Yannick Hold-Geoffroy
Adobe Research
GimbalDiffusion: Gravity-Aware Camera Control for Video Generation
Dec 09, 2025



Abstract:Recent progress in text-to-video generation has achieved remarkable realism, yet fine-grained control over camera motion and orientation remains elusive. Existing approaches typically encode camera trajectories through relative or ambiguous representations, limiting explicit geometric control. We introduce GimbalDiffusion, a framework that enables camera control grounded in physical-world coordinates, using gravity as a global reference. Instead of describing motion relative to previous frames, our method defines camera trajectories in an absolute coordinate system, allowing precise and interpretable control over camera parameters without requiring an initial reference frame. We leverage panoramic 360-degree videos to construct a wide variety of camera trajectories, well beyond the predominantly straight, forward-facing trajectories seen in conventional video data. To further enhance camera guidance, we introduce null-pitch conditioning, an annotation strategy that reduces the model's reliance on text content when conflicting with camera specifications (e.g., generating grass while the camera points towards the sky). Finally, we establish a benchmark for camera-aware video generation by rebalancing SpatialVID-HQ for comprehensive evaluation under wide camera pitch variation. Together, these contributions advance the controllability and robustness of text-to-video models, enabling precise, gravity-aligned camera manipulation within generative frameworks.
IntrinsicEdit: Precise generative image manipulation in intrinsic space
May 15, 2025



Abstract:Generative diffusion models have advanced image editing with high-quality results and intuitive interfaces such as prompts and semantic drawing. However, these interfaces lack precise control, and the associated methods typically specialize on a single editing task. We introduce a versatile, generative workflow that operates in an intrinsic-image latent space, enabling semantic, local manipulation with pixel precision for a range of editing operations. Building atop the RGB-X diffusion framework, we address key challenges of identity preservation and intrinsic-channel entanglement. By incorporating exact diffusion inversion and disentangled channel manipulation, we enable precise, efficient editing with automatic resolution of global illumination effects -- all without additional data collection or model fine-tuning. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across a variety of tasks on complex images, including color and texture adjustments, object insertion and removal, global relighting, and their combinations.
GaSLight: Gaussian Splats for Spatially-Varying Lighting in HDR
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:We present GaSLight, a method that generates spatially-varying lighting from regular images. Our method proposes using HDR Gaussian Splats as light source representation, marking the first time regular images can serve as light sources in a 3D renderer. Our two-stage process first enhances the dynamic range of images plausibly and accurately by leveraging the priors embedded in diffusion models. Next, we employ Gaussian Splats to model 3D lighting, achieving spatially variant lighting. Our approach yields state-of-the-art results on HDR estimations and their applications in illuminating virtual objects and scenes. To facilitate the benchmarking of images as light sources, we introduce a novel dataset of calibrated and unsaturated HDR to evaluate images as light sources. We assess our method using a combination of this novel dataset and an existing dataset from the literature. The code to reproduce our method will be available upon acceptance.
WorldPrompter: Traversable Text-to-Scene Generation
Apr 02, 2025



Abstract:Scene-level 3D generation is a challenging research topic, with most existing methods generating only partial scenes and offering limited navigational freedom. We introduce WorldPrompter, a novel generative pipeline for synthesizing traversable 3D scenes from text prompts. We leverage panoramic videos as an intermediate representation to model the 360{\deg} details of a scene. WorldPrompter incorporates a conditional 360{\deg} panoramic video generator, capable of producing a 128-frame video that simulates a person walking through and capturing a virtual environment. The resulting video is then reconstructed as Gaussian splats by a fast feedforward 3D reconstructor, enabling a true walkable experience within the 3D scene. Experiments demonstrate that our panoramic video generation model achieves convincing view consistency across frames, enabling high-quality panoramic Gaussian splat reconstruction and facilitating traversal over an area of the scene. Qualitative and quantitative results also show it outperforms the state-of-the-art 360{\deg} video generators and 3D scene generation models.
MatSwap: Light-aware material transfers in images
Feb 11, 2025
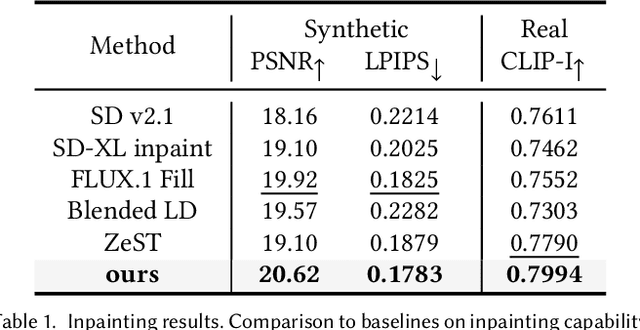
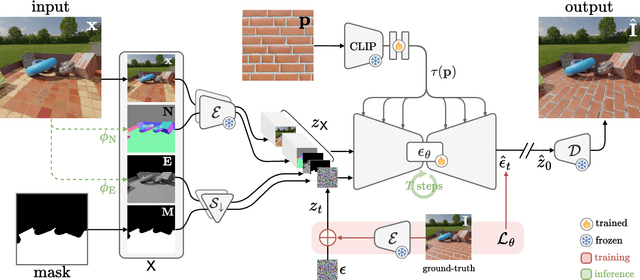
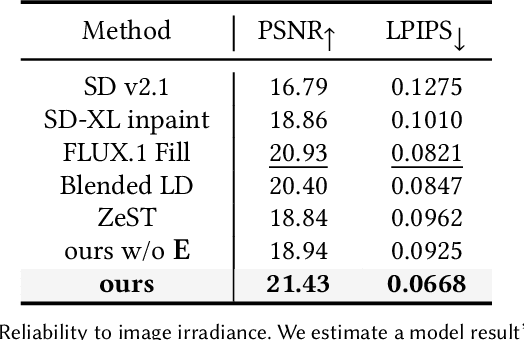
Abstract:We present MatSwap, a method to transfer materials to designated surfaces in an image photorealistically. Such a task is non-trivial due to the large entanglement of material appearance, geometry, and lighting in a photograph. In the literature, material editing methods typically rely on either cumbersome text engineering or extensive manual annotations requiring artist knowledge and 3D scene properties that are impractical to obtain. In contrast, we propose to directly learn the relationship between the input material -- as observed on a flat surface -- and its appearance within the scene, without the need for explicit UV mapping. To achieve this, we rely on a custom light- and geometry-aware diffusion model. We fine-tune a large-scale pre-trained text-to-image model for material transfer using our synthetic dataset, preserving its strong priors to ensure effective generalization to real images. As a result, our method seamlessly integrates a desired material into the target location in the photograph while retaining the identity of the scene. We evaluate our method on synthetic and real images and show that it compares favorably to recent work both qualitatively and quantitatively. We will release our code and data upon publication.
SynthLight: Portrait Relighting with Diffusion Model by Learning to Re-render Synthetic Faces
Jan 16, 2025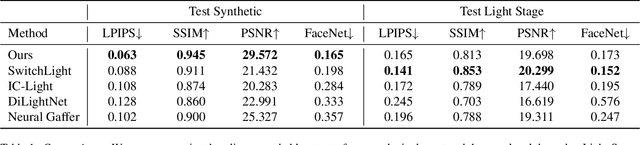

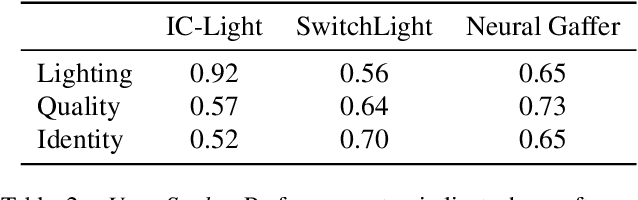
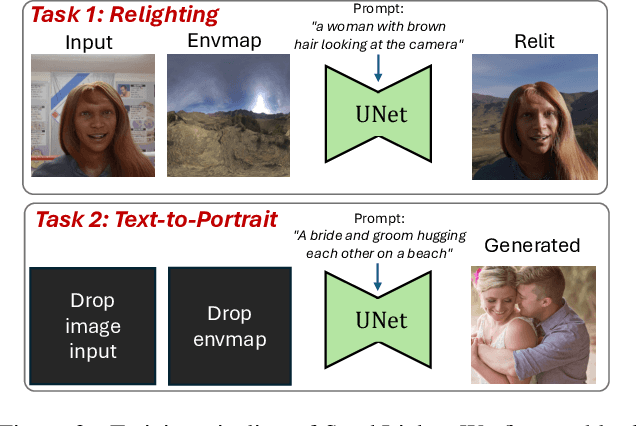
Abstract:We introduce SynthLight, a diffusion model for portrait relighting. Our approach frames image relighting as a re-rendering problem, where pixels are transformed in response to changes in environmental lighting conditions. Using a physically-based rendering engine, we synthesize a dataset to simulate this lighting-conditioned transformation with 3D head assets under varying lighting. We propose two training and inference strategies to bridge the gap between the synthetic and real image domains: (1) multi-task training that takes advantage of real human portraits without lighting labels; (2) an inference time diffusion sampling procedure based on classifier-free guidance that leverages the input portrait to better preserve details. Our method generalizes to diverse real photographs and produces realistic illumination effects, including specular highlights and cast shadows, while preserving the subject's identity. Our quantitative experiments on Light Stage data demonstrate results comparable to state-of-the-art relighting methods. Our qualitative results on in-the-wild images showcase rich and unprecedented illumination effects. Project Page: \url{https://vrroom.github.io/synthlight/}
Text2Relight: Creative Portrait Relighting with Text Guidance
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:We present a lighting-aware image editing pipeline that, given a portrait image and a text prompt, performs single image relighting. Our model modifies the lighting and color of both the foreground and background to align with the provided text description. The unbounded nature in creativeness of a text allows us to describe the lighting of a scene with any sensory features including temperature, emotion, smell, time, and so on. However, the modeling of such mapping between the unbounded text and lighting is extremely challenging due to the lack of dataset where there exists no scalable data that provides large pairs of text and relighting, and therefore, current text-driven image editing models does not generalize to lighting-specific use cases. We overcome this problem by introducing a novel data synthesis pipeline: First, diverse and creative text prompts that describe the scenes with various lighting are automatically generated under a crafted hierarchy using a large language model (*e.g.,* ChatGPT). A text-guided image generation model creates a lighting image that best matches the text. As a condition of the lighting images, we perform image-based relighting for both foreground and background using a single portrait image or a set of OLAT (One-Light-at-A-Time) images captured from lightstage system. Particularly for the background relighting, we represent the lighting image as a set of point lights and transfer them to other background images. A generative diffusion model learns the synthesized large-scale data with auxiliary task augmentation (*e.g.,* portrait delighting and light positioning) to correlate the latent text and lighting distribution for text-guided portrait relighting.
Motion Modes: What Could Happen Next?
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:Predicting diverse object motions from a single static image remains challenging, as current video generation models often entangle object movement with camera motion and other scene changes. While recent methods can predict specific motions from motion arrow input, they rely on synthetic data and predefined motions, limiting their application to complex scenes. We introduce Motion Modes, a training-free approach that explores a pre-trained image-to-video generator's latent distribution to discover various distinct and plausible motions focused on selected objects in static images. We achieve this by employing a flow generator guided by energy functions designed to disentangle object and camera motion. Additionally, we use an energy inspired by particle guidance to diversify the generated motions, without requiring explicit training data. Experimental results demonstrate that Motion Modes generates realistic and varied object animations, surpassing previous methods and even human predictions regarding plausibility and diversity. Project Webpage: https://motionmodes.github.io/
Generative Portrait Shadow Removal
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:We introduce a high-fidelity portrait shadow removal model that can effectively enhance the image of a portrait by predicting its appearance under disturbing shadows and highlights. Portrait shadow removal is a highly ill-posed problem where multiple plausible solutions can be found based on a single image. While existing works have solved this problem by predicting the appearance residuals that can propagate local shadow distribution, such methods are often incomplete and lead to unnatural predictions, especially for portraits with hard shadows. We overcome the limitations of existing local propagation methods by formulating the removal problem as a generation task where a diffusion model learns to globally rebuild the human appearance from scratch as a condition of an input portrait image. For robust and natural shadow removal, we propose to train the diffusion model with a compositional repurposing framework: a pre-trained text-guided image generation model is first fine-tuned to harmonize the lighting and color of the foreground with a background scene by using a background harmonization dataset; and then the model is further fine-tuned to generate a shadow-free portrait image via a shadow-paired dataset. To overcome the limitation of losing fine details in the latent diffusion model, we propose a guided-upsampling network to restore the original high-frequency details (wrinkles and dots) from the input image. To enable our compositional training framework, we construct a high-fidelity and large-scale dataset using a lightstage capturing system and synthetic graphics simulation. Our generative framework effectively removes shadows caused by both self and external occlusions while maintaining original lighting distribution and high-frequency details. Our method also demonstrates robustness to diverse subjects captured in real environments.
COMPOSE: Comprehensive Portrait Shadow Editing
Aug 25, 2024



Abstract:Existing portrait relighting methods struggle with precise control over facial shadows, particularly when faced with challenges such as handling hard shadows from directional light sources or adjusting shadows while remaining in harmony with existing lighting conditions. In many situations, completely altering input lighting is undesirable for portrait retouching applications: one may want to preserve some authenticity in the captured environment. Existing shadow editing methods typically restrict their application to just the facial region and often offer limited lighting control options, such as shadow softening or rotation. In this paper, we introduce COMPOSE: a novel shadow editing pipeline for human portraits, offering precise control over shadow attributes such as shape, intensity, and position, all while preserving the original environmental illumination of the portrait. This level of disentanglement and controllability is obtained thanks to a novel decomposition of the environment map representation into ambient light and an editable gaussian dominant light source. COMPOSE is a four-stage pipeline that consists of light estimation and editing, light diffusion, shadow synthesis, and finally shadow editing. We define facial shadows as the result of a dominant light source, encoded using our novel gaussian environment map representation. Utilizing an OLAT dataset, we have trained models to: (1) predict this light source representation from images, and (2) generate realistic shadows using this representation. We also demonstrate comprehensive and intuitive shadow editing with our pipeline. Through extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations, we have demonstrated the robust capability of our system in shadow editing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge