Mengwei Ren
Controllable Layered Image Generation for Real-World Editing
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Recent image generation models have shown impressive progress, yet they often struggle to yield controllable and consistent results when users attempt to edit specific elements within an existing image. Layered representations enable flexible, user-driven content creation, but existing approaches often fail to produce layers with coherent compositing relationships, and their object layers typically lack realistic visual effects such as shadows and reflections. To overcome these limitations, we propose LASAGNA, a novel, unified framework that generates an image jointly with its composing layers--a photorealistic background and a high-quality transparent foreground with compelling visual effects. Unlike prior work, LASAGNA efficiently learns correct image composition from a wide range of conditioning inputs--text prompts, foreground, background, and location masks--offering greater controllability for real-world applications. To enable this, we introduce LASAGNA-48K, a new dataset composed of clean backgrounds and RGBA foregrounds with physically grounded visual effects. We also propose LASAGNABENCH, the first benchmark for layer editing. We demonstrate that LASAGNA excels in generating highly consistent and coherent results across multiple image layers simultaneously, enabling diverse post-editing applications that accurately preserve identity and visual effects. LASAGNA-48K and LASAGNABENCH will be publicly released to foster open research in the community. The project page is https://rayjryang.github.io/LASAGNA-Page/.
Both Semantics and Reconstruction Matter: Making Representation Encoders Ready for Text-to-Image Generation and Editing
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Modern Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) typically operate in low-level Variational Autoencoder (VAE) latent spaces that are primarily optimized for pixel-level reconstruction. To unify vision generation and understanding, a burgeoning trend is to adopt high-dimensional features from representation encoders as generative latents. However, we empirically identify two fundamental obstacles in this paradigm: (1) the discriminative feature space lacks compact regularization, making diffusion models prone to off-manifold latents that lead to inaccurate object structures; and (2) the encoder's inherently weak pixel-level reconstruction hinders the generator from learning accurate fine-grained geometry and texture. In this paper, we propose a systematic framework to adapt understanding-oriented encoder features for generative tasks. We introduce a semantic-pixel reconstruction objective to regularize the latent space, enabling the compression of both semantic information and fine-grained details into a highly compact representation (96 channels with 16x16 spatial downsampling). This design ensures that the latent space remains semantically rich and achieves state-of-the-art image reconstruction, while remaining compact enough for accurate generation. Leveraging this representation, we design a unified Text-to-Image (T2I) and image editing model. Benchmarking against various feature spaces, we demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction, faster convergence, and substantial performance gains in both T2I and editing tasks, validating that representation encoders can be effectively adapted into robust generative components.
VGent: Visual Grounding via Modular Design for Disentangling Reasoning and Prediction
Dec 11, 2025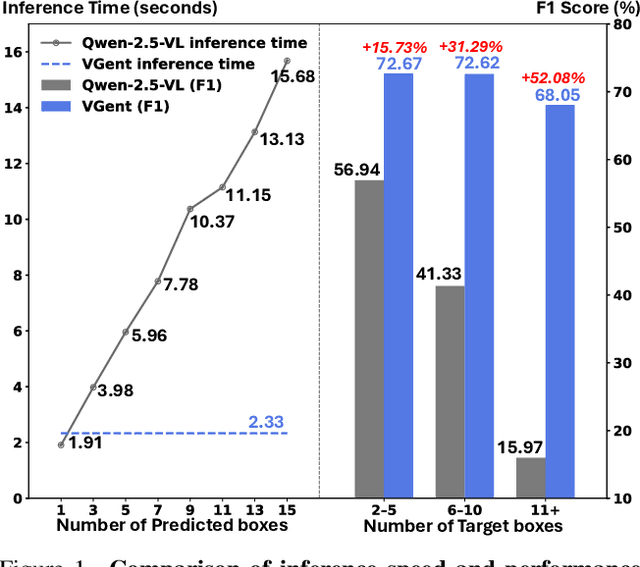
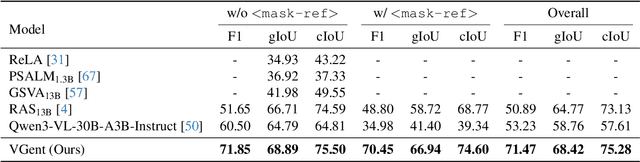
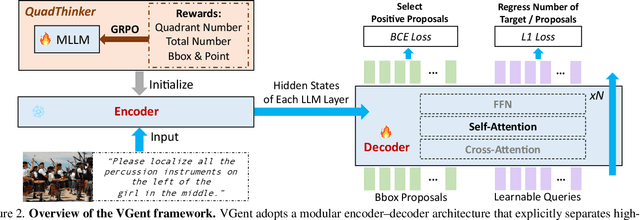
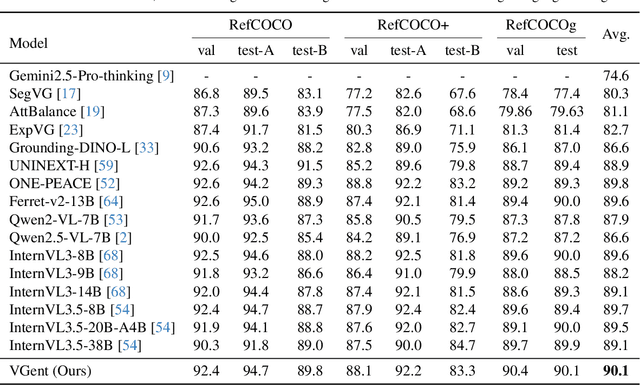
Abstract:Current visual grounding models are either based on a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) that performs auto-regressive decoding, which is slow and risks hallucinations, or on re-aligning an LLM with vision features to learn new special or object tokens for grounding, which may undermine the LLM's pretrained reasoning ability. In contrast, we propose VGent, a modular encoder-decoder architecture that explicitly disentangles high-level reasoning and low-level bounding box prediction. Specifically, a frozen MLLM serves as the encoder to provide untouched powerful reasoning capabilities, while a decoder takes high-quality boxes proposed by detectors as queries and selects target box(es) via cross-attending on encoder's hidden states. This design fully leverages advances in both object detection and MLLM, avoids the pitfalls of auto-regressive decoding, and enables fast inference. Moreover, it supports modular upgrades of both the encoder and decoder to benefit the whole system: we introduce (i) QuadThinker, an RL-based training paradigm for enhancing multi-target reasoning ability of the encoder; (ii) mask-aware label for resolving detection-segmentation ambiguity; and (iii) global target recognition to improve the recognition of all the targets which benefits the selection among augmented proposals. Experiments on multi-target visual grounding benchmarks show that VGent achieves a new state-of-the-art with +20.6% F1 improvement over prior methods, and further boosts gIoU by +8.2% and cIoU by +5.8% under visual reference challenges, while maintaining constant, fast inference latency.
WiCV at CVPR 2025: The Women in Computer Vision Workshop
Nov 11, 2025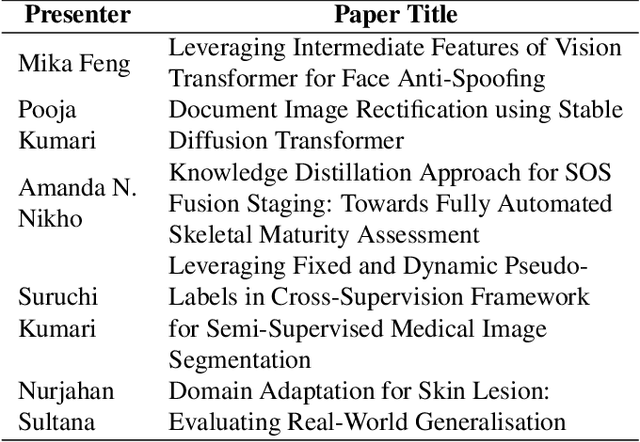
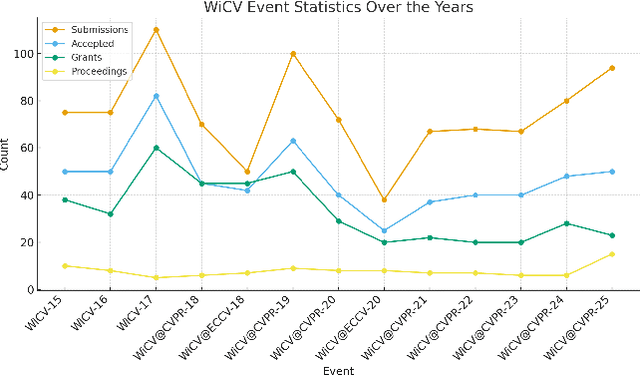
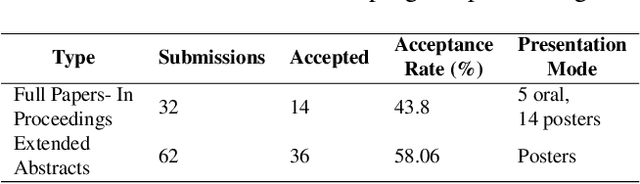

Abstract:The Women in Computer Vision Workshop (WiCV@CVPR 2025) was held in conjunction with the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2025) in Nashville, Tennessee, United States. This report presents an overview of the workshop program, participation statistics, mentorship outcomes, and historical trends from previous WiCV editions. The goal is to document the impact and evolution of WiCV as a reference for future editions and for other initiatives aimed at advancing diversity, equity, and inclusion within the AI and computer vision communities. WiCV@CVPR 2025 marked the 16th edition of this long-standing event dedicated to increasing the visibility, inclusion, and professional growth of women and underrepresented minorities in the computer vision community. This year's workshop featured 14 accepted papers in the CVPR Workshop Proceedings out of 32 full-paper submissions. Five of these were selected for oral presentations, while all 14 were also presented as posters, along with 36 extended abstract posters accepted from 62 short-paper submissions, which are not included in the proceedings. The mentoring program matched 80 mentees with 37 mentors from both academia and industry. The 2025 edition attracted over 100 onsite participants, fostering rich technical and networking interactions across all career stages. Supported by 10 sponsors and approximately $44,000 USD in travel grants and diversity awards, WiCV continued its mission to empower emerging researchers and amplify diverse voices in computer vision.
SynthLight: Portrait Relighting with Diffusion Model by Learning to Re-render Synthetic Faces
Jan 16, 2025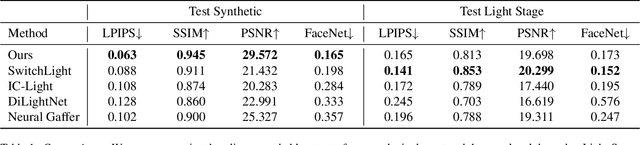

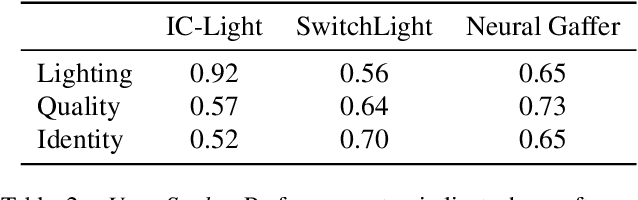
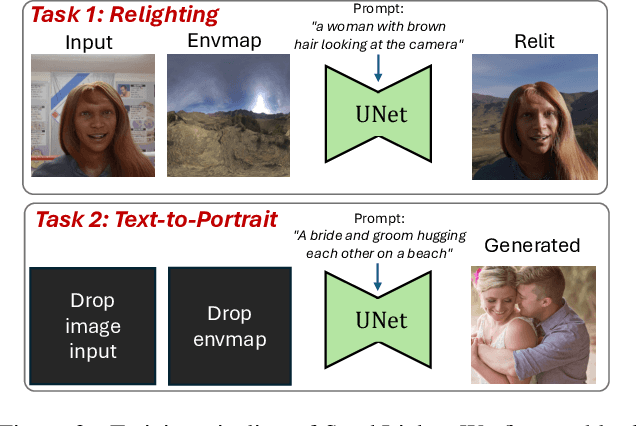
Abstract:We introduce SynthLight, a diffusion model for portrait relighting. Our approach frames image relighting as a re-rendering problem, where pixels are transformed in response to changes in environmental lighting conditions. Using a physically-based rendering engine, we synthesize a dataset to simulate this lighting-conditioned transformation with 3D head assets under varying lighting. We propose two training and inference strategies to bridge the gap between the synthetic and real image domains: (1) multi-task training that takes advantage of real human portraits without lighting labels; (2) an inference time diffusion sampling procedure based on classifier-free guidance that leverages the input portrait to better preserve details. Our method generalizes to diverse real photographs and produces realistic illumination effects, including specular highlights and cast shadows, while preserving the subject's identity. Our quantitative experiments on Light Stage data demonstrate results comparable to state-of-the-art relighting methods. Our qualitative results on in-the-wild images showcase rich and unprecedented illumination effects. Project Page: \url{https://vrroom.github.io/synthlight/}
Text2Relight: Creative Portrait Relighting with Text Guidance
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:We present a lighting-aware image editing pipeline that, given a portrait image and a text prompt, performs single image relighting. Our model modifies the lighting and color of both the foreground and background to align with the provided text description. The unbounded nature in creativeness of a text allows us to describe the lighting of a scene with any sensory features including temperature, emotion, smell, time, and so on. However, the modeling of such mapping between the unbounded text and lighting is extremely challenging due to the lack of dataset where there exists no scalable data that provides large pairs of text and relighting, and therefore, current text-driven image editing models does not generalize to lighting-specific use cases. We overcome this problem by introducing a novel data synthesis pipeline: First, diverse and creative text prompts that describe the scenes with various lighting are automatically generated under a crafted hierarchy using a large language model (*e.g.,* ChatGPT). A text-guided image generation model creates a lighting image that best matches the text. As a condition of the lighting images, we perform image-based relighting for both foreground and background using a single portrait image or a set of OLAT (One-Light-at-A-Time) images captured from lightstage system. Particularly for the background relighting, we represent the lighting image as a set of point lights and transfer them to other background images. A generative diffusion model learns the synthesized large-scale data with auxiliary task augmentation (*e.g.,* portrait delighting and light positioning) to correlate the latent text and lighting distribution for text-guided portrait relighting.
Generative Image Layer Decomposition with Visual Effects
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in large generative models, particularly diffusion-based methods, have significantly enhanced the capabilities of image editing. However, achieving precise control over image composition tasks remains a challenge. Layered representations, which allow for independent editing of image components, are essential for user-driven content creation, yet existing approaches often struggle to decompose image into plausible layers with accurately retained transparent visual effects such as shadows and reflections. We propose $\textbf{LayerDecomp}$, a generative framework for image layer decomposition which outputs photorealistic clean backgrounds and high-quality transparent foregrounds with faithfully preserved visual effects. To enable effective training, we first introduce a dataset preparation pipeline that automatically scales up simulated multi-layer data with synthesized visual effects. To further enhance real-world applicability, we supplement this simulated dataset with camera-captured images containing natural visual effects. Additionally, we propose a consistency loss which enforces the model to learn accurate representations for the transparent foreground layer when ground-truth annotations are not available. Our method achieves superior quality in layer decomposition, outperforming existing approaches in object removal and spatial editing tasks across several benchmarks and multiple user studies, unlocking various creative possibilities for layer-wise image editing. The project page is https://rayjryang.github.io/LayerDecomp.
Baking Gaussian Splatting into Diffusion Denoiser for Fast and Scalable Single-stage Image-to-3D Generation
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:Existing feed-forward image-to-3D methods mainly rely on 2D multi-view diffusion models that cannot guarantee 3D consistency. These methods easily collapse when changing the prompt view direction and mainly handle object-centric prompt images. In this paper, we propose a novel single-stage 3D diffusion model, DiffusionGS, for object and scene generation from a single view. DiffusionGS directly outputs 3D Gaussian point clouds at each timestep to enforce view consistency and allow the model to generate robustly given prompt views of any directions, beyond object-centric inputs. Plus, to improve the capability and generalization ability of DiffusionGS, we scale up 3D training data by developing a scene-object mixed training strategy. Experiments show that our method enjoys better generation quality (2.20 dB higher in PSNR and 23.25 lower in FID) and over 5x faster speed (~6s on an A100 GPU) than SOTA methods. The user study and text-to-3D applications also reveals the practical values of our method. Our Project page at https://caiyuanhao1998.github.io/project/DiffusionGS/ shows the video and interactive generation results.
Learning General-Purpose Biomedical Volume Representations using Randomized Synthesis
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:Current volumetric biomedical foundation models struggle to generalize as public 3D datasets are small and do not cover the broad diversity of medical procedures, conditions, anatomical regions, and imaging protocols. We address this by creating a representation learning method that instead anticipates strong domain shifts at training time itself. We first propose a data engine that synthesizes highly variable training samples that enable generalization to new biomedical contexts. To then train a single 3D network for any voxel-level task, we develop a contrastive learning method that pretrains the network to be stable against nuisance imaging variation simulated by the data engine, a key inductive bias for generalization. This network's features can be used as robust representations of input images for downstream tasks and its weights provide a strong, dataset-agnostic initialization for finetuning on new datasets. As a result, we set new standards across both multimodality registration and few-shot segmentation, a first for any 3D biomedical vision model, all without (pre-)training on any existing dataset of real images.
WiCV@CVPR2024: The Thirteenth Women In Computer Vision Workshop at the Annual CVPR Conference
Nov 03, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present the details of Women in Computer Vision Workshop - WiCV 2024, organized alongside the CVPR 2024 in Seattle, Washington, United States. WiCV aims to amplify the voices of underrepresented women in the computer vision community, fostering increased visibility in both academia and industry. We believe that such events play a vital role in addressing gender imbalances within the field. The annual WiCV@CVPR workshop offers a)~opportunity for collaboration between researchers from minority groups, b) mentorship for female junior researchers, c) financial support to presenters to alleviate financial burdens and d)~a diverse array of role models who can inspire younger researchers at the outset of their careers. In this paper, we present a comprehensive report on the workshop program, historical trends from the past WiCV@CVPR events, and a summary of statistics related to presenters, attendees, and sponsorship for the WiCV 2024 workshop.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge