Qi Zhou
Graph-Augmented Reasoning with Large Language Models for Tobacco Pest and Disease Management
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:This paper proposes a graph-augmented reasoning framework for tobacco pest and disease management that integrates structured domain knowledge into large language models. Building on GraphRAG, we construct a domain-specific knowledge graph and retrieve query-relevant subgraphs to provide relational evidence during answer generation. The framework adopts ChatGLM as the Transformer backbone with LoRA-based parameter-efficient fine-tuning, and employs a graph neural network to learn node representations that capture symptom-disease-treatment dependencies. By explicitly modeling diseases, symptoms, pesticides, and control measures as linked entities, the system supports evidence-aware retrieval beyond surface-level text similarity. Retrieved graph evidence is incorporated into the LLM input to guide generation toward domain-consistent recommendations and to mitigate hallucinated or inappropriate treatments. Experimental results show consistent improvements over text-only baselines, with the largest gains observed on multi-hop and comparative reasoning questions that require chaining multiple relations.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Examining Student Interactions with a Pedagogical AI-Assistant for Essay Writing and their Impact on Students Writing Quality
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:The dynamic nature of interactions between students and GenAI, as well as their relationship to writing quality, remains underexplored. While most research has examined how general-purpose GenAI can support writing, fewer studies have investigated how students interact with pedagogically designed systems across different phases of the writing process. To address this gap, we evaluated a GenAI-driven essay-writing assistant (EWA) designed to support higher education students in argumentative writing. Drawing on 1,282 interaction logs from 32 undergraduates during a two-hour writing session, Sequential Pattern Mining and K-Means clustering were used to identify behavioral patterns. Two clusters emerged: Cluster 1 emphasized outline planning and essay structure, while Cluster 2 focused on content development. A Mann-Whitney U test revealed a moderate effect size (r = 0.36) in the essay Organization dimension, with Cluster 1 showing higher scores. Qualitative analysis indicated that students with better performance actively wrote and shared essay sections with EWA for feedback, rather than interacted passively by asking questions. These findings suggest implications for teaching and system design. Teachers can encourage active engagement, while future EWAs may integrate automatic labeling and monitoring to prompt students to move from questioning to writing, enabling fuller benefits from GenAI-supported learning.
Minimum Width of Deep Narrow Networks for Universal Approximation
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Determining the minimum width of fully connected neural networks has become a fundamental problem in recent theoretical studies of deep neural networks. In this paper, we study the lower bounds and upper bounds of the minimum width required for fully connected neural networks in order to have universal approximation capability, which is important in network design and training. We show that $w_{min}\leq\max(2d_x+1, d_y)$ for networks with ELU, SELU, and the upper bound of this inequality is attained when $d_y=2d_x$, where $d_x$, $d_y$ denote the input and output dimensions, respectively. Besides, we show that $d_x+1\leq w_{min}\leq d_x+d_y$ for networks with LeakyReLU, ELU, CELU, SELU, Softplus, by proving that ReLU can be approximated by these activation functions. In addition, in the case that the activation function is injective or can be uniformly approximated by a sequence of injective functions (e.g., ReLU), we present a new proof of the inequality $w_{min}\ge d_y+\mathbf{1}_{d_x<d_y\leq2d_x}$ by constructing a more intuitive example via a new geometric approach based on Poincar$\acute{\text{e}}$-Miranda Theorem.
Large Foundation Model for Ads Recommendation
Aug 20, 2025


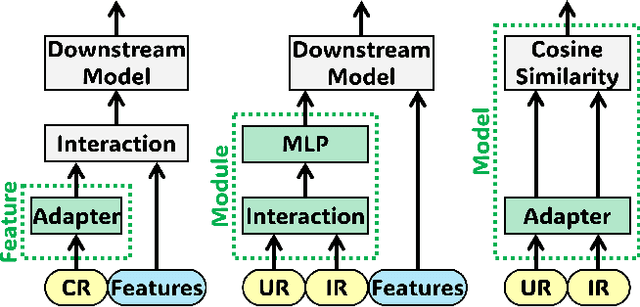
Abstract:Online advertising relies on accurate recommendation models, with recent advances using pre-trained large-scale foundation models (LFMs) to capture users' general interests across multiple scenarios and tasks. However, existing methods have critical limitations: they extract and transfer only user representations (URs), ignoring valuable item representations (IRs) and user-item cross representations (CRs); and they simply use a UR as a feature in downstream applications, which fails to bridge upstream-downstream gaps and overlooks more transfer granularities. In this paper, we propose LFM4Ads, an All-Representation Multi-Granularity transfer framework for ads recommendation. It first comprehensively transfers URs, IRs, and CRs, i.e., all available representations in the pre-trained foundation model. To effectively utilize the CRs, it identifies the optimal extraction layer and aggregates them into transferable coarse-grained forms. Furthermore, we enhance the transferability via multi-granularity mechanisms: non-linear adapters for feature-level transfer, an Isomorphic Interaction Module for module-level transfer, and Standalone Retrieval for model-level transfer. LFM4Ads has been successfully deployed in Tencent's industrial-scale advertising platform, processing tens of billions of daily samples while maintaining terabyte-scale model parameters with billions of sparse embedding keys across approximately two thousand features. Since its production deployment in Q4 2024, LFM4Ads has achieved 10+ successful production launches across various advertising scenarios, including primary ones like Weixin Moments and Channels. These launches achieve an overall GMV lift of 2.45% across the entire platform, translating to estimated annual revenue increases in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
InfiAlign: A Scalable and Sample-Efficient Framework for Aligning LLMs to Enhance Reasoning Capabilities
Aug 07, 2025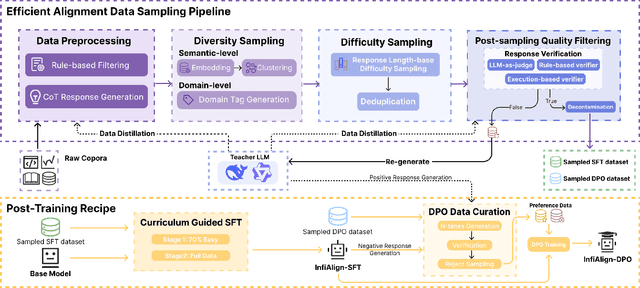
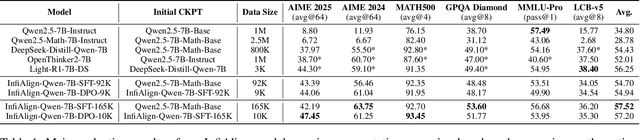
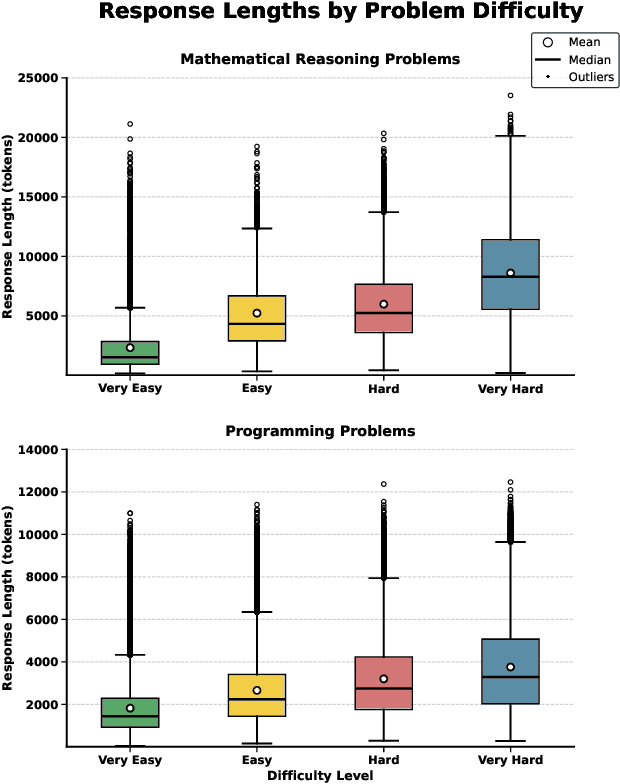
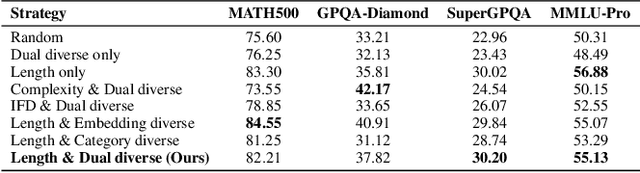
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have exhibited impressive reasoning abilities on a wide range of complex tasks. However, enhancing these capabilities through post-training remains resource intensive, particularly in terms of data and computational cost. Although recent efforts have sought to improve sample efficiency through selective data curation, existing methods often rely on heuristic or task-specific strategies that hinder scalability. In this work, we introduce InfiAlign, a scalable and sample-efficient post-training framework that integrates supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to align LLMs for enhanced reasoning. At the core of InfiAlign is a robust data selection pipeline that automatically curates high-quality alignment data from open-source reasoning datasets using multidimensional quality metrics. This pipeline enables significant performance gains while drastically reducing data requirements and remains extensible to new data sources. When applied to the Qwen2.5-Math-7B-Base model, our SFT model achieves performance on par with DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B, while using only approximately 12% of the training data, and demonstrates strong generalization across diverse reasoning tasks. Additional improvements are obtained through the application of DPO, with particularly notable gains in mathematical reasoning tasks. The model achieves an average improvement of 3.89% on AIME 24/25 benchmarks. Our results highlight the effectiveness of combining principled data selection with full-stage post-training, offering a practical solution for aligning large reasoning models in a scalable and data-efficient manner. The model checkpoints are available at https://huggingface.co/InfiX-ai/InfiAlign-Qwen-7B-SFT.
An RRT* algorithm based on Riemannian metric model for optimal path planning
Jul 02, 2025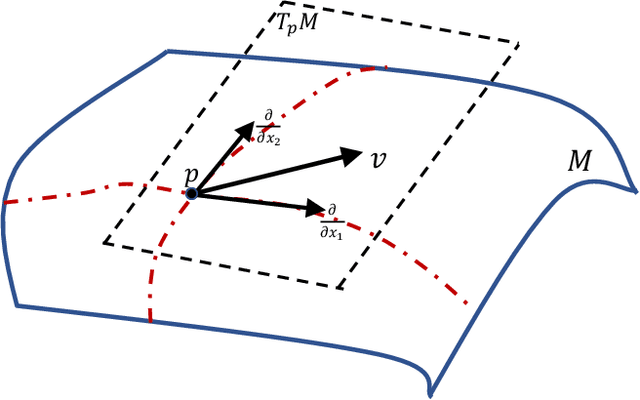
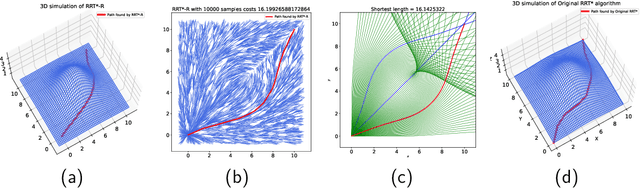
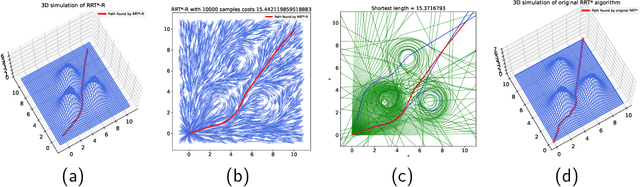
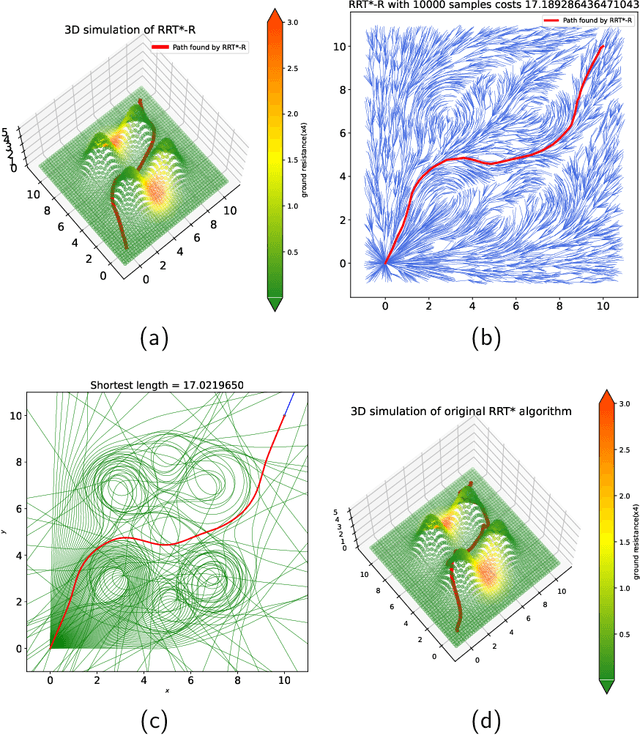
Abstract:This paper presents a Riemannian metric-based model to solve the optimal path planning problem on two-dimensional smooth submanifolds in high-dimensional space. Our model is based on constructing a new Riemannian metric on a two-dimensional projection plane, which is induced by the high-dimensional Euclidean metric on two-dimensional smooth submanifold and reflects the environmental information of the robot. The optimal path planning problem in high-dimensional space is therefore transformed into a geometric problem on the two-dimensional plane with new Riemannian metric. Based on the new Riemannian metric, we proposed an incremental algorithm RRT*-R on the projection plane. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is suitable for scenarios with uneven fields in multiple dimensions. The proposed algorithm can help the robot to effectively avoid areas with drastic changes in height, ground resistance and other environmental factors. More importantly, the RRT*-R algorithm shows better smoothness and optimization properties compared with the original RRT* algorithm using Euclidean distance in high-dimensional workspace. The length of the entire path by RRT*-R is a good approximation of the theoretical minimum geodesic distance on projection plane.
InfiFPO: Implicit Model Fusion via Preference Optimization in Large Language Models
May 20, 2025Abstract:Model fusion combines multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) with different strengths into a more powerful, integrated model through lightweight training methods. Existing works on model fusion focus primarily on supervised fine-tuning (SFT), leaving preference alignment (PA) --a critical phase for enhancing LLM performance--largely unexplored. The current few fusion methods on PA phase, like WRPO, simplify the process by utilizing only response outputs from source models while discarding their probability information. To address this limitation, we propose InfiFPO, a preference optimization method for implicit model fusion. InfiFPO replaces the reference model in Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with a fused source model that synthesizes multi-source probabilities at the sequence level, circumventing complex vocabulary alignment challenges in previous works and meanwhile maintaining the probability information. By introducing probability clipping and max-margin fusion strategies, InfiFPO enables the pivot model to align with human preferences while effectively distilling knowledge from source models. Comprehensive experiments on 11 widely-used benchmarks demonstrate that InfiFPO consistently outperforms existing model fusion and preference optimization methods. When using Phi-4 as the pivot model, InfiFPO improve its average performance from 79.95 to 83.33 on 11 benchmarks, significantly improving its capabilities in mathematics, coding, and reasoning tasks.
InfiGFusion: Graph-on-Logits Distillation via Efficient Gromov-Wasserstein for Model Fusion
May 20, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have intensified efforts to fuse heterogeneous open-source models into a unified system that inherits their complementary strengths. Existing logit-based fusion methods maintain inference efficiency but treat vocabulary dimensions independently, overlooking semantic dependencies encoded by cross-dimension interactions. These dependencies reflect how token types interact under a model's internal reasoning and are essential for aligning models with diverse generation behaviors. To explicitly model these dependencies, we propose \textbf{InfiGFusion}, the first structure-aware fusion framework with a novel \textit{Graph-on-Logits Distillation} (GLD) loss. Specifically, we retain the top-$k$ logits per output and aggregate their outer products across sequence positions to form a global co-activation graph, where nodes represent vocabulary channels and edges quantify their joint activations. To ensure scalability and efficiency, we design a sorting-based closed-form approximation that reduces the original $O(n^4)$ cost of Gromov-Wasserstein distance to $O(n \log n)$, with provable approximation guarantees. Experiments across multiple fusion settings show that GLD consistently improves fusion quality and stability. InfiGFusion outperforms SOTA models and fusion baselines across 11 benchmarks spanning reasoning, coding, and mathematics. It shows particular strength in complex reasoning tasks, with +35.6 improvement on Multistep Arithmetic and +37.06 on Causal Judgement over SFT, demonstrating superior multi-step and relational inference.
Fair-PP: A Synthetic Dataset for Aligning LLM with Personalized Preferences of Social Equity
May 17, 2025Abstract:Human preference plays a crucial role in the refinement of large language models (LLMs). However, collecting human preference feedback is costly and most existing datasets neglect the correlation between personalization and preferences. To address this issue, we introduce Fair-PP, a synthetic dataset of personalized preferences targeting social equity, derived from real-world social survey data, which includes 28 social groups, 98 equity topics, and 5 personal preference dimensions. Leveraging GPT-4o-mini, we engage in role-playing based on seven representative persona portrayals guided by existing social survey data, yielding a total of 238,623 preference records. Through Fair-PP, we also contribute (i) An automated framework for generating preference data, along with a more fine-grained dataset of personalized preferences; (ii) analysis of the positioning of the existing mainstream LLMs across five major global regions within the personalized preference space; and (iii) a sample reweighting method for personalized preference alignment, enabling alignment with a target persona while maximizing the divergence from other personas. Empirical experiments show our method outperforms the baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge