Yupeng Deng
SegEarth-OV3: Exploring SAM 3 for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Most existing methods for training-free Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS) are based on CLIP. While these approaches have made progress, they often face challenges in precise localization or require complex pipelines to combine separate modules, especially in remote sensing scenarios where numerous dense and small targets are present. Recently, Segment Anything Model 3 (SAM 3) was proposed, unifying segmentation and recognition in a promptable framework. In this paper, we present a preliminary exploration of applying SAM 3 to the remote sensing OVSS task without any training. First, we implement a mask fusion strategy that combines the outputs from SAM 3's semantic segmentation head and the Transformer decoder (instance head). This allows us to leverage the strengths of both heads for better land coverage. Second, we utilize the presence score from the presence head to filter out categories that do not exist in the scene, reducing false positives caused by the vast vocabulary sizes and patch-level processing in geospatial scenes. We evaluate our method on extensive remote sensing datasets. Experiments show that this simple adaptation achieves promising performance, demonstrating the potential of SAM 3 for remote sensing OVSS. Our code is released at https://github.com/earth-insights/SegEarth-OV-3.
GLD-Road:A global-local decoding road network extraction model for remote sensing images
Jun 11, 2025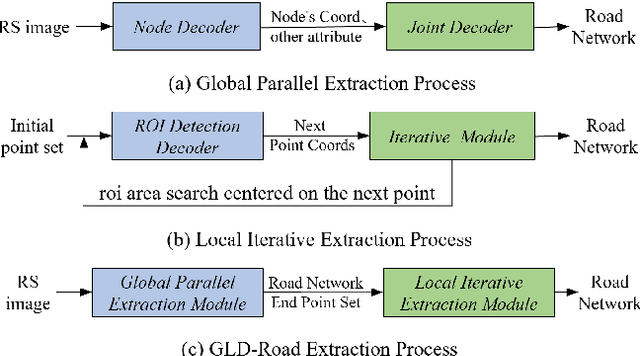
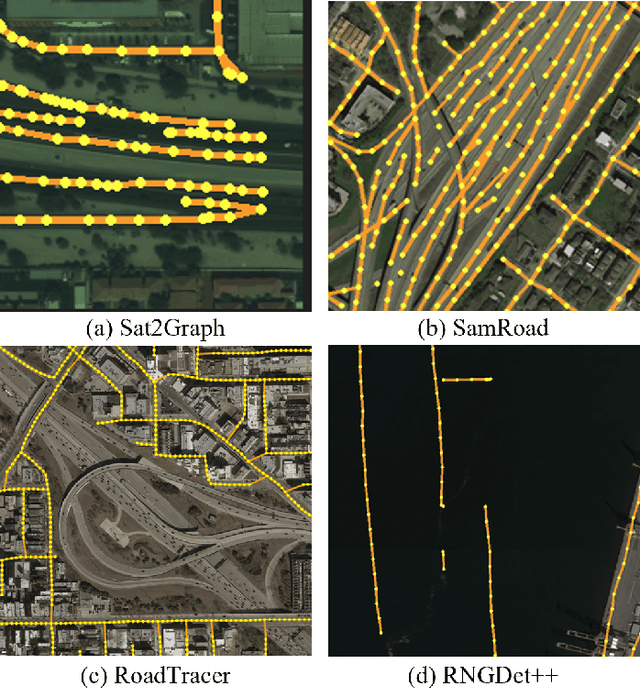
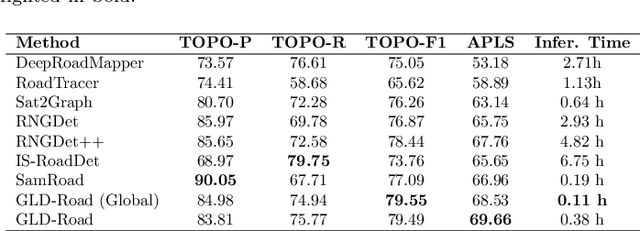

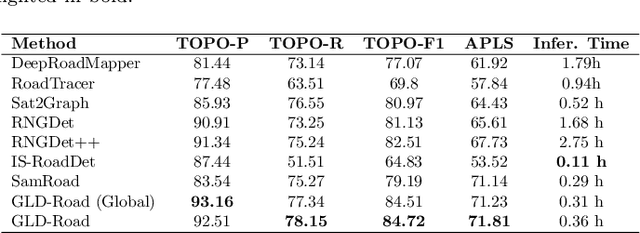
Abstract:Road networks are crucial for mapping, autonomous driving, and disaster response. While manual annotation is costly, deep learning offers efficient extraction. Current methods include postprocessing (prone to errors), global parallel (fast but misses nodes), and local iterative (accurate but slow). We propose GLD-Road, a two-stage model combining global efficiency and local precision. First, it detects road nodes and connects them via a Connect Module. Then, it iteratively refines broken roads using local searches, drastically reducing computation. Experiments show GLD-Road outperforms state-of-the-art methods, improving APLS by 1.9% (City-Scale) and 0.67% (SpaceNet3). It also reduces retrieval time by 40% vs. Sat2Graph (global) and 92% vs. RNGDet++ (local). The experimental results are available at https://github.com/ucas-dlg/GLD-Road.
SegEarth-R1: Geospatial Pixel Reasoning via Large Language Model
Apr 13, 2025Abstract:Remote sensing has become critical for understanding environmental dynamics, urban planning, and disaster management. However, traditional remote sensing workflows often rely on explicit segmentation or detection methods, which struggle to handle complex, implicit queries that require reasoning over spatial context, domain knowledge, and implicit user intent. Motivated by this, we introduce a new task, \ie, geospatial pixel reasoning, which allows implicit querying and reasoning and generates the mask of the target region. To advance this task, we construct and release the first large-scale benchmark dataset called EarthReason, which comprises 5,434 manually annotated image masks with over 30,000 implicit question-answer pairs. Moreover, we propose SegEarth-R1, a simple yet effective language-guided segmentation baseline that integrates a hierarchical visual encoder, a large language model (LLM) for instruction parsing, and a tailored mask generator for spatial correlation. The design of SegEarth-R1 incorporates domain-specific adaptations, including aggressive visual token compression to handle ultra-high-resolution remote sensing images, a description projection module to fuse language and multi-scale features, and a streamlined mask prediction pipeline that directly queries description embeddings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SegEarth-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance on both reasoning and referring segmentation tasks, significantly outperforming traditional and LLM-based segmentation methods. Our data and code will be released at https://github.com/earth-insights/SegEarth-R1.
LRSCLIP: A Vision-Language Foundation Model for Aligning Remote Sensing Image with Longer Text
Mar 25, 2025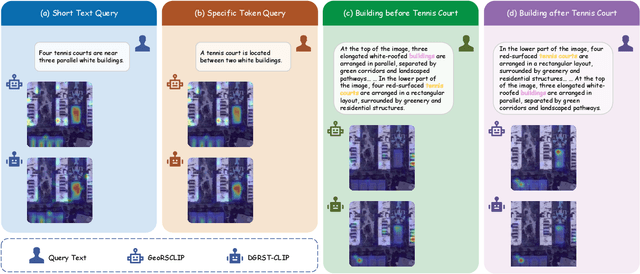
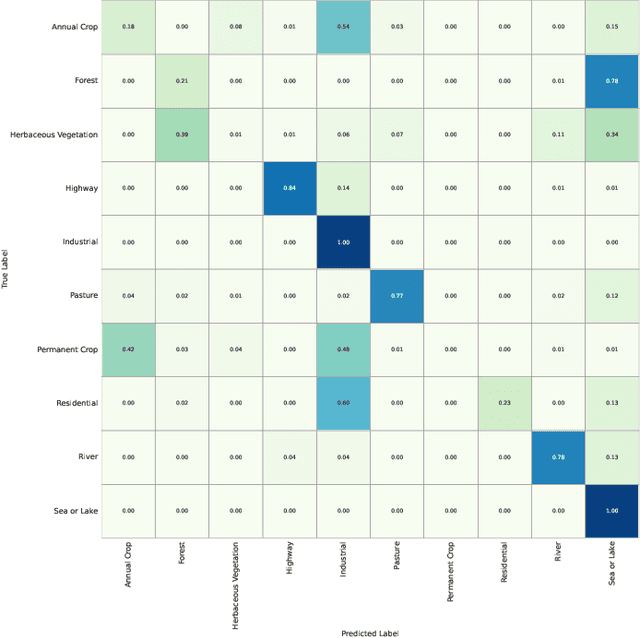
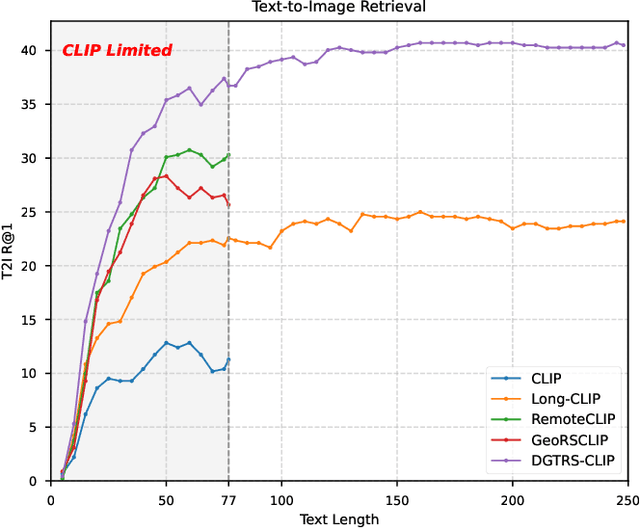
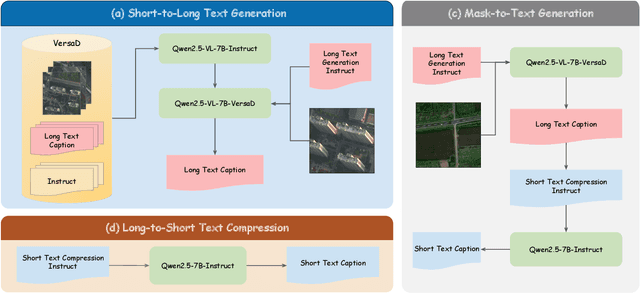
Abstract:This study addresses the technical bottlenecks in handling long text and the "hallucination" issue caused by insufficient short text information in remote sensing vision-language foundation models (VLFM). We propose a novel vision-language foundation model, LRSCLIP, and a multimodal dataset, LRS2M. The main contributions are as follows: (1) By integrating multi-source remote sensing data and adopting a large language model labeling strategy, we construct the LRS2M dataset, which contains 2 million image-text pairs, providing both short and long texts for the first time, thus solving the problem of semantic granularity limitations in existing datasets; (2) The design of the LRSCLIP architecture based on Long-CLIP's KPS module, which extends CLIP's text processing capacity and achieves fine-grained cross-modal feature alignment through a dual-text loss weighting mechanism. Experimental results show that LRSCLIP improves retrieval accuracy by 10\%-20\% over the Long-CLIP baseline in the zero-shot long-text cross-modal retrieval task. For the zero-shot short-text cross-modal retrieval task, LRSCLIP achieves improvements over the current best model, GeoRSCLIP, with increases of 0.17\%, 0.67\%, and 0.92\% in Text to Image R@1, Image to Text R@1, and mR on RSITMD, respectively, and 0.04\%, 2.93\%, and 1.28\% on RSICD. In the zero-shot image classification task (average accuracy=75.75\%) and semantic localization task (Rmi=0.7653), LRSCLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance. These results validate the dual advantages of fine-grained semantic understanding and global feature matching in LRSCLIP. This work provides a new benchmark model and data support for remote sensing multimodal learning. The related code has been open source and is available at https://github.com/MitsuiChen14/LRSCLIP.
CrossEarth: Geospatial Vision Foundation Model for Domain Generalizable Remote Sensing Semantic Segmentation
Oct 31, 2024


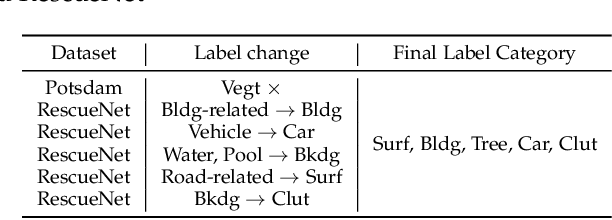
Abstract:The field of Remote Sensing Domain Generalization (RSDG) has emerged as a critical and valuable research frontier, focusing on developing models that generalize effectively across diverse scenarios. Despite the substantial domain gaps in RS images that are characterized by variabilities such as location, wavelength, and sensor type, research in this area remains underexplored: (1) Current cross-domain methods primarily focus on Domain Adaptation (DA), which adapts models to predefined domains rather than to unseen ones; (2) Few studies targeting the RSDG issue, especially for semantic segmentation tasks, where existing models are developed for specific unknown domains, struggling with issues of underfitting on other unknown scenarios; (3) Existing RS foundation models tend to prioritize in-domain performance over cross-domain generalization. To this end, we introduce the first vision foundation model for RSDG semantic segmentation, CrossEarth. CrossEarth demonstrates strong cross-domain generalization through a specially designed data-level Earth-Style Injection pipeline and a model-level Multi-Task Training pipeline. In addition, for the semantic segmentation task, we have curated an RSDG benchmark comprising 28 cross-domain settings across various regions, spectral bands, platforms, and climates, providing a comprehensive framework for testing the generalizability of future RSDG models. Extensive experiments on this benchmark demonstrate the superiority of CrossEarth over existing state-of-the-art methods.
Extracting polygonal footprints in off-nadir images with Segment Anything Model
Aug 16, 2024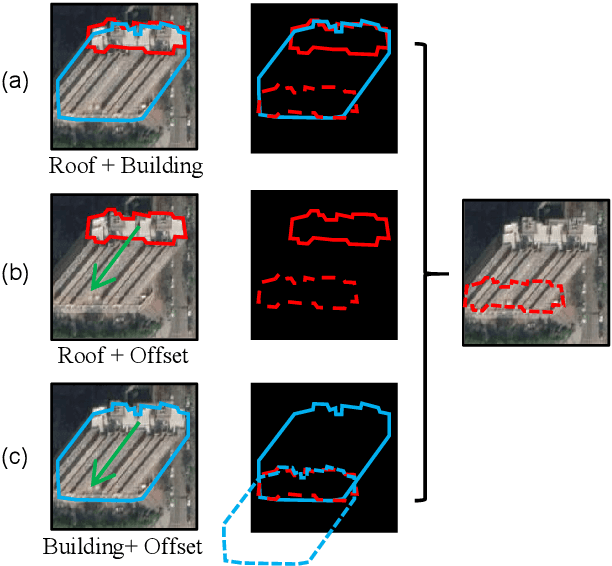
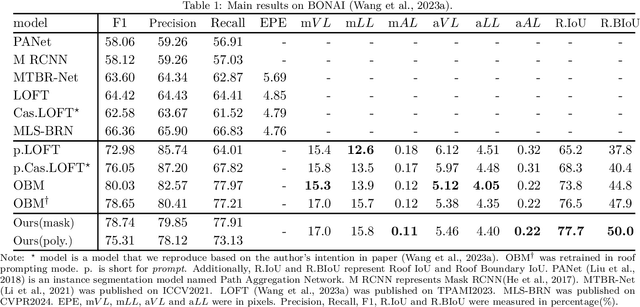
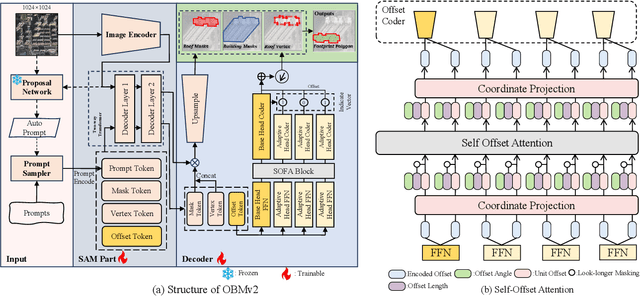
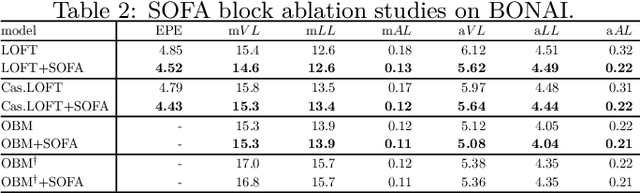
Abstract:Building Footprint Extraction (BFE) in off-nadir aerial images often relies on roof segmentation and roof-to-footprint offset prediction, then drugging roof-to-footprint via the offset. However, the results from this multi-stage inference are not applicable in data production, because of the low quality of masks given by prediction. To solve this problem, we proposed OBMv2 in this paper, which supports both end-to-end and promptable polygonal footprint prediction. Different from OBM, OBMv2 using a newly proposed Self Offset Attention (SOFA) to bridge the performance gap on bungalow and skyscraper, which realized a real end-to-end footprint polygon prediction without postprocessing. %, such as Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) and Distance NMS (DNMS). % To fully use information contained in roof masks, building masks and offsets, we proposed a Multi-level Information SyStem (MISS) for footprint prediction, with which OBMv2 can predict footprints even with insufficient predictions. Additionally, to squeeze information from the same model, we were inspired by Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) in Nature Language Processing and proposed "RAG in BFE" problem. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, experiments were conducted on open datasets BONAI and OmniCity-view3. A generalization test was also conducted on Huizhou test set. The code will be available at \url{https://github.com/likaiucas/OBM}.
Open-CD: A Comprehensive Toolbox for Change Detection
Jul 22, 2024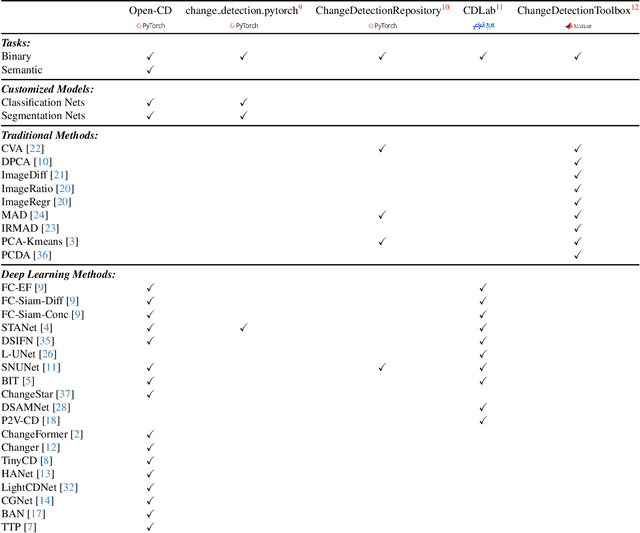
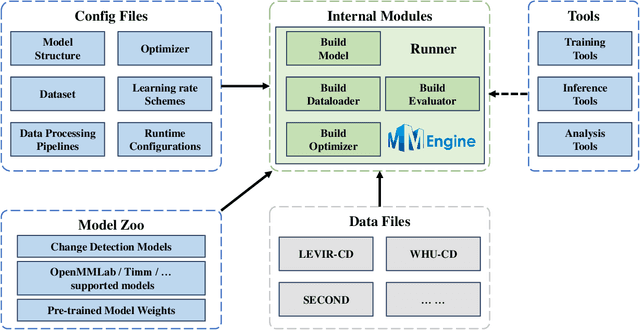
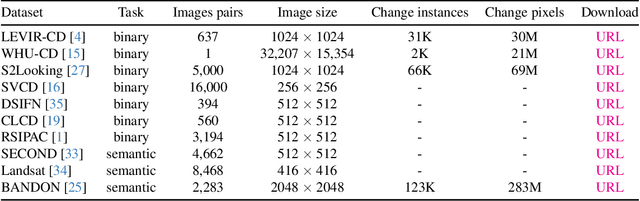
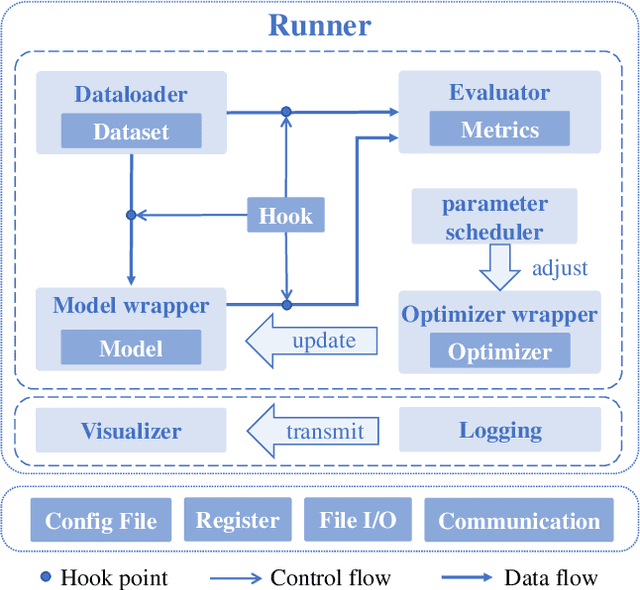
Abstract:We present Open-CD, a change detection toolbox that contains a rich set of change detection methods as well as related components and modules. The toolbox started from a series of open source general vision task tools, including OpenMMLab Toolkits, PyTorch Image Models, etc. It gradually evolves into a unified platform that covers many popular change detection methods and contemporary modules. It not only includes training and inference codes, but also provides some useful scripts for data analysis. We believe this toolbox is by far the most complete change detection toolbox. In this report, we introduce the various features, supported methods and applications of Open-CD. In addition, we also conduct a benchmarking study on different methods and components. We wish that the toolbox and benchmark could serve the growing research community by providing a flexible toolkit to reimplement existing methods and develop their own new change detectors. Code and models are available at \url{https://github.com/likyoo/open-cd}. Pioneeringly, this report also includes brief descriptions of the algorithms supported in Open-CD, mainly contributed by their authors. We sincerely encourage researchers in this field to participate in this project and work together to create a more open community. This toolkit and report will be kept updated.
DiffMatch: Visual-Language Guidance Makes Better Semi-supervised Change Detector
May 08, 2024Abstract:Change Detection (CD) aims to identify pixels with semantic changes between images. However, annotating massive numbers of pixel-level images is labor-intensive and costly, especially for multi-temporal images, which require pixel-wise comparisons by human experts. Considering the excellent performance of visual language models (VLMs) for zero-shot, open-vocabulary, etc. with prompt-based reasoning, it is promising to utilize VLMs to make better CD under limited labeled data. In this paper, we propose a VLM guidance-based semi-supervised CD method, namely DiffMatch. The insight of DiffMatch is to synthesize free change labels using VLMs to provide additional supervision signals for unlabeled data. However, almost all current VLMs are designed for single-temporal images and cannot be directly applied to bi- or multi-temporal images. Motivated by this, we first propose a VLM-based mixed change event generation (CEG) strategy to yield pseudo labels for unlabeled CD data. Since the additional supervised signals provided by these VLM-driven pseudo labels may conflict with the pseudo labels from the consistency regularization paradigm (e.g. FixMatch), we propose the dual projection head for de-entangling different signal sources. Further, we explicitly decouple the bi-temporal images semantic representation through two auxiliary segmentation decoders, which are also guided by VLM. Finally, to make the model more adequately capture change representations, we introduce metric-aware supervision by feature-level contrastive loss in auxiliary branches. Extensive experiments show the advantage of DiffMatch. For instance, DiffMatch improves the FixMatch baseline by +5.3 IoU on WHU-CD and by +2.4 IoU on LEVIR-CD with 5% labels. In addition, our CEG strategy, in an un-supervised manner, can achieve performance far superior to state-of-the-art un-supervised CD methods.
CoDA: Instructive Chain-of-Domain Adaptation with Severity-Aware Visual Prompt Tuning
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) aims to adapt models from labeled source domains to unlabeled target domains. When adapting to adverse scenes, existing UDA methods fail to perform well due to the lack of instructions, leading their models to overlook discrepancies within all adverse scenes. To tackle this, we propose CoDA which instructs models to distinguish, focus, and learn from these discrepancies at scene and image levels. Specifically, CoDA consists of a Chain-of-Domain (CoD) strategy and a Severity-Aware Visual Prompt Tuning (SAVPT) mechanism. CoD focuses on scene-level instructions to divide all adverse scenes into easy and hard scenes, guiding models to adapt from source to easy domains with easy scene images, and then to hard domains with hard scene images, thereby laying a solid foundation for whole adaptations. Building upon this foundation, we employ SAVPT to dive into more detailed image-level instructions to boost performance. SAVPT features a novel metric Severity that divides all adverse scene images into low-severity and high-severity images. Then Severity directs visual prompts and adapters, instructing models to concentrate on unified severity features instead of scene-specific features, without adding complexity to the model architecture. CoDA achieves SOTA performances on widely-used benchmarks under all adverse scenes. Notably, CoDA outperforms the existing ones by 4.6%, and 10.3% mIoU on the Foggy Driving, and Foggy Zurich benchmarks, respectively. Our code is available at https://github.com/Cuzyoung/CoDA
Rebuild City Buildings from Off-Nadir Aerial Images with Offset-Building Model
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:Accurate measurement of the offset from roof-to-footprint in very-high-resolution remote sensing imagery is crucial for urban information extraction tasks. With the help of deep learning, existing methods typically rely on two-stage CNN models to extract regions of interest on building feature maps. At the first stage, a Region Proposal Network (RPN) is applied to extract thousands of ROIs (Region of Interests) which will post-imported into a Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks (RCNN) to extract wanted information. However, because of inflexible RPN, these methods often lack effective user interaction, encounter difficulties in instance correspondence, and struggle to keep up with the advancements in general artificial intelligence. This paper introduces an interactive Transformer model combined with a prompt encoder to precisely extract building segmentation as well as the offset vectors from roofs to footprints. In our model, a powerful module, namely ROAM, was tailored for common problems in predicting roof-to-footprint offsets. We tested our model's feasibility on the publicly available BONAI dataset, achieving a significant reduction in Prompt-Instance-Level offset errors ranging from 14.6% to 16.3%. Additionally, we developed a Distance-NMS algorithm tailored for large-scale building offsets, significantly enhancing the accuracy of predicted building offset angles and lengths in a straightforward and efficient manner. To further validate the model's robustness, we created a new test set using 0.5m remote sensing imagery from Huizhou, China, for inference testing. Our code, training methods, and the updated dataset will be accessable at https://github.com/likaiucas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge