Xukun Zhu
Code Graph Model (CGM): A Graph-Integrated Large Language Model for Repository-Level Software Engineering Tasks
May 22, 2025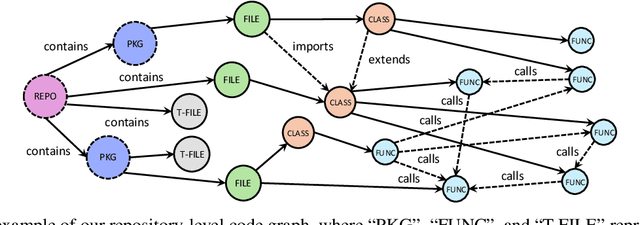
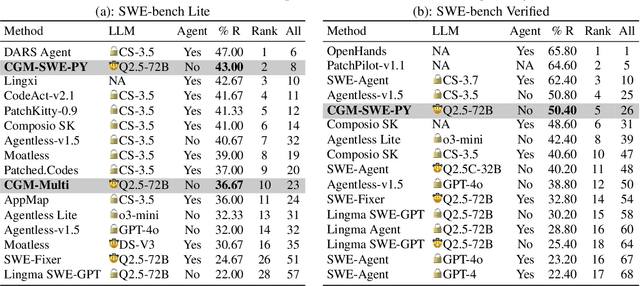
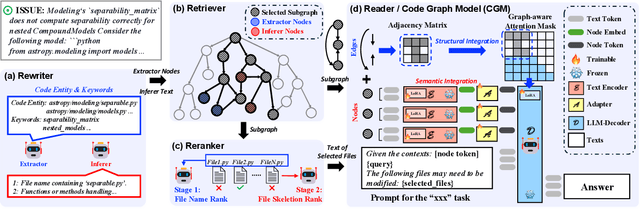
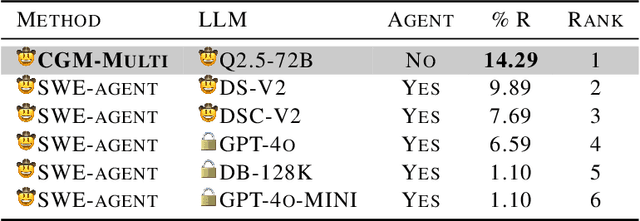
Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in function-level code generation, yet repository-level software engineering tasks remain challenging. Current solutions predominantly rely on proprietary LLM agents, which introduce unpredictability and limit accessibility, raising concerns about data privacy and model customization. This paper investigates whether open-source LLMs can effectively address repository-level tasks without requiring agent-based approaches. We demonstrate this is possible by enabling LLMs to comprehend functions and files within codebases through their semantic information and structural dependencies. To this end, we introduce Code Graph Models (CGMs), which integrate repository code graph structures into the LLM's attention mechanism and map node attributes to the LLM's input space using a specialized adapter. When combined with an agentless graph RAG framework, our approach achieves a 43.00% resolution rate on the SWE-bench Lite benchmark using the open-source Qwen2.5-72B model. This performance ranks first among open weight models, second among methods with open-source systems, and eighth overall, surpassing the previous best open-source model-based method by 12.33%.
VillagerAgent: A Graph-Based Multi-Agent Framework for Coordinating Complex Task Dependencies in Minecraft
Jun 09, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we aim to evaluate multi-agent systems against complex dependencies, including spatial, causal, and temporal constraints. First, we construct a new benchmark, named VillagerBench, within the Minecraft environment.VillagerBench comprises diverse tasks crafted to test various aspects of multi-agent collaboration, from workload distribution to dynamic adaptation and synchronized task execution. Second, we introduce a Directed Acyclic Graph Multi-Agent Framework VillagerAgent to resolve complex inter-agent dependencies and enhance collaborative efficiency. This solution incorporates a task decomposer that creates a directed acyclic graph (DAG) for structured task management, an agent controller for task distribution, and a state manager for tracking environmental and agent data. Our empirical evaluation on VillagerBench demonstrates that VillagerAgent outperforms the existing AgentVerse model, reducing hallucinations and improving task decomposition efficacy. The results underscore VillagerAgent's potential in advancing multi-agent collaboration, offering a scalable and generalizable solution in dynamic environments. The source code is open-source on GitHub (https://github.com/cnsdqd-dyb/VillagerAgent).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge