Shuangqi Li
LoRIF: Low-Rank Influence Functions for Scalable Training Data Attribution
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Training data attribution (TDA) identifies which training examples most influenced a model's prediction. The best-performing TDA methods exploits gradients to define an influence function. To overcome the scalability challenge arising from gradient computation, the most popular strategy is random projection (e.g., TRAK, LoGRA). However, this still faces two bottlenecks when scaling to large training sets and high-quality attribution: \emph{(i)} storing and loading projected per-example gradients for all $N$ training examples, where query latency is dominated by I/O; and \emph{(ii)} forming the $D \times D$ inverse Hessian approximation, which costs $O(D^2)$ memory. Both bottlenecks scale with the projection dimension $D$, yet increasing $D$ is necessary for attribution quality -- creating a quality-scalability tradeoff. We introduce \textbf{LoRIF (Low-Rank Influence Functions)}, which exploits low-rank structures of gradient to address both bottlenecks. First, we store rank-$c$ factors of the projected per-example gradients rather than full matrices, reducing storage and query-time I/O from $O(D)$ to $O(c\sqrt{D})$ per layer per sample. Second, we use truncated SVD with the Woodbury identity to approximate the Hessian term in an $r$-dimensional subspace, reducing memory from $O(D^2)$ to $O(Dr)$. On models from 0.1B to 70B parameters trained on datasets with millions of examples, LoRIF achieves up to 20$\times$ storage reduction and query-time speedup compared to LoGRA, while matching or exceeding its attribution quality. LoRIF makes gradient-based TDA practical at frontier scale.
Learning to Weight Parameters for Data Attribution
Jun 06, 2025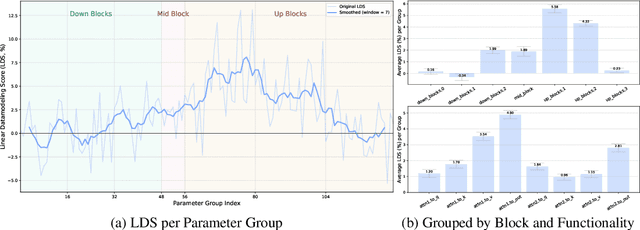

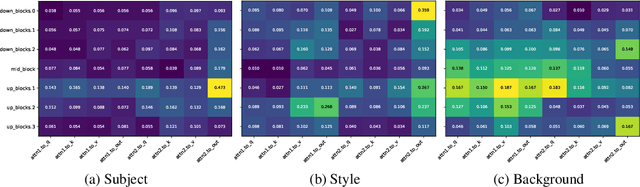
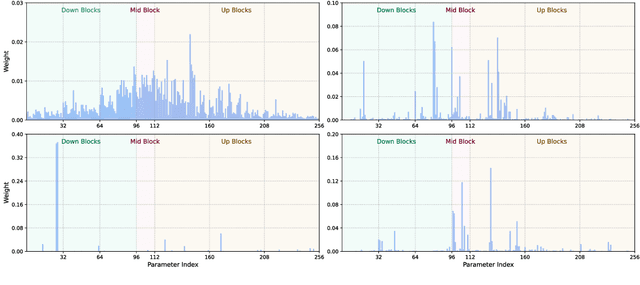
Abstract:We study data attribution in generative models, aiming to identify which training examples most influence a given output. Existing methods achieve this by tracing gradients back to training data. However, they typically treat all network parameters uniformly, ignoring the fact that different layers encode different types of information and may thus draw information differently from the training set. We propose a method that models this by learning parameter importance weights tailored for attribution, without requiring labeled data. This allows the attribution process to adapt to the structure of the model, capturing which training examples contribute to specific semantic aspects of an output, such as subject, style, or background. Our method improves attribution accuracy across diffusion models and enables fine-grained insights into how outputs borrow from training data.
Enhancing Compositional Text-to-Image Generation with Reliable Random Seeds
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capability in generating realistic images from arbitrary text prompts. However, they often produce inconsistent results for compositional prompts such as "two dogs" or "a penguin on the right of a bowl". Understanding these inconsistencies is crucial for reliable image generation. In this paper, we highlight the significant role of initial noise in these inconsistencies, where certain noise patterns are more reliable for compositional prompts than others. Our analyses reveal that different initial random seeds tend to guide the model to place objects in distinct image areas, potentially adhering to specific patterns of camera angles and image composition associated with the seed. To improve the model's compositional ability, we propose a method for mining these reliable cases, resulting in a curated training set of generated images without requiring any manual annotation. By fine-tuning text-to-image models on these generated images, we significantly enhance their compositional capabilities. For numerical composition, we observe relative increases of 29.3% and 19.5% for Stable Diffusion and PixArt-{\alpha}, respectively. Spatial composition sees even larger gains, with 60.7% for Stable Diffusion and 21.1% for PixArt-{\alpha}.
Controlling the Fidelity and Diversity of Deep Generative Models via Pseudo Density
Jul 11, 2024



Abstract:We introduce an approach to bias deep generative models, such as GANs and diffusion models, towards generating data with either enhanced fidelity or increased diversity. Our approach involves manipulating the distribution of training and generated data through a novel metric for individual samples, named pseudo density, which is based on the nearest-neighbor information from real samples. Our approach offers three distinct techniques to adjust the fidelity and diversity of deep generative models: 1) Per-sample perturbation, enabling precise adjustments for individual samples towards either more common or more unique characteristics; 2) Importance sampling during model inference to enhance either fidelity or diversity in the generated data; 3) Fine-tuning with importance sampling, which guides the generative model to learn an adjusted distribution, thus controlling fidelity and diversity. Furthermore, our fine-tuning method demonstrates the ability to improve the Frechet Inception Distance (FID) for pre-trained generative models with minimal iterations.
Interlock-Free Multi-Aspect Rationalization for Text Classification
May 13, 2022


Abstract:Explanation is important for text classification tasks. One prevalent type of explanation is rationales, which are text snippets of input text that suffice to yield the prediction and are meaningful to humans. A lot of research on rationalization has been based on the selective rationalization framework, which has recently been shown to be problematic due to the interlocking dynamics. In this paper, we show that we address the interlocking problem in the multi-aspect setting, where we aim to generate multiple rationales for multiple outputs. More specifically, we propose a multi-stage training method incorporating an additional self-supervised contrastive loss that helps to generate more semantically diverse rationales. Empirical results on the beer review dataset show that our method improves significantly the rationalization performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge