Jean-François Lalonde
End-to-End LiDAR optimization for 3D point cloud registration
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:LiDAR sensors are a key modality for 3D perception, yet they are typically designed independently of downstream tasks such as point cloud registration. Conventional registration operates on pre-acquired datasets with fixed LiDAR configurations, leading to suboptimal data collection and significant computational overhead for sampling, noise filtering, and parameter tuning. In this work, we propose an adaptive LiDAR sensing framework that dynamically adjusts sensor parameters, jointly optimizing LiDAR acquisition and registration hyperparameters. By integrating registration feedback into the sensing loop, our approach optimally balances point density, noise, and sparsity, improving registration accuracy and efficiency. Evaluations in the CARLA simulation demonstrate that our method outperforms fixed-parameter baselines while retaining generalization abilities, highlighting the potential of adaptive LiDAR for autonomous perception and robotic applications.
SyncLight: Controllable and Consistent Multi-View Relighting
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:We present SyncLight, the first method to enable consistent, parametric relighting across multiple uncalibrated views of a static scene. While single-view relighting has advanced significantly, existing generative approaches struggle to maintain the rigorous lighting consistency essential for multi-camera broadcasts, stereoscopic cinema, and virtual production. SyncLight addresses this by enabling precise control over light intensity and color across a multi-view capture of a scene, conditioned on a single reference edit. Our method leverages a multi-view diffusion transformer trained using a latent bridge matching formulation, achieving high-fidelity relighting of the entire image set in a single inference step. To facilitate training, we introduce a large-scale hybrid dataset comprising diverse synthetic environments -- curated from existing sources and newly designed scenes -- alongside high-fidelity, real-world multi-view captures under calibrated illumination. Surprisingly, though trained only on image pairs, SyncLight generalizes zero-shot to an arbitrary number of viewpoints, effectively propagating lighting changes across all views, without requiring camera pose information. SyncLight enables practical relighting workflows for multi-view capture systems.
Lighting in Motion: Spatiotemporal HDR Lighting Estimation
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:We present Lighting in Motion (LiMo), a diffusion-based approach to spatiotemporal lighting estimation. LiMo targets both realistic high-frequency detail prediction and accurate illuminance estimation. To account for both, we propose generating a set of mirrored and diffuse spheres at different exposures, based on their 3D positions in the input. Making use of diffusion priors, we fine-tune powerful existing diffusion models on a large-scale customized dataset of indoor and outdoor scenes, paired with spatiotemporal light probes. For accurate spatial conditioning, we demonstrate that depth alone is insufficient and we introduce a new geometric condition to provide the relative position of the scene to the target 3D position. Finally, we combine diffuse and mirror predictions at different exposures into a single HDRI map leveraging differentiable rendering. We thoroughly evaluate our method and design choices to establish LiMo as state-of-the-art for both spatial control and prediction accuracy.
GimbalDiffusion: Gravity-Aware Camera Control for Video Generation
Dec 09, 2025



Abstract:Recent progress in text-to-video generation has achieved remarkable realism, yet fine-grained control over camera motion and orientation remains elusive. Existing approaches typically encode camera trajectories through relative or ambiguous representations, limiting explicit geometric control. We introduce GimbalDiffusion, a framework that enables camera control grounded in physical-world coordinates, using gravity as a global reference. Instead of describing motion relative to previous frames, our method defines camera trajectories in an absolute coordinate system, allowing precise and interpretable control over camera parameters without requiring an initial reference frame. We leverage panoramic 360-degree videos to construct a wide variety of camera trajectories, well beyond the predominantly straight, forward-facing trajectories seen in conventional video data. To further enhance camera guidance, we introduce null-pitch conditioning, an annotation strategy that reduces the model's reliance on text content when conflicting with camera specifications (e.g., generating grass while the camera points towards the sky). Finally, we establish a benchmark for camera-aware video generation by rebalancing SpatialVID-HQ for comprehensive evaluation under wide camera pitch variation. Together, these contributions advance the controllability and robustness of text-to-video models, enabling precise, gravity-aligned camera manipulation within generative frameworks.
GaSLight: Gaussian Splats for Spatially-Varying Lighting in HDR
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:We present GaSLight, a method that generates spatially-varying lighting from regular images. Our method proposes using HDR Gaussian Splats as light source representation, marking the first time regular images can serve as light sources in a 3D renderer. Our two-stage process first enhances the dynamic range of images plausibly and accurately by leveraging the priors embedded in diffusion models. Next, we employ Gaussian Splats to model 3D lighting, achieving spatially variant lighting. Our approach yields state-of-the-art results on HDR estimations and their applications in illuminating virtual objects and scenes. To facilitate the benchmarking of images as light sources, we introduce a novel dataset of calibrated and unsaturated HDR to evaluate images as light sources. We assess our method using a combination of this novel dataset and an existing dataset from the literature. The code to reproduce our method will be available upon acceptance.
SpotLight: Shadow-Guided Object Relighting via Diffusion
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:Recent work has shown that diffusion models can be used as powerful neural rendering engines that can be leveraged for inserting virtual objects into images. Unlike typical physics-based renderers, however, neural rendering engines are limited by the lack of manual control over the lighting setup, which is often essential for improving or personalizing the desired image outcome. In this paper, we show that precise lighting control can be achieved for object relighting simply by specifying the desired shadows of the object. Rather surprisingly, we show that injecting only the shadow of the object into a pre-trained diffusion-based neural renderer enables it to accurately shade the object according to the desired light position, while properly harmonizing the object (and its shadow) within the target background image. Our method, SpotLight, leverages existing neural rendering approaches and achieves controllable relighting results with no additional training. Specifically, we demonstrate its use with two neural renderers from the recent literature. We show that SpotLight achieves superior object compositing results, both quantitatively and perceptually, as confirmed by a user study, outperforming existing diffusion-based models specifically designed for relighting.
Material Transforms from Disentangled NeRF Representations
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we first propose a novel method for transferring material transformations across different scenes. Building on disentangled Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) representations, our approach learns to map Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Functions (BRDF) from pairs of scenes observed in varying conditions, such as dry and wet. The learned transformations can then be applied to unseen scenes with similar materials, therefore effectively rendering the transformation learned with an arbitrary level of intensity. Extensive experiments on synthetic scenes and real-world objects validate the effectiveness of our approach, showing that it can learn various transformations such as wetness, painting, coating, etc. Our results highlight not only the versatility of our method but also its potential for practical applications in computer graphics. We publish our method implementation, along with our synthetic/real datasets on https://github.com/astra-vision/BRDFTransform
ZeroComp: Zero-shot Object Compositing from Image Intrinsics via Diffusion
Oct 10, 2024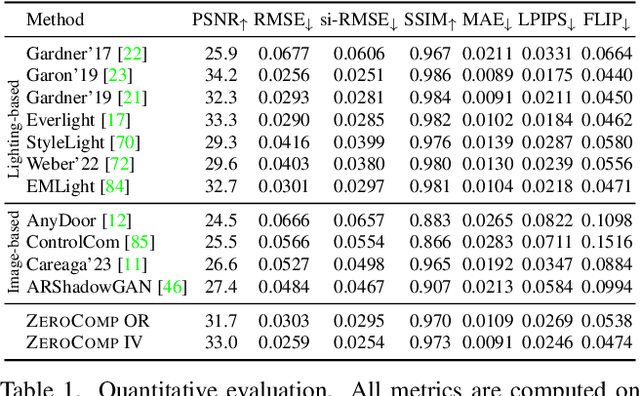
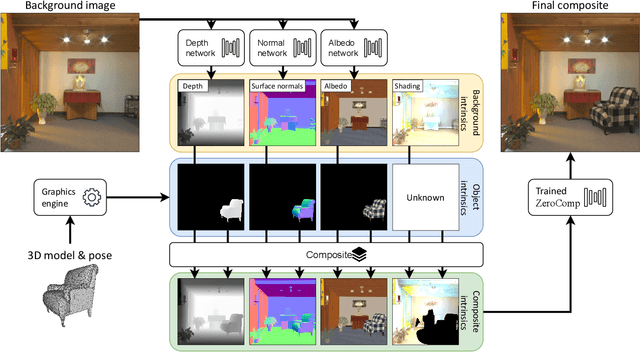
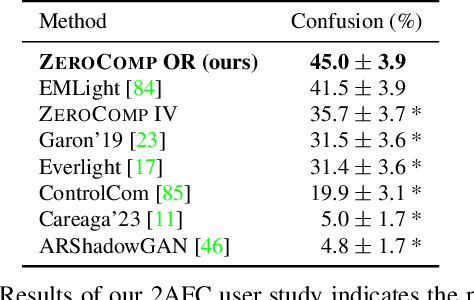
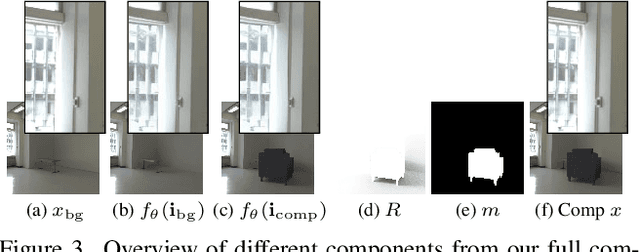
Abstract:We present ZeroComp, an effective zero-shot 3D object compositing approach that does not require paired composite-scene images during training. Our method leverages ControlNet to condition from intrinsic images and combines it with a Stable Diffusion model to utilize its scene priors, together operating as an effective rendering engine. During training, ZeroComp uses intrinsic images based on geometry, albedo, and masked shading, all without the need for paired images of scenes with and without composite objects. Once trained, it seamlessly integrates virtual 3D objects into scenes, adjusting shading to create realistic composites. We developed a high-quality evaluation dataset and demonstrate that ZeroComp outperforms methods using explicit lighting estimations and generative techniques in quantitative and human perception benchmarks. Additionally, ZeroComp extends to real and outdoor image compositing, even when trained solely on synthetic indoor data, showcasing its effectiveness in image compositing.
DarSwin-Unet: Distortion Aware Encoder-Decoder Architecture
Jul 24, 2024



Abstract:Wide-angle fisheye images are becoming increasingly common for perception tasks in applications such as robotics, security, and mobility (e.g. drones, avionics). However, current models often either ignore the distortions in wide-angle images or are not suitable to perform pixel-level tasks. In this paper, we present an encoder-decoder model based on a radial transformer architecture that adapts to distortions in wide-angle lenses by leveraging the physical characteristics defined by the radial distortion profile. In contrast to the original model, which only performs classification tasks, we introduce a U-Net architecture, DarSwin-Unet, designed for pixel level tasks. Furthermore, we propose a novel strategy that minimizes sparsity when sampling the image for creating its input tokens. Our approach enhances the model capability to handle pixel-level tasks in wide-angle fisheye images, making it more effective for real-world applications. Compared to other baselines, DarSwin-Unet achieves the best results across different datasets, with significant gains when trained on bounded levels of distortions (very low, low, medium, and high) and tested on all, including out-of-distribution distortions. We demonstrate its performance on depth estimation and show through extensive experiments that DarSwin-Unet can perform zero-shot adaptation to unseen distortions of different wide-angle lenses.
PanDORA: Casual HDR Radiance Acquisition for Indoor Scenes
Jul 08, 2024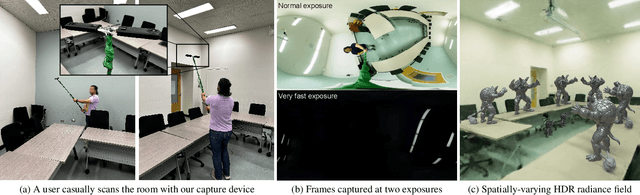
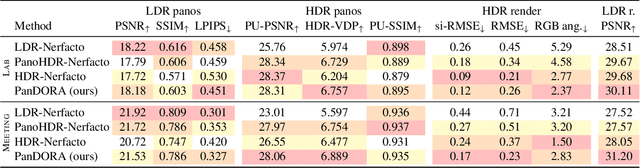
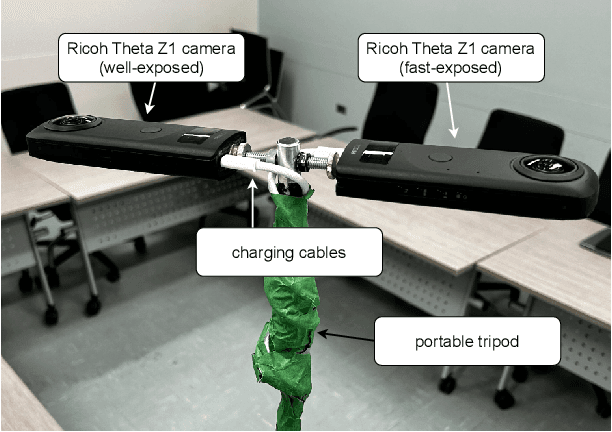
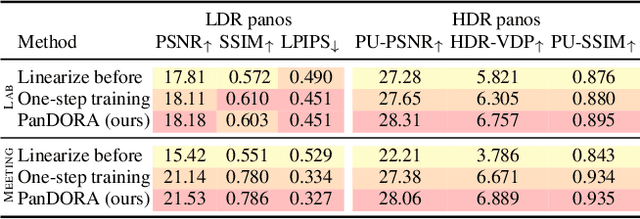
Abstract:Most novel view synthesis methods such as NeRF are unable to capture the true high dynamic range (HDR) radiance of scenes since they are typically trained on photos captured with standard low dynamic range (LDR) cameras. While the traditional exposure bracketing approach which captures several images at different exposures has recently been adapted to the multi-view case, we find such methods to fall short of capturing the full dynamic range of indoor scenes, which includes very bright light sources. In this paper, we present PanDORA: a PANoramic Dual-Observer Radiance Acquisition system for the casual capture of indoor scenes in high dynamic range. Our proposed system comprises two 360{\deg} cameras rigidly attached to a portable tripod. The cameras simultaneously acquire two 360{\deg} videos: one at a regular exposure and the other at a very fast exposure, allowing a user to simply wave the apparatus casually around the scene in a matter of minutes. The resulting images are fed to a NeRF-based algorithm that reconstructs the scene's full high dynamic range. Compared to HDR baselines from previous work, our approach reconstructs the full HDR radiance of indoor scenes without sacrificing the visual quality while retaining the ease of capture from recent NeRF-like approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge