweight framework that forges a dynamic many-to-many bridge between the two modalities. CLI consists of two synergistic, parameter-efficient components: an Adaptive Multi-Projection (AMP) module that harmonizes features from diverse vision layers, and an Adaptive Gating Fusion (AGF) mechanism that empowers the LLM to selectively inject the most relevant visual information based on its real-time decoding context. We validate the effectiveness and versatility of CLI by integrating it into LLaVA-OneVision and LLaVA-1.5. Extensive experiments on 18 diverse benchmarks demonstrate significant performance improvements, establishing CLI as a scalable paradigm that unlocks deeper multimodal understanding by granting LLMs on-demand access to the full visual hierarchy.
C2LLM Technical Report: A New Frontier in Code Retrieval via Adaptive Cross-Attention Pooling
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:We present C2LLM - Contrastive Code Large Language Models, a family of code embedding models in both 0.5B and 7B sizes. Building upon Qwen-2.5-Coder backbones, C2LLM adopts a Pooling by Multihead Attention (PMA) module for generating sequence embedding from token embeddings, effectively 1) utilizing the LLM's causal representations acquired during pretraining, while also 2) being able to aggregate information from all tokens in the sequence, breaking the information bottleneck in EOS-based sequence embeddings, and 3) supporting flexible adaptation of embedding dimension, serving as an alternative to MRL. Trained on three million publicly available data, C2LLM models set new records on MTEB-Code among models of similar sizes, with C2LLM-7B ranking 1st on the overall leaderboard.
F2LLM Technical Report: Matching SOTA Embedding Performance with 6 Million Open-Source Data
Oct 02, 2025

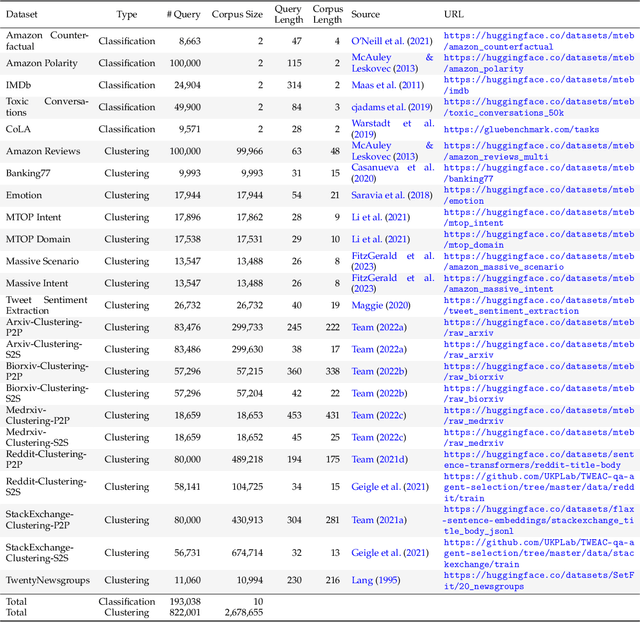
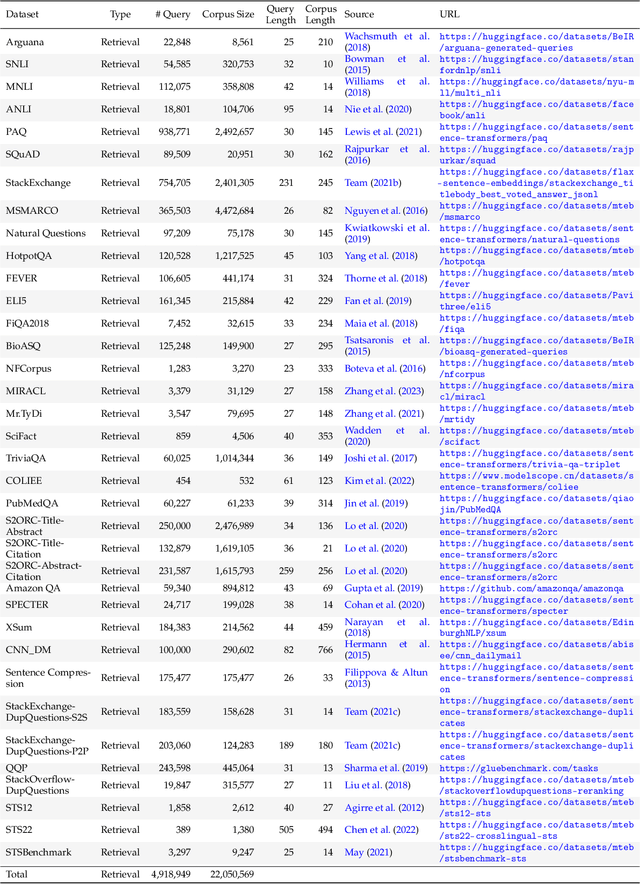
Abstract:We introduce F2LLM - Foundation to Feature Large Language Models, a suite of state-of-the-art embedding models in three sizes: 0.6B, 1.7B, and 4B. Unlike previous top-ranking embedding models that require massive contrastive pretraining, sophisticated training pipelines, and costly synthetic training data, F2LLM is directly finetuned from foundation models on 6 million query-document-negative tuples curated from open-source, non-synthetic datasets, striking a strong balance between training cost, model size, and embedding performance. On the MTEB English leaderboard, F2LLM-4B ranks 2nd among models with approximately 4B parameters and 7th overall, while F2LLM-1.7B ranks 1st among models in the 1B-2B size range. To facilitate future research in the field, we release the models, training dataset, and code, positioning F2LLM as a strong, reproducible, and budget-friendly baseline for future works.
Systematic Analysis of MCP Security
Aug 18, 2025Abstract:The Model Context Protocol (MCP) has emerged as a universal standard that enables AI agents to seamlessly connect with external tools, significantly enhancing their functionality. However, while MCP brings notable benefits, it also introduces significant vulnerabilities, such as Tool Poisoning Attacks (TPA), where hidden malicious instructions exploit the sycophancy of large language models (LLMs) to manipulate agent behavior. Despite these risks, current academic research on MCP security remains limited, with most studies focusing on narrow or qualitative analyses that fail to capture the diversity of real-world threats. To address this gap, we present the MCP Attack Library (MCPLIB), which categorizes and implements 31 distinct attack methods under four key classifications: direct tool injection, indirect tool injection, malicious user attacks, and LLM inherent attack. We further conduct a quantitative analysis of the efficacy of each attack. Our experiments reveal key insights into MCP vulnerabilities, including agents' blind reliance on tool descriptions, sensitivity to file-based attacks, chain attacks exploiting shared context, and difficulty distinguishing external data from executable commands. These insights, validated through attack experiments, underscore the urgency for robust defense strategies and informed MCP design. Our contributions include 1) constructing a comprehensive MCP attack taxonomy, 2) introducing a unified attack framework MCPLIB, and 3) conducting empirical vulnerability analysis to enhance MCP security mechanisms. This work provides a foundational framework, supporting the secure evolution of MCP ecosystems.
Code Graph Model (CGM): A Graph-Integrated Large Language Model for Repository-Level Software Engineering Tasks
May 22, 2025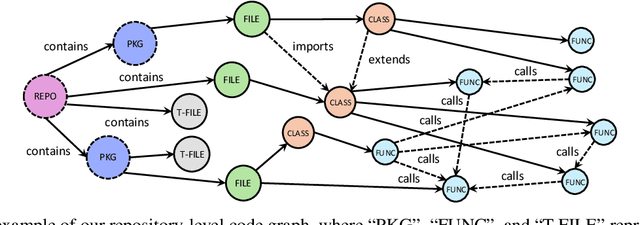
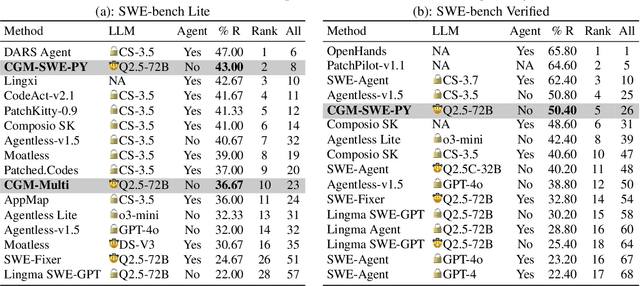
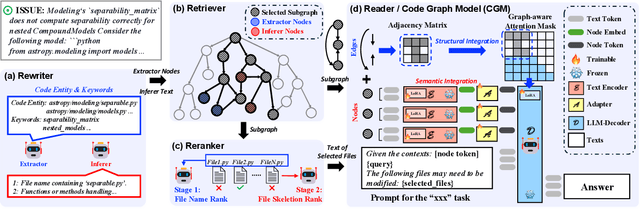
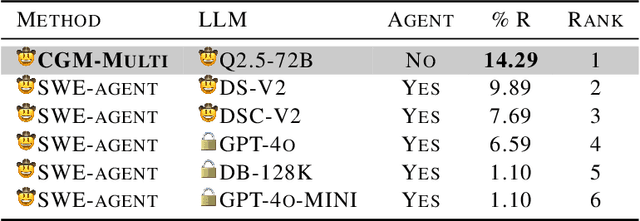
Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in function-level code generation, yet repository-level software engineering tasks remain challenging. Current solutions predominantly rely on proprietary LLM agents, which introduce unpredictability and limit accessibility, raising concerns about data privacy and model customization. This paper investigates whether open-source LLMs can effectively address repository-level tasks without requiring agent-based approaches. We demonstrate this is possible by enabling LLMs to comprehend functions and files within codebases through their semantic information and structural dependencies. To this end, we introduce Code Graph Models (CGMs), which integrate repository code graph structures into the LLM's attention mechanism and map node attributes to the LLM's input space using a specialized adapter. When combined with an agentless graph RAG framework, our approach achieves a 43.00% resolution rate on the SWE-bench Lite benchmark using the open-source Qwen2.5-72B model. This performance ranks first among open weight models, second among methods with open-source systems, and eighth overall, surpassing the previous best open-source model-based method by 12.33%.
GALLa: Graph Aligned Large Language Models for Improved Source Code Understanding
Sep 06, 2024Abstract:Programming languages possess rich semantic information such as data flow that is represented by graphs and not available from the surface form of source code. Recent code language models have scaled to billions of parameters, but model source code solely as text tokens while ignoring any other structural information. Conversely, models that do encode structural information of code make modifications to the Transformer architecture, limiting their scale and compatibility with pretrained LLMs. In this work, we take the best of both worlds with GALLa - Graph Aligned Large Language Model. GALLa utilizes graph neural networks and cross-modal alignment technologies to inject the structural information of code into LLMs as an auxiliary task during finetuning. This framework is both model-agnostic and task-agnostic, as it can be applied to any code LLM for any code downstream task, and requires the structural graph data only at training time from a corpus unrelated to the finetuning data, while incurring no cost at inference time over the baseline LLM. Experiments on five code tasks with four different baseline LLMs ranging in size from 350M to 8B validate the effectiveness of GALLa, demonstrating consistent improvement over the baseline, even for powerful models such as LLaMA3.
REPOFUSE: Repository-Level Code Completion with Fused Dual Context
Feb 23, 2024


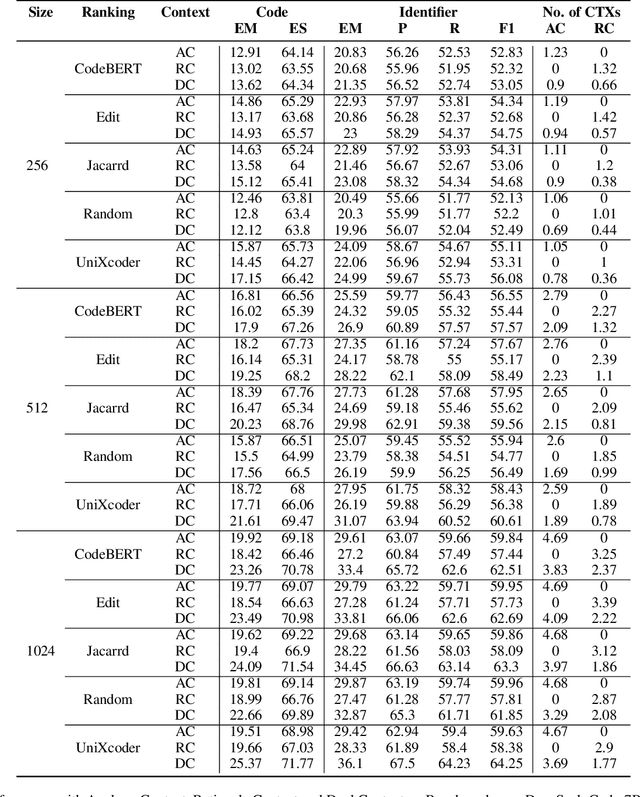
Abstract:The success of language models in code assistance has spurred the proposal of repository-level code completion as a means to enhance prediction accuracy, utilizing the context from the entire codebase. However, this amplified context can inadvertently increase inference latency, potentially undermining the developer experience and deterring tool adoption - a challenge we termed the Context-Latency Conundrum. This paper introduces REPOFUSE, a pioneering solution designed to enhance repository-level code completion without the latency trade-off. REPOFUSE uniquely fuses two types of context: the analogy context, rooted in code analogies, and the rationale context, which encompasses in-depth semantic relationships. We propose a novel rank truncated generation (RTG) technique that efficiently condenses these contexts into prompts with restricted size. This enables REPOFUSE to deliver precise code completions while maintaining inference efficiency. Through testing with the CrossCodeEval suite, REPOFUSE has demonstrated a significant leap over existing models, achieving a 40.90% to 59.75% increase in exact match (EM) accuracy for code completions and a 26.8% enhancement in inference speed. Beyond experimental validation, REPOFUSE has been integrated into the workflow of a large enterprise, where it actively supports various coding tasks.
CodeFuse-13B: A Pretrained Multi-lingual Code Large Language Model
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:Code Large Language Models (Code LLMs) have gained significant attention in the industry due to their wide applications in the full lifecycle of software engineering. However, the effectiveness of existing models in understanding non-English inputs for multi-lingual code-related tasks is still far from well studied. This paper introduces CodeFuse-13B, an open-sourced pre-trained code LLM. It is specifically designed for code-related tasks with both English and Chinese prompts and supports over 40 programming languages. CodeFuse achieves its effectiveness by utilizing a high quality pre-training dataset that is carefully filtered by program analyzers and optimized during the training process. Extensive experiments are conducted using real-world usage scenarios, the industry-standard benchmark HumanEval-x, and the specially designed CodeFuseEval for Chinese prompts. To assess the effectiveness of CodeFuse, we actively collected valuable human feedback from the AntGroup's software development process where CodeFuse has been successfully deployed. The results demonstrate that CodeFuse-13B achieves a HumanEval pass@1 score of 37.10%, positioning it as one of the top multi-lingual code LLMs with similar parameter sizes. In practical scenarios, such as code generation, code translation, code comments, and testcase generation, CodeFuse performs better than other models when confronted with Chinese prompts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge