Raphaël Achddou
Noise Synthesis for Low-Light Image Denoising with Diffusion Models
Mar 14, 2025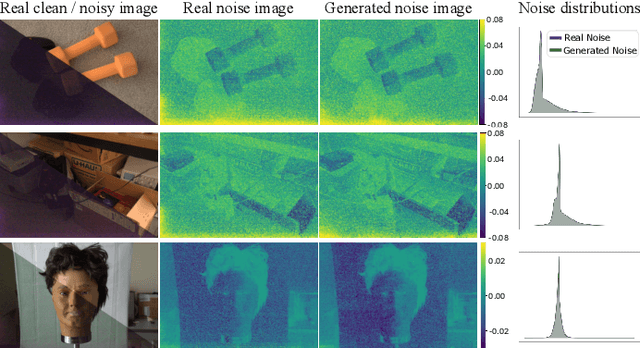
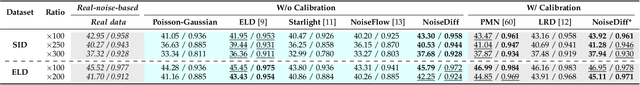
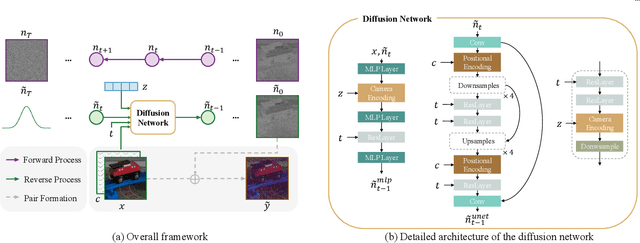
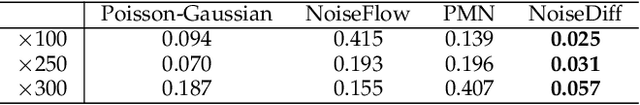
Abstract:Low-light photography produces images with low signal-to-noise ratios due to limited photons. In such conditions, common approximations like the Gaussian noise model fall short, and many denoising techniques fail to remove noise effectively. Although deep-learning methods perform well, they require large datasets of paired images that are impractical to acquire. As a remedy, synthesizing realistic low-light noise has gained significant attention. In this paper, we investigate the ability of diffusion models to capture the complex distribution of low-light noise. We show that a naive application of conventional diffusion models is inadequate for this task and propose three key adaptations that enable high-precision noise generation without calibration or post-processing: a two-branch architecture to better model signal-dependent and signal-independent noise, the incorporation of positional information to capture fixed-pattern noise, and a tailored diffusion noise schedule. Consequently, our model enables the generation of large datasets for training low-light denoising networks, leading to state-of-the-art performance. Through comprehensive analysis, including statistical evaluation and noise decomposition, we provide deeper insights into the characteristics of the generated data.
Nested Learning For Multi-Granular Tasks
Jul 13, 2020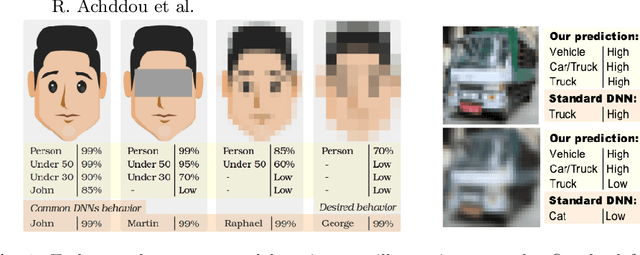
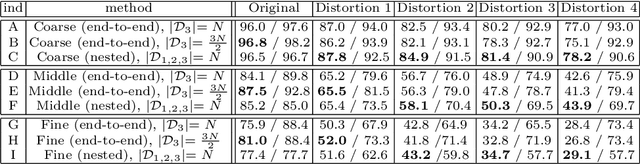
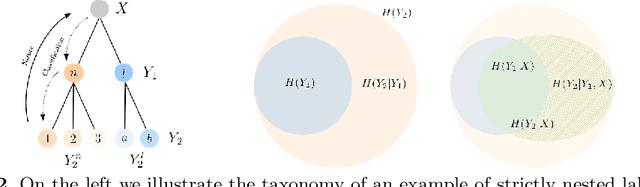
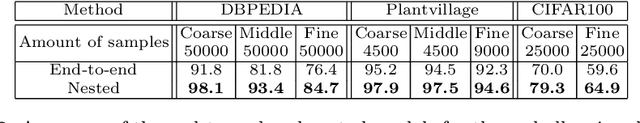
Abstract:Standard deep neural networks (DNNs) are commonly trained in an end-to-end fashion for specific tasks such as object recognition, face identification, or character recognition, among many examples. This specificity often leads to overconfident models that generalize poorly to samples that are not from the original training distribution. Moreover, such standard DNNs do not allow to leverage information from heterogeneously annotated training data, where for example, labels may be provided with different levels of granularity. Furthermore, DNNs do not produce results with simultaneous different levels of confidence for different levels of detail, they are most commonly an all or nothing approach. To address these challenges, we introduce the concept of nested learning: how to obtain a hierarchical representation of the input such that a coarse label can be extracted first, and sequentially refine this representation, if the sample permits, to obtain successively refined predictions, all of them with the corresponding confidence. We explicitly enforce this behavior by creating a sequence of nested information bottlenecks. Looking at the problem of nested learning from an information theory perspective, we design a network topology with two important properties. First, a sequence of low dimensional (nested) feature embeddings are enforced. Then we show how the explicit combination of nested outputs can improve both the robustness and the accuracy of finer predictions. Experimental results on Cifar-10, Cifar-100, MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, Dbpedia, and Plantvillage demonstrate that nested learning outperforms the same network trained in the standard end-to-end fashion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge