Deblina Bhattacharjee
WiCV at CVPR 2025: The Women in Computer Vision Workshop
Nov 11, 2025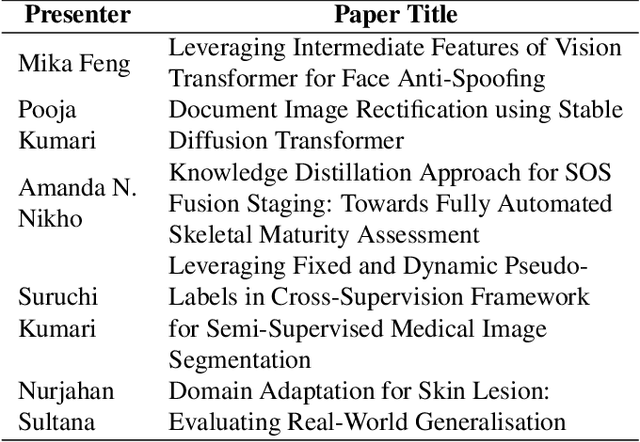
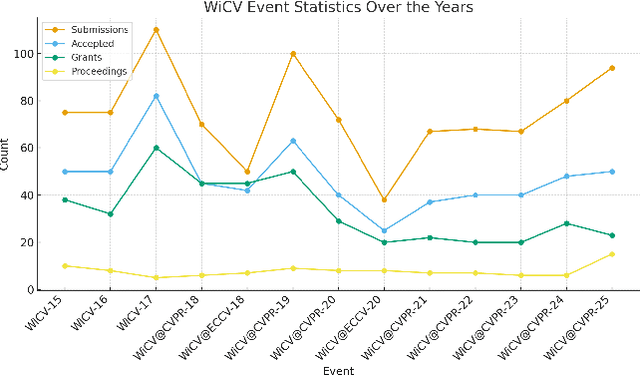
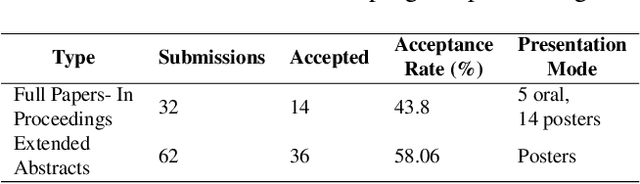

Abstract:The Women in Computer Vision Workshop (WiCV@CVPR 2025) was held in conjunction with the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2025) in Nashville, Tennessee, United States. This report presents an overview of the workshop program, participation statistics, mentorship outcomes, and historical trends from previous WiCV editions. The goal is to document the impact and evolution of WiCV as a reference for future editions and for other initiatives aimed at advancing diversity, equity, and inclusion within the AI and computer vision communities. WiCV@CVPR 2025 marked the 16th edition of this long-standing event dedicated to increasing the visibility, inclusion, and professional growth of women and underrepresented minorities in the computer vision community. This year's workshop featured 14 accepted papers in the CVPR Workshop Proceedings out of 32 full-paper submissions. Five of these were selected for oral presentations, while all 14 were also presented as posters, along with 36 extended abstract posters accepted from 62 short-paper submissions, which are not included in the proceedings. The mentoring program matched 80 mentees with 37 mentors from both academia and industry. The 2025 edition attracted over 100 onsite participants, fostering rich technical and networking interactions across all career stages. Supported by 10 sponsors and approximately $44,000 USD in travel grants and diversity awards, WiCV continued its mission to empower emerging researchers and amplify diverse voices in computer vision.
WiCV@CVPR2024: The Thirteenth Women In Computer Vision Workshop at the Annual CVPR Conference
Nov 03, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present the details of Women in Computer Vision Workshop - WiCV 2024, organized alongside the CVPR 2024 in Seattle, Washington, United States. WiCV aims to amplify the voices of underrepresented women in the computer vision community, fostering increased visibility in both academia and industry. We believe that such events play a vital role in addressing gender imbalances within the field. The annual WiCV@CVPR workshop offers a)~opportunity for collaboration between researchers from minority groups, b) mentorship for female junior researchers, c) financial support to presenters to alleviate financial burdens and d)~a diverse array of role models who can inspire younger researchers at the outset of their careers. In this paper, we present a comprehensive report on the workshop program, historical trends from the past WiCV@CVPR events, and a summary of statistics related to presenters, attendees, and sponsorship for the WiCV 2024 workshop.
Unlocking Comics: The AI4VA Dataset for Visual Understanding
Oct 27, 2024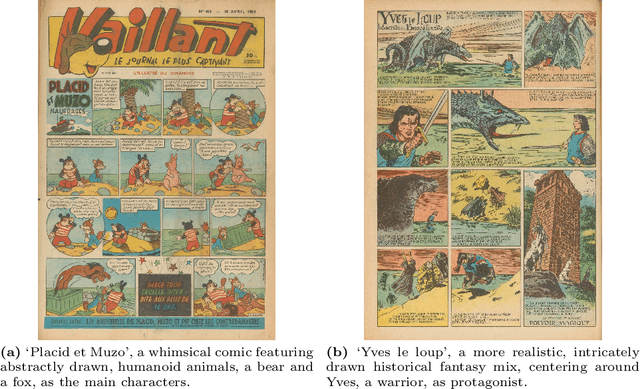


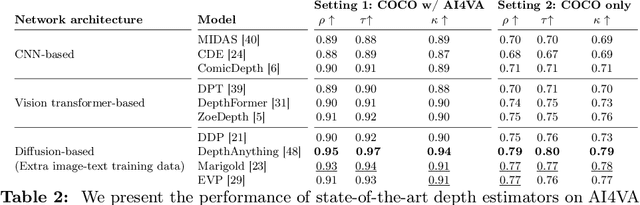
Abstract:In the evolving landscape of deep learning, there is a pressing need for more comprehensive datasets capable of training models across multiple modalities. Concurrently, in digital humanities, there is a growing demand to leverage technology for diverse media adaptation and creation, yet limited by sparse datasets due to copyright and stylistic constraints. Addressing this gap, our paper presents a novel dataset comprising Franco-Belgian comics from the 1950s annotated for tasks including depth estimation, semantic segmentation, saliency detection, and character identification. It consists of two distinct and consistent styles and incorporates object concepts and labels taken from natural images. By including such diverse information across styles, this dataset not only holds promise for computational creativity but also offers avenues for the digitization of art and storytelling innovation. This dataset is a crucial component of the AI4VA Workshop Challenges~\url{https://sites.google.com/view/ai4vaeccv2024}, where we specifically explore depth and saliency. Dataset details at \url{https://github.com/IVRL/AI4VA}.
Data Augmentation via Latent Diffusion for Saliency Prediction
Sep 11, 2024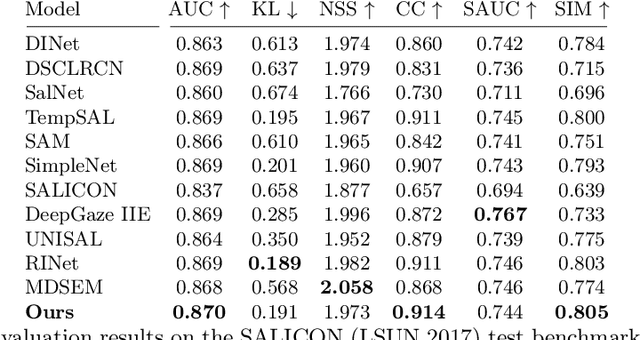
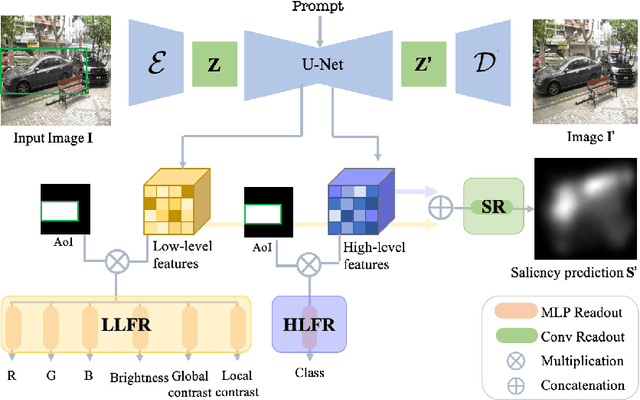
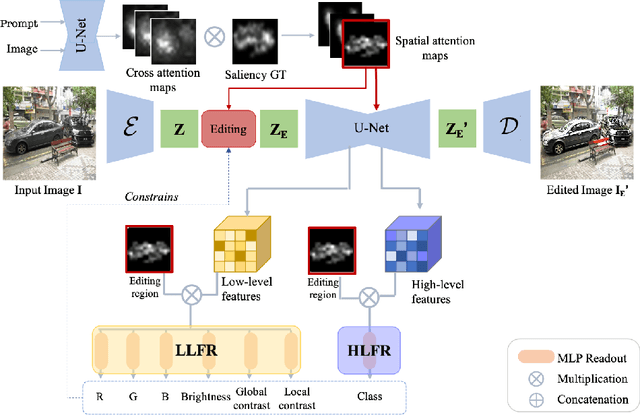

Abstract:Saliency prediction models are constrained by the limited diversity and quantity of labeled data. Standard data augmentation techniques such as rotating and cropping alter scene composition, affecting saliency. We propose a novel data augmentation method for deep saliency prediction that edits natural images while preserving the complexity and variability of real-world scenes. Since saliency depends on high-level and low-level features, our approach involves learning both by incorporating photometric and semantic attributes such as color, contrast, brightness, and class. To that end, we introduce a saliency-guided cross-attention mechanism that enables targeted edits on the photometric properties, thereby enhancing saliency within specific image regions. Experimental results show that our data augmentation method consistently improves the performance of various saliency models. Moreover, leveraging the augmentation features for saliency prediction yields superior performance on publicly available saliency benchmarks. Our predictions align closely with human visual attention patterns in the edited images, as validated by a user study.
CoDA: Instructive Chain-of-Domain Adaptation with Severity-Aware Visual Prompt Tuning
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) aims to adapt models from labeled source domains to unlabeled target domains. When adapting to adverse scenes, existing UDA methods fail to perform well due to the lack of instructions, leading their models to overlook discrepancies within all adverse scenes. To tackle this, we propose CoDA which instructs models to distinguish, focus, and learn from these discrepancies at scene and image levels. Specifically, CoDA consists of a Chain-of-Domain (CoD) strategy and a Severity-Aware Visual Prompt Tuning (SAVPT) mechanism. CoD focuses on scene-level instructions to divide all adverse scenes into easy and hard scenes, guiding models to adapt from source to easy domains with easy scene images, and then to hard domains with hard scene images, thereby laying a solid foundation for whole adaptations. Building upon this foundation, we employ SAVPT to dive into more detailed image-level instructions to boost performance. SAVPT features a novel metric Severity that divides all adverse scene images into low-severity and high-severity images. Then Severity directs visual prompts and adapters, instructing models to concentrate on unified severity features instead of scene-specific features, without adding complexity to the model architecture. CoDA achieves SOTA performances on widely-used benchmarks under all adverse scenes. Notably, CoDA outperforms the existing ones by 4.6%, and 10.3% mIoU on the Foggy Driving, and Foggy Zurich benchmarks, respectively. Our code is available at https://github.com/Cuzyoung/CoDA
OMH: Structured Sparsity via Optimally Matched Hierarchy for Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation
Mar 11, 2024



Abstract:Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation (USS) involves segmenting images without relying on predefined labels, aiming to alleviate the burden of extensive human labeling. Existing methods utilize features generated by self-supervised models and specific priors for clustering. However, their clustering objectives are not involved in the optimization of the features during training. Additionally, due to the lack of clear class definitions in USS, the resulting segments may not align well with the clustering objective. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Optimally Matched Hierarchy (OMH) to simultaneously address the above issues. The core of our method lies in imposing structured sparsity on the feature space, which allows the features to encode information with different levels of granularity. The structure of this sparsity stems from our hierarchy (OMH). To achieve this, we learn a soft but sparse hierarchy among parallel clusters through Optimal Transport. Our OMH yields better unsupervised segmentation performance compared to existing USS methods. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the benefits of OMH when utilizing our differentiable paradigm. We will make our code publicly available.
Vision Transformer Adapters for Generalizable Multitask Learning
Aug 23, 2023Abstract:We introduce the first multitasking vision transformer adapters that learn generalizable task affinities which can be applied to novel tasks and domains. Integrated into an off-the-shelf vision transformer backbone, our adapters can simultaneously solve multiple dense vision tasks in a parameter-efficient manner, unlike existing multitasking transformers that are parametrically expensive. In contrast to concurrent methods, we do not require retraining or fine-tuning whenever a new task or domain is added. We introduce a task-adapted attention mechanism within our adapter framework that combines gradient-based task similarities with attention-based ones. The learned task affinities generalize to the following settings: zero-shot task transfer, unsupervised domain adaptation, and generalization without fine-tuning to novel domains. We demonstrate that our approach outperforms not only the existing convolutional neural network-based multitasking methods but also the vision transformer-based ones. Our project page is at \url{https://ivrl.github.io/VTAGML}.
Dense Multitask Learning to Reconfigure Comics
Jul 16, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we develop a MultiTask Learning (MTL) model to achieve dense predictions for comics panels to, in turn, facilitate the transfer of comics from one publication channel to another by assisting authors in the task of reconfiguring their narratives. Our MTL method can successfully identify the semantic units as well as the embedded notion of 3D in comic panels. This is a significantly challenging problem because comics comprise disparate artistic styles, illustrations, layouts, and object scales that depend on the authors creative process. Typically, dense image-based prediction techniques require a large corpus of data. Finding an automated solution for dense prediction in the comics domain, therefore, becomes more difficult with the lack of ground-truth dense annotations for the comics images. To address these challenges, we develop the following solutions: 1) we leverage a commonly-used strategy known as unsupervised image-to-image translation, which allows us to utilize a large corpus of real-world annotations; 2) we utilize the results of the translations to develop our multitasking approach that is based on a vision transformer backbone and a domain transferable attention module; 3) we study the feasibility of integrating our MTL dense-prediction method with an existing retargeting method, thereby reconfiguring comics.
MulT: An End-to-End Multitask Learning Transformer
May 17, 2022

Abstract:We propose an end-to-end Multitask Learning Transformer framework, named MulT, to simultaneously learn multiple high-level vision tasks, including depth estimation, semantic segmentation, reshading, surface normal estimation, 2D keypoint detection, and edge detection. Based on the Swin transformer model, our framework encodes the input image into a shared representation and makes predictions for each vision task using task-specific transformer-based decoder heads. At the heart of our approach is a shared attention mechanism modeling the dependencies across the tasks. We evaluate our model on several multitask benchmarks, showing that our MulT framework outperforms both the state-of-the art multitask convolutional neural network models and all the respective single task transformer models. Our experiments further highlight the benefits of sharing attention across all the tasks, and demonstrate that our MulT model is robust and generalizes well to new domains. Our project website is at https://ivrl.github.io/MulT/.
Estimating Image Depth in the Comics Domain
Oct 07, 2021

Abstract:Estimating the depth of comics images is challenging as such images a) are monocular; b) lack ground-truth depth annotations; c) differ across different artistic styles; d) are sparse and noisy. We thus, use an off-the-shelf unsupervised image to image translation method to translate the comics images to natural ones and then use an attention-guided monocular depth estimator to predict their depth. This lets us leverage the depth annotations of existing natural images to train the depth estimator. Furthermore, our model learns to distinguish between text and images in the comics panels to reduce text-based artefacts in the depth estimates. Our method consistently outperforms the existing state-ofthe-art approaches across all metrics on both the DCM and eBDtheque images. Finally, we introduce a dataset to evaluate depth prediction on comics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge