Mohamed Abid
Domain Agnostic Image-to-image Translation using Low-Resolution Conditioning
May 11, 2023Abstract:Generally, image-to-image translation (i2i) methods aim at learning mappings across domains with the assumption that the images used for translation share content (e.g., pose) but have their own domain-specific information (a.k.a. style). Conditioned on a target image, such methods extract the target style and combine it with the source image content, keeping coherence between the domains. In our proposal, we depart from this traditional view and instead consider the scenario where the target domain is represented by a very low-resolution (LR) image, proposing a domain-agnostic i2i method for fine-grained problems, where the domains are related. More specifically, our domain-agnostic approach aims at generating an image that combines visual features from the source image with low-frequency information (e.g. pose, color) of the LR target image. To do so, we present a novel approach that relies on training the generative model to produce images that both share distinctive information of the associated source image and correctly match the LR target image when downscaled. We validate our method on the CelebA-HQ and AFHQ datasets by demonstrating improvements in terms of visual quality. Qualitative and quantitative results show that when dealing with intra-domain image translation, our method generates realistic samples compared to state-of-the-art methods such as StarGAN v2. Ablation studies also reveal that our method is robust to changes in color, it can be applied to out-of-distribution images, and it allows for manual control over the final results.
Defensive Approximation: Enhancing CNNs Security through Approximate Computing
Jun 13, 2020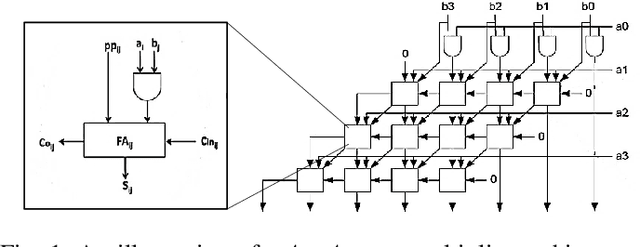
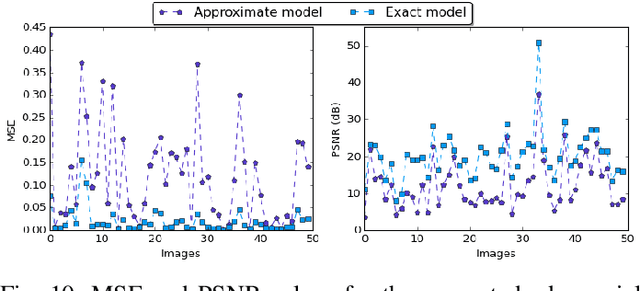
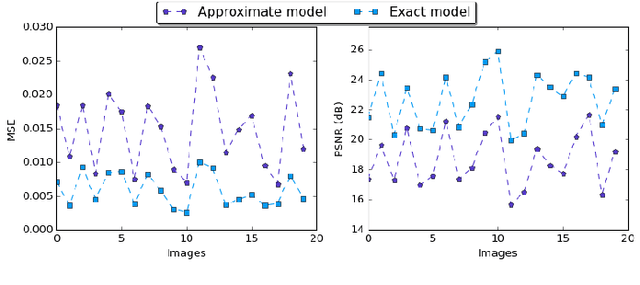
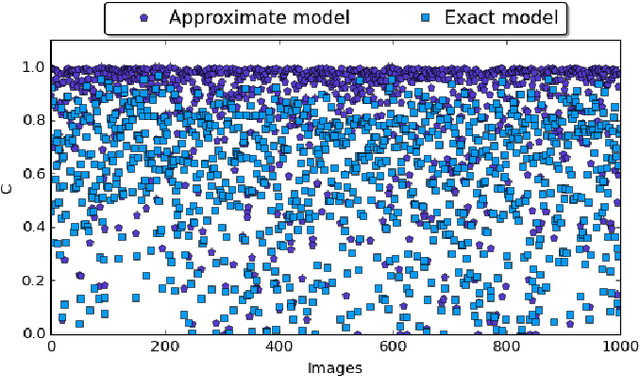
Abstract:In the past few years, an increasing number of machine-learning and deep learning structures, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), have been applied to solving a wide range of real-life problems. However, these architectures are vulnerable to adversarial attacks. In this paper, we propose for the first time to use hardware-supported approximate computing to improve the robustness of machine learning classifiers. We show that our approximate computing implementation achieves robustness across a wide range of attack scenarios. Specifically, for black-box and grey-box attack scenarios, we show that successful adversarial attacks against the exact classifier have poor transferability to the approximate implementation. Surprisingly, the robustness advantages also apply to white-box attacks where the attacker has access to the internal implementation of the approximate classifier. We explain some of the possible reasons for this robustness through analysis of the internal operation of the approximate implementation. Furthermore, our approximate computing model maintains the same level in terms of classification accuracy, does not require retraining, and reduces resource utilization and energy consumption of the CNN. We conducted extensive experiments on a set of strong adversarial attacks; We empirically show that the proposed implementation increases the robustness of a LeNet-5 and an Alexnet CNNs by up to 99% and 87%, respectively for strong grey-box adversarial attacks along with up to 67% saving in energy consumption due to the simpler nature of the approximate logic. We also show that a white-box attack requires a remarkably higher noise budget to fool the approximate classifier, causing an average of 4db degradation of the PSNR of the input image relative to the images that succeed in fooling the exact classifier
Automatic Application Level Set Approach in Detection Calcifications in Mammographic Image
Sep 01, 2011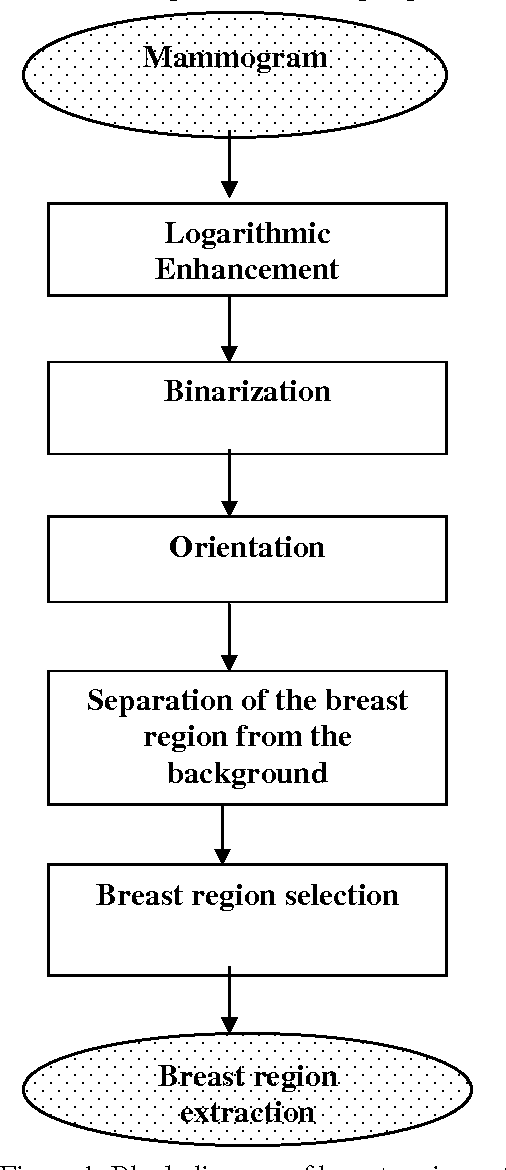
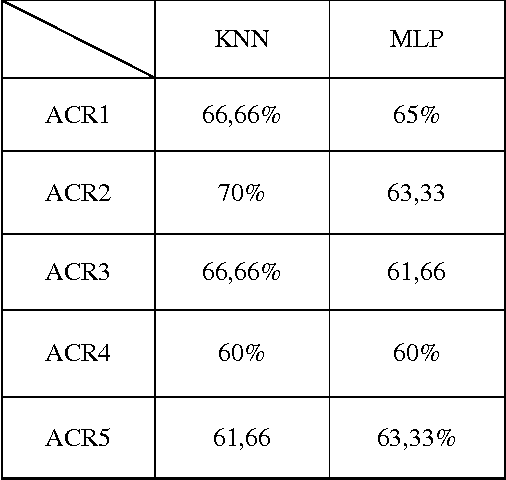
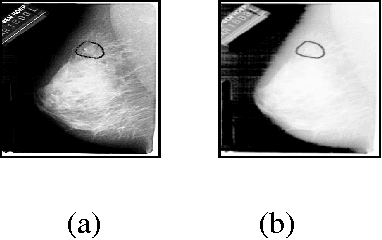
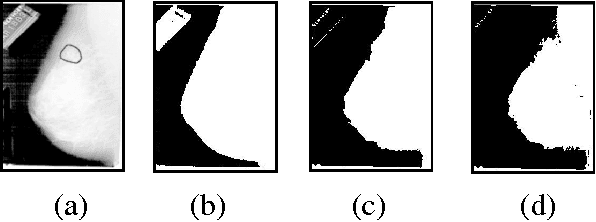
Abstract:Breast cancer is considered as one of a major health problem that constitutes the strongest cause behind mortality among women in the world. So, in this decade, breast cancer is the second most common type of cancer, in term of appearance frequency, and the fifth most common cause of cancer related death. In order to reduce the workload on radiologists, a variety of CAD systems; Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CADi) and Computer-Aided Detection (CADe) have been proposed. In this paper, we interested on CADe tool to help radiologist to detect cancer. The proposed CADe is based on a three-step work flow; namely, detection, analysis and classification. This paper deals with the problem of automatic detection of Region Of Interest (ROI) based on Level Set approach depended on edge and region criteria. This approach gives good visual information from the radiologist. After that, the features extraction using textures characteristics and the vector classification using Multilayer Perception (MLP) and k-Nearest Neighbours (KNN) are adopted to distinguish different ACR (American College of Radiology) classification. Moreover, we use the Digital Database for Screening Mammography (DDSM) for experiments and these results in term of accuracy varied between 60 % and 70% are acceptable and must be ameliorated to aid radiologist.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge