Sabine Süsstrunk
Subtractive Modulative Network with Learnable Periodic Activations
Feb 18, 2026Abstract:We propose the Subtractive Modulative Network (SMN), a novel, parameter-efficient Implicit Neural Representation (INR) architecture inspired by classical subtractive synthesis. The SMN is designed as a principled signal processing pipeline, featuring a learnable periodic activation layer (Oscillator) that generates a multi-frequency basis, and a series of modulative mask modules (Filters) that actively generate high-order harmonics. We provide both theoretical analysis and empirical validation for our design. Our SMN achieves a PSNR of $40+$ dB on two image datasets, comparing favorably against state-of-the-art methods in terms of both reconstruction accuracy and parameter efficiency. Furthermore, consistent advantage is observed on the challenging 3D NeRF novel view synthesis task. Supplementary materials are available at https://inrainbws.github.io/smn/.
* 4 pages, 3 figures, 3 tables
Neural Particle Automata: Learning Self-Organizing Particle Dynamics
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:We introduce Neural Particle Automata (NPA), a Lagrangian generalization of Neural Cellular Automata (NCA) from static lattices to dynamic particle systems. Unlike classical Eulerian NCA where cells are pinned to pixels or voxels, NPA model each cell as a particle with a continuous position and internal state, both updated by a shared, learnable neural rule. This particle-based formulation yields clear individuation of cells, allows heterogeneous dynamics, and concentrates computation only on regions where activity is present. At the same time, particle systems pose challenges: neighborhoods are dynamic, and a naive implementation of local interactions scale quadratically with the number of particles. We address these challenges by replacing grid-based neighborhood perception with differentiable Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) operators backed by memory-efficient, CUDA-accelerated kernels, enabling scalable end-to-end training. Across tasks including morphogenesis, point-cloud classification, and particle-based texture synthesis, we show that NPA retain key NCA behaviors such as robustness and self-regeneration, while enabling new behaviors specific to particle systems. Together, these results position NPA as a compact neural model for learning self-organizing particle dynamics.
Zooming into Comics: Region-Aware RL Improves Fine-Grained Comic Understanding in Vision-Language Models
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Complex visual narratives, such as comics, present a significant challenge to Vision-Language Models (VLMs). Despite excelling on natural images, VLMs often struggle with stylized line art, onomatopoeia, and densely packed multi-panel layouts. To address this gap, we introduce AI4VA-FG, the first fine-grained and comprehensive benchmark for VLM-based comic understanding. It spans tasks from foundational recognition and detection to high-level character reasoning and narrative construction, supported by dense annotations for characters, poses, and depth. Beyond that, we evaluate state-of-the-art proprietary models, including GPT-4o and Gemini-2.5, and open-source models such as Qwen2.5-VL, revealing substantial performance deficits across core tasks of our benchmarks and underscoring that comic understanding remains an unsolved challenge. To enhance VLMs' capabilities in this domain, we systematically investigate post-training strategies, including supervised fine-tuning on solutions (SFT-S), supervised fine-tuning on reasoning trajectories (SFT-R), and reinforcement learning (RL). Beyond that, inspired by the emerging "Thinking with Images" paradigm, we propose Region-Aware Reinforcement Learning (RARL) for VLMs, which trains models to dynamically attend to relevant regions through zoom-in operations. We observe that when applied to the Qwen2.5-VL model, RL and RARL yield significant gains in low-level entity recognition and high-level storyline ordering, paving the way for more accurate and efficient VLM applications in the comics domain.
Canonical Latent Representations in Conditional Diffusion Models
Jun 11, 2025
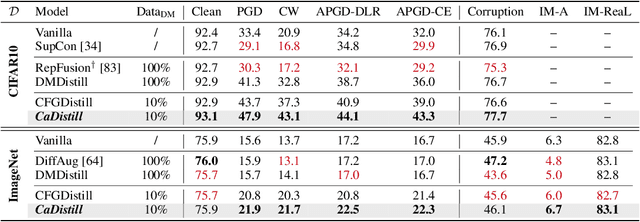
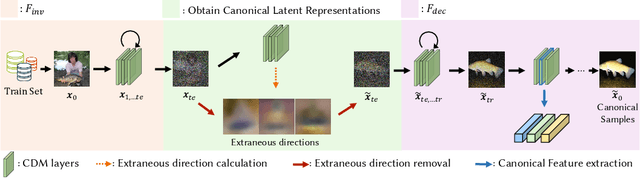

Abstract:Conditional diffusion models (CDMs) have shown impressive performance across a range of generative tasks. Their ability to model the full data distribution has opened new avenues for analysis-by-synthesis in downstream discriminative learning. However, this same modeling capacity causes CDMs to entangle the class-defining features with irrelevant context, posing challenges to extracting robust and interpretable representations. To this end, we identify Canonical LAtent Representations (CLAReps), latent codes whose internal CDM features preserve essential categorical information while discarding non-discriminative signals. When decoded, CLAReps produce representative samples for each class, offering an interpretable and compact summary of the core class semantics with minimal irrelevant details. Exploiting CLAReps, we develop a novel diffusion-based feature-distillation paradigm, CaDistill. While the student has full access to the training set, the CDM as teacher transfers core class knowledge only via CLAReps, which amounts to merely 10 % of the training data in size. After training, the student achieves strong adversarial robustness and generalization ability, focusing more on the class signals instead of spurious background cues. Our findings suggest that CDMs can serve not just as image generators but also as compact, interpretable teachers that can drive robust representation learning.
VibrantLeaves: A principled parametric image generator for training deep restoration models
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:Even though Deep Neural Networks are extremely powerful for image restoration tasks, they have several limitations. They are poorly understood and suffer from strong biases inherited from the training sets. One way to address these shortcomings is to have a better control over the training sets, in particular by using synthetic sets. In this paper, we propose a synthetic image generator relying on a few simple principles. In particular, we focus on geometric modeling, textures, and a simple modeling of image acquisition. These properties, integrated in a classical Dead Leaves model, enable the creation of efficient training sets. Standard image denoising and super-resolution networks can be trained on such datasets, reaching performance almost on par with training on natural image datasets. As a first step towards explainability, we provide a careful analysis of the considered principles, identifying which image properties are necessary to obtain good performances. Besides, such training also yields better robustness to various geometric and radiometric perturbations of the test sets.
VGRP-Bench: Visual Grid Reasoning Puzzle Benchmark for Large Vision-Language Models
Apr 02, 2025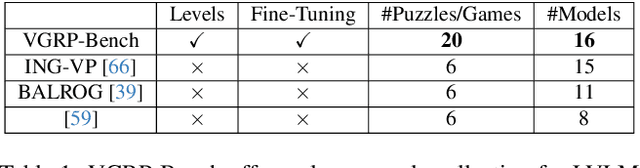
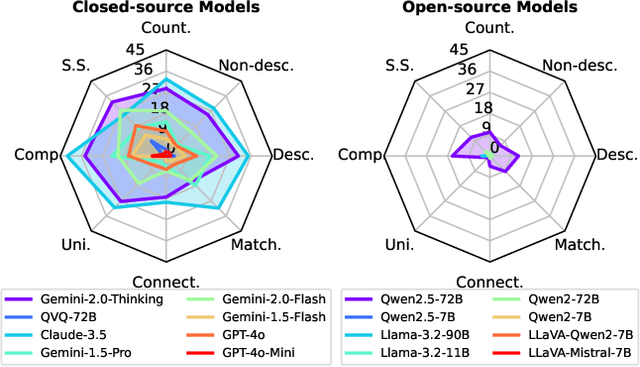
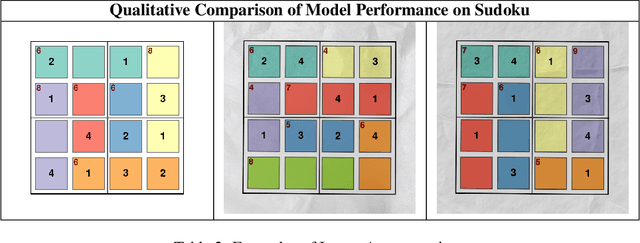
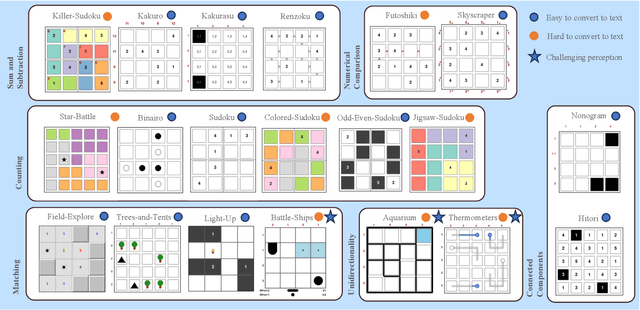
Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) struggle with puzzles, which require precise perception, rule comprehension, and logical reasoning. Assessing and enhancing their performance in this domain is crucial, as it reflects their ability to engage in structured reasoning - an essential skill for real-world problem-solving. However, existing benchmarks primarily evaluate pre-trained models without additional training or fine-tuning, often lack a dedicated focus on reasoning, and fail to establish a systematic evaluation framework. To address these limitations, we introduce VGRP-Bench, a Visual Grid Reasoning Puzzle Benchmark featuring 20 diverse puzzles. VGRP-Bench spans multiple difficulty levels, and includes extensive experiments not only on existing chat LVLMs (e.g., GPT-4o), but also on reasoning LVLMs (e.g., Gemini-Thinking). Our results reveal that even the state-of-the-art LVLMs struggle with these puzzles, highlighting fundamental limitations in their puzzle-solving capabilities. Most importantly, through systematic experiments, we identify and analyze key factors influencing LVLMs' puzzle-solving performance, including the number of clues, grid size, and rule complexity. Furthermore, we explore two Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) strategies that can be used in post-training: SFT on solutions (S-SFT) and SFT on synthetic reasoning processes (R-SFT). While both methods significantly improve performance on trained puzzles, they exhibit limited generalization to unseen ones. We will release VGRP-Bench to facilitate further research on LVLMs for complex, real-world problem-solving. Project page: https://yufan-ren.com/subpage/VGRP-Bench/.
FDS: Frequency-Aware Denoising Score for Text-Guided Latent Diffusion Image Editing
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:Text-guided image editing using Text-to-Image (T2I) models often fails to yield satisfactory results, frequently introducing unintended modifications, such as the loss of local detail and color changes. In this paper, we analyze these failure cases and attribute them to the indiscriminate optimization across all frequency bands, even though only specific frequencies may require adjustment. To address this, we introduce a simple yet effective approach that enables the selective optimization of specific frequency bands within localized spatial regions for precise edits. Our method leverages wavelets to decompose images into different spatial resolutions across multiple frequency bands, enabling precise modifications at various levels of detail. To extend the applicability of our approach, we provide a comparative analysis of different frequency-domain techniques. Additionally, we extend our method to 3D texture editing by performing frequency decomposition on the triplane representation, enabling frequency-aware adjustments for 3D textures. Quantitative evaluations and user studies demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in producing high-quality and precise edits.
Noise Synthesis for Low-Light Image Denoising with Diffusion Models
Mar 14, 2025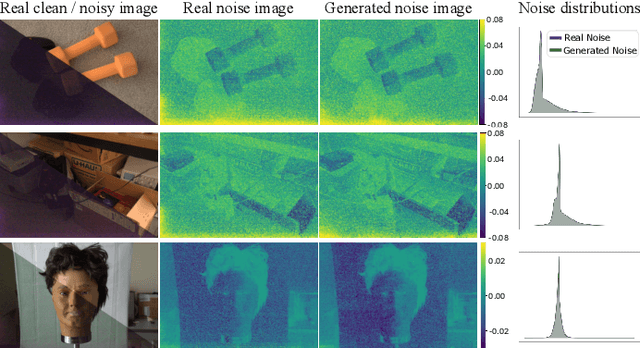
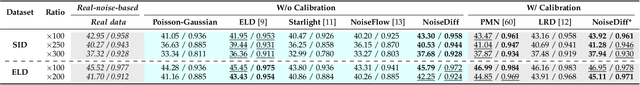
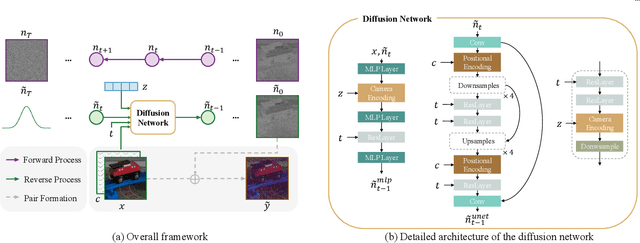
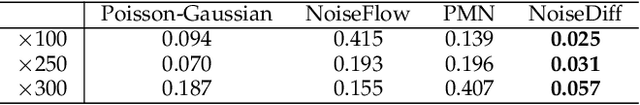
Abstract:Low-light photography produces images with low signal-to-noise ratios due to limited photons. In such conditions, common approximations like the Gaussian noise model fall short, and many denoising techniques fail to remove noise effectively. Although deep-learning methods perform well, they require large datasets of paired images that are impractical to acquire. As a remedy, synthesizing realistic low-light noise has gained significant attention. In this paper, we investigate the ability of diffusion models to capture the complex distribution of low-light noise. We show that a naive application of conventional diffusion models is inadequate for this task and propose three key adaptations that enable high-precision noise generation without calibration or post-processing: a two-branch architecture to better model signal-dependent and signal-independent noise, the incorporation of positional information to capture fixed-pattern noise, and a tailored diffusion noise schedule. Consequently, our model enables the generation of large datasets for training low-light denoising networks, leading to state-of-the-art performance. Through comprehensive analysis, including statistical evaluation and noise decomposition, we provide deeper insights into the characteristics of the generated data.
Unlocking Comics: The AI4VA Dataset for Visual Understanding
Oct 27, 2024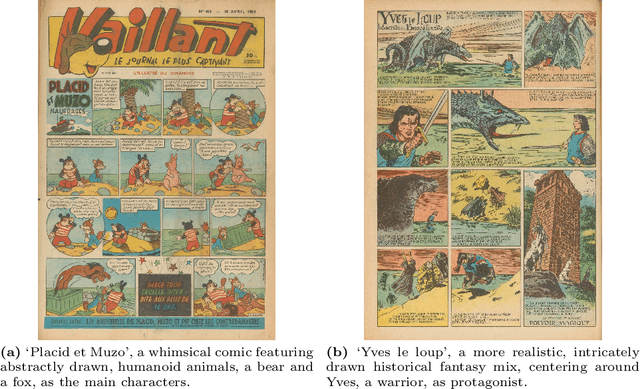


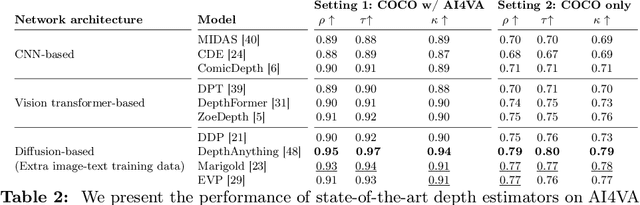
Abstract:In the evolving landscape of deep learning, there is a pressing need for more comprehensive datasets capable of training models across multiple modalities. Concurrently, in digital humanities, there is a growing demand to leverage technology for diverse media adaptation and creation, yet limited by sparse datasets due to copyright and stylistic constraints. Addressing this gap, our paper presents a novel dataset comprising Franco-Belgian comics from the 1950s annotated for tasks including depth estimation, semantic segmentation, saliency detection, and character identification. It consists of two distinct and consistent styles and incorporates object concepts and labels taken from natural images. By including such diverse information across styles, this dataset not only holds promise for computational creativity but also offers avenues for the digitization of art and storytelling innovation. This dataset is a crucial component of the AI4VA Workshop Challenges~\url{https://sites.google.com/view/ai4vaeccv2024}, where we specifically explore depth and saliency. Dataset details at \url{https://github.com/IVRL/AI4VA}.
Data Augmentation via Latent Diffusion for Saliency Prediction
Sep 11, 2024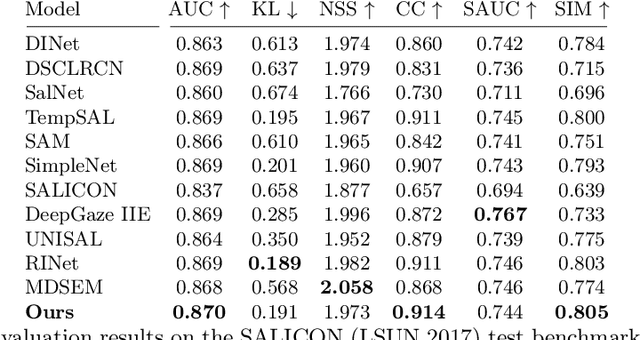
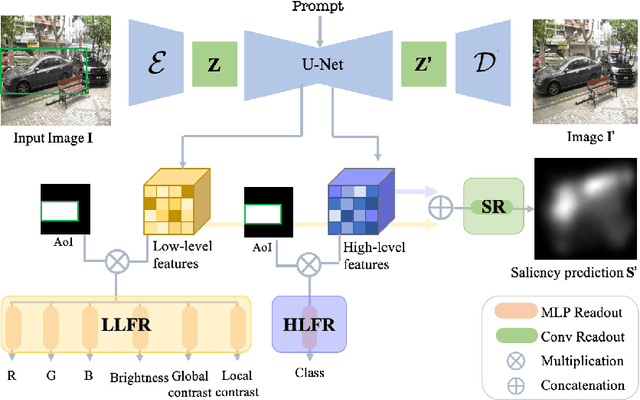
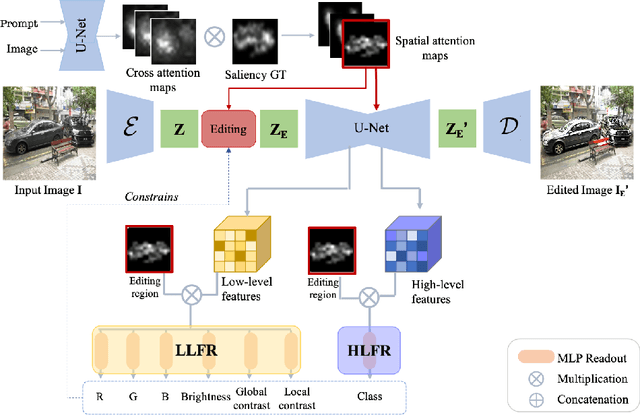

Abstract:Saliency prediction models are constrained by the limited diversity and quantity of labeled data. Standard data augmentation techniques such as rotating and cropping alter scene composition, affecting saliency. We propose a novel data augmentation method for deep saliency prediction that edits natural images while preserving the complexity and variability of real-world scenes. Since saliency depends on high-level and low-level features, our approach involves learning both by incorporating photometric and semantic attributes such as color, contrast, brightness, and class. To that end, we introduce a saliency-guided cross-attention mechanism that enables targeted edits on the photometric properties, thereby enhancing saliency within specific image regions. Experimental results show that our data augmentation method consistently improves the performance of various saliency models. Moreover, leveraging the augmentation features for saliency prediction yields superior performance on publicly available saliency benchmarks. Our predictions align closely with human visual attention patterns in the edited images, as validated by a user study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge