Jiansheng Chen
Step-DeepResearch Technical Report
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:As LLMs shift toward autonomous agents, Deep Research has emerged as a pivotal metric. However, existing academic benchmarks like BrowseComp often fail to meet real-world demands for open-ended research, which requires robust skills in intent recognition, long-horizon decision-making, and cross-source verification. To address this, we introduce Step-DeepResearch, a cost-effective, end-to-end agent. We propose a Data Synthesis Strategy Based on Atomic Capabilities to reinforce planning and report writing, combined with a progressive training path from agentic mid-training to SFT and RL. Enhanced by a Checklist-style Judger, this approach significantly improves robustness. Furthermore, to bridge the evaluation gap in the Chinese domain, we establish ADR-Bench for realistic deep research scenarios. Experimental results show that Step-DeepResearch (32B) scores 61.4% on Scale AI Research Rubrics. On ADR-Bench, it significantly outperforms comparable models and rivals SOTA closed-source models like OpenAI and Gemini DeepResearch. These findings prove that refined training enables medium-sized models to achieve expert-level capabilities at industry-leading cost-efficiency.
XYZCylinder: Feedforward Reconstruction for Driving Scenes Based on A Unified Cylinder Lifting Method
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Recently, more attention has been paid to feedforward reconstruction paradigms, which mainly learn a fixed view transformation implicitly and reconstruct the scene with a single representation. However, their generalization capability and reconstruction accuracy are still limited while reconstructing driving scenes, which results from two aspects: (1) The fixed view transformation fails when the camera configuration changes, limiting the generalization capability across different driving scenes equipped with different camera configurations. (2) The small overlapping regions between sparse views of the $360^\circ$ panorama and the complexity of driving scenes increase the learning difficulty, reducing the reconstruction accuracy. To handle these difficulties, we propose \textbf{XYZCylinder}, a feedforward model based on a unified cylinder lifting method which involves camera modeling and feature lifting. Specifically, to improve the generalization capability, we design a Unified Cylinder Camera Modeling (UCCM) strategy, which avoids the learning of viewpoint-dependent spatial correspondence and unifies different camera configurations with adjustable parameters. To improve the reconstruction accuracy, we propose a hybrid representation with several dedicated modules based on newly designed Cylinder Plane Feature Group (CPFG) to lift 2D image features to 3D space. Experimental results show that XYZCylinder achieves state-of-the-art performance under different evaluation settings, and can be generalized to other driving scenes in a zero-shot manner. Project page: \href{https://yuyuyu223.github.io/XYZCYlinder-projectpage/}{here}.
Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
Jul 24, 2025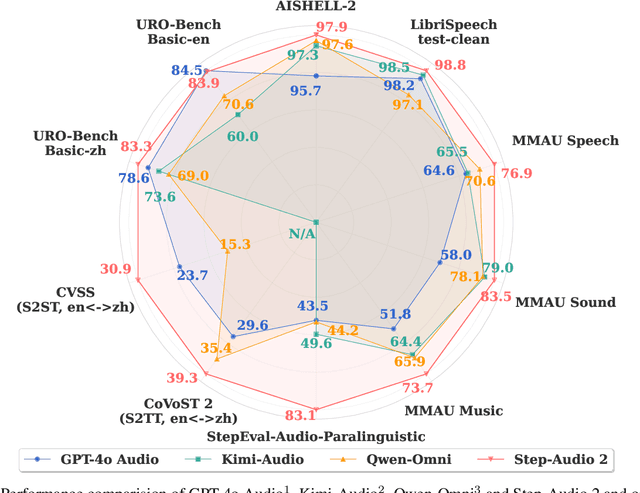

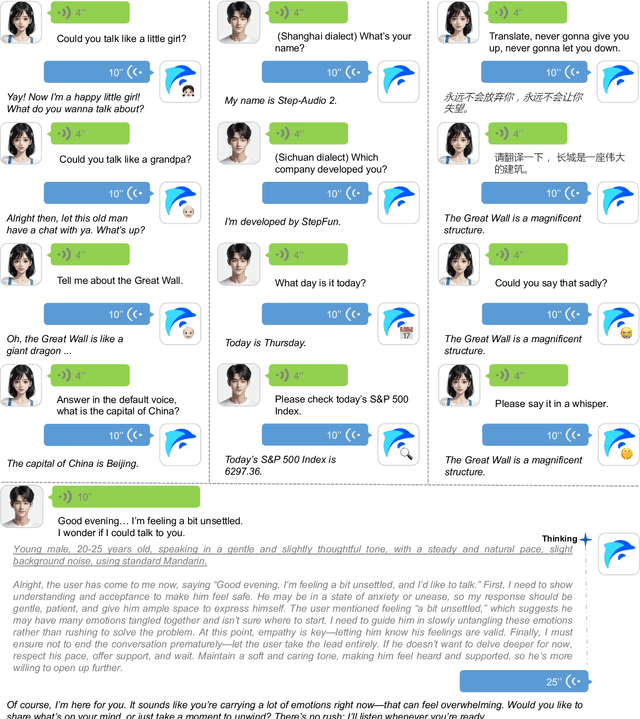

Abstract:This paper presents Step-Audio 2, an end-to-end multi-modal large language model designed for industry-strength audio understanding and speech conversation. By integrating a latent audio encoder and reasoning-centric reinforcement learning (RL), Step-Audio 2 achieves promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio understanding. To facilitate genuine end-to-end speech conversation, Step-Audio 2 incorporates the generation of discrete audio tokens into language modeling, significantly enhancing its responsiveness to paralinguistic information such as speaking styles and emotions. To effectively leverage the rich textual and acoustic knowledge in real-world data, Step-Audio 2 integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is able to call external tools such as web search to mitigate hallucination and audio search to switch timbres. Trained on millions of hours of speech and audio data, Step-Audio 2 delivers intelligence and expressiveness across diverse conversational scenarios. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various audio understanding and conversational benchmarks compared to other open-source and commercial solutions. Please visit https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio2 for more information.
From Black Boxes to Transparent Minds: Evaluating and Enhancing the Theory of Mind in Multimodal Large Language Models
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:As large language models evolve, there is growing anticipation that they will emulate human-like Theory of Mind (ToM) to assist with routine tasks. However, existing methods for evaluating machine ToM focus primarily on unimodal models and largely treat these models as black boxes, lacking an interpretative exploration of their internal mechanisms. In response, this study adopts an approach based on internal mechanisms to provide an interpretability-driven assessment of ToM in multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Specifically, we first construct a multimodal ToM test dataset, GridToM, which incorporates diverse belief testing tasks and perceptual information from multiple perspectives. Next, our analysis shows that attention heads in multimodal large models can distinguish cognitive information across perspectives, providing evidence of ToM capabilities. Furthermore, we present a lightweight, training-free approach that significantly enhances the model's exhibited ToM by adjusting in the direction of the attention head.
Step-Audio-AQAA: a Fully End-to-End Expressive Large Audio Language Model
Jun 10, 2025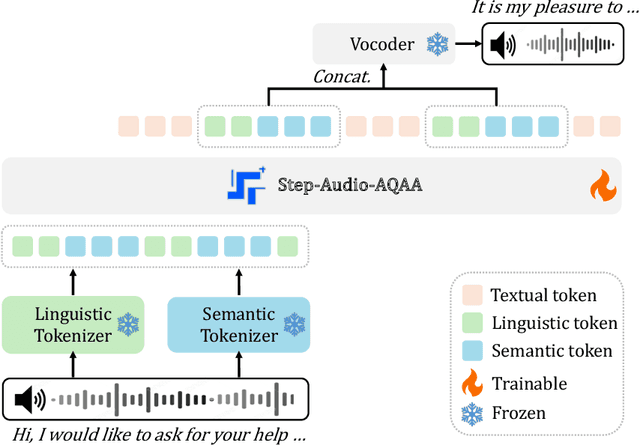
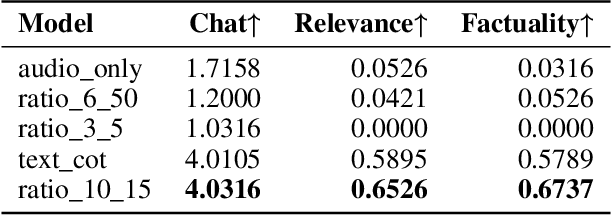
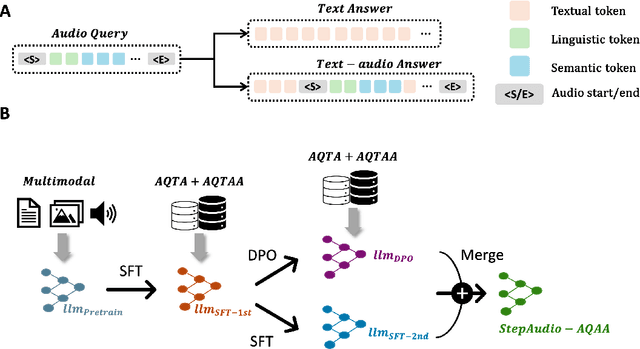
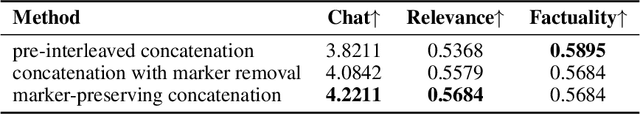
Abstract:Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) have significantly advanced intelligent human-computer interaction, yet their reliance on text-based outputs limits their ability to generate natural speech responses directly, hindering seamless audio interactions. To address this, we introduce Step-Audio-AQAA, a fully end-to-end LALM designed for Audio Query-Audio Answer (AQAA) tasks. The model integrates a dual-codebook audio tokenizer for linguistic and semantic feature extraction, a 130-billion-parameter backbone LLM and a neural vocoder for high-fidelity speech synthesis. Our post-training approach employs interleaved token-output of text and audio to enhance semantic coherence and combines Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with model merge to improve performance. Evaluations on the StepEval-Audio-360 benchmark demonstrate that Step-Audio-AQAA excels especially in speech control, outperforming the state-of-art LALMs in key areas. This work contributes a promising solution for end-to-end LALMs and highlights the critical role of token-based vocoder in enhancing overall performance for AQAA tasks.
DeCoDe: Defer-and-Complement Decision-Making via Decoupled Concept Bottleneck Models
May 25, 2025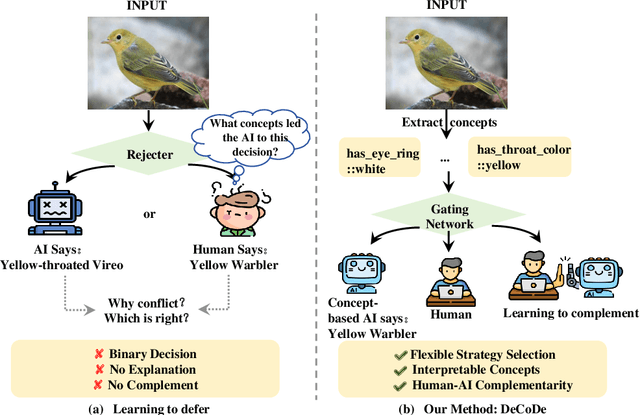
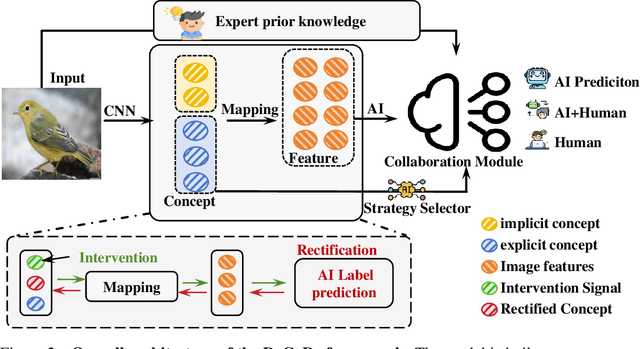
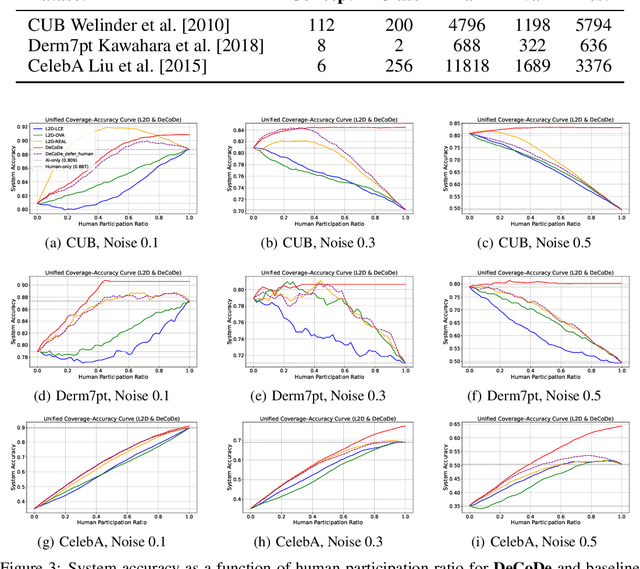

Abstract:In human-AI collaboration, a central challenge is deciding whether the AI should handle a task, be deferred to a human expert, or be addressed through collaborative effort. Existing Learning to Defer approaches typically make binary choices between AI and humans, neglecting their complementary strengths. They also lack interpretability, a critical property in high-stakes scenarios where users must understand and, if necessary, correct the model's reasoning. To overcome these limitations, we propose Defer-and-Complement Decision-Making via Decoupled Concept Bottleneck Models (DeCoDe), a concept-driven framework for human-AI collaboration. DeCoDe makes strategy decisions based on human-interpretable concept representations, enhancing transparency throughout the decision process. It supports three flexible modes: autonomous AI prediction, deferral to humans, and human-AI collaborative complementarity, selected via a gating network that takes concept-level inputs and is trained using a novel surrogate loss that balances accuracy and human effort. This approach enables instance-specific, interpretable, and adaptive human-AI collaboration. Experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that DeCoDe significantly outperforms AI-only, human-only, and traditional deferral baselines, while maintaining strong robustness and interpretability even under noisy expert annotations.
QAVA: Query-Agnostic Visual Attack to Large Vision-Language Models
Apr 15, 2025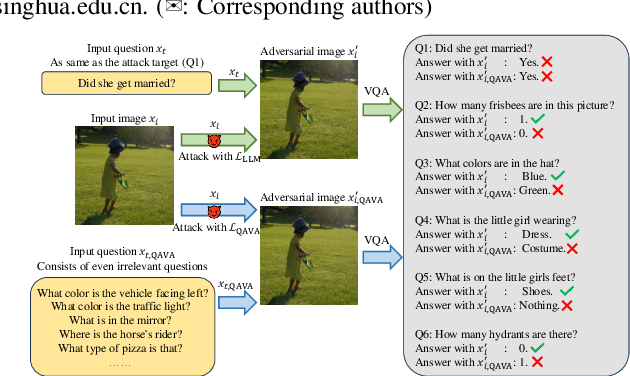
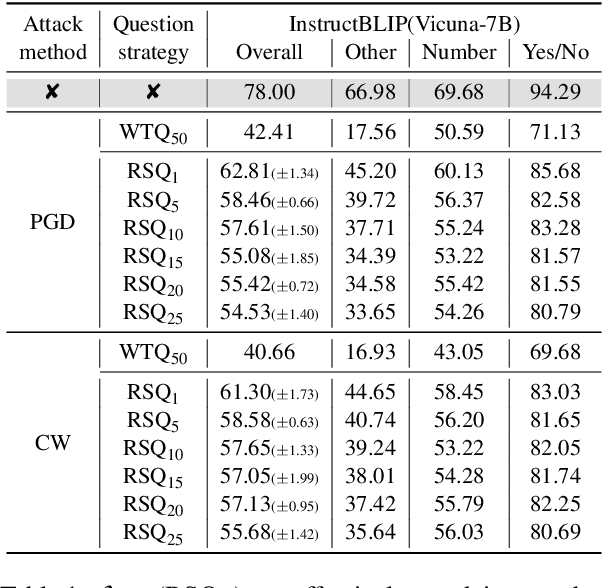
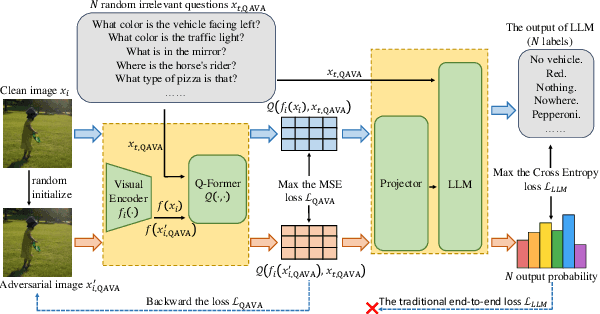
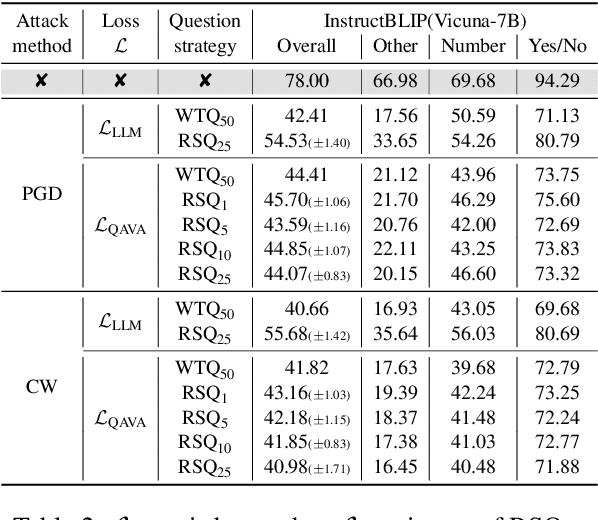
Abstract:In typical multimodal tasks, such as Visual Question Answering (VQA), adversarial attacks targeting a specific image and question can lead large vision-language models (LVLMs) to provide incorrect answers. However, it is common for a single image to be associated with multiple questions, and LVLMs may still answer other questions correctly even for an adversarial image attacked by a specific question. To address this, we introduce the query-agnostic visual attack (QAVA), which aims to create robust adversarial examples that generate incorrect responses to unspecified and unknown questions. Compared to traditional adversarial attacks focused on specific images and questions, QAVA significantly enhances the effectiveness and efficiency of attacks on images when the question is unknown, achieving performance comparable to attacks on known target questions. Our research broadens the scope of visual adversarial attacks on LVLMs in practical settings, uncovering previously overlooked vulnerabilities, particularly in the context of visual adversarial threats. The code is available at https://github.com/btzyd/qava.
CIBR: Cross-modal Information Bottleneck Regularization for Robust CLIP Generalization
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) has achieved remarkable success in cross-modal tasks such as zero-shot image classification and text-image retrieval by effectively aligning visual and textual representations. However, the theoretical foundations underlying CLIP's strong generalization remain unclear. In this work, we address this gap by proposing the Cross-modal Information Bottleneck (CIB) framework. CIB offers a principled interpretation of CLIP's contrastive learning objective as an implicit Information Bottleneck optimization. Under this view, the model maximizes shared cross-modal information while discarding modality-specific redundancies, thereby preserving essential semantic alignment across modalities. Building on this insight, we introduce a Cross-modal Information Bottleneck Regularization (CIBR) method that explicitly enforces these IB principles during training. CIBR introduces a penalty term to discourage modality-specific redundancy, thereby enhancing semantic alignment between image and text features. We validate CIBR on extensive vision-language benchmarks, including zero-shot classification across seven diverse image datasets and text-image retrieval on MSCOCO and Flickr30K. The results show consistent performance gains over standard CLIP. These findings provide the first theoretical understanding of CLIP's generalization through the IB lens. They also demonstrate practical improvements, offering guidance for future cross-modal representation learning.
LRSCLIP: A Vision-Language Foundation Model for Aligning Remote Sensing Image with Longer Text
Mar 25, 2025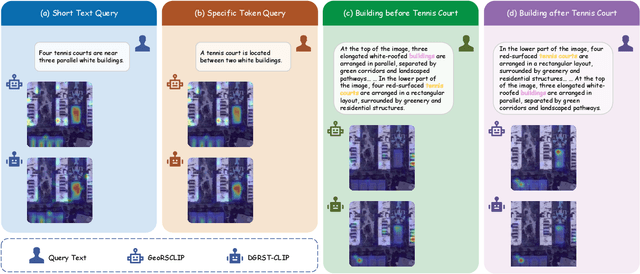
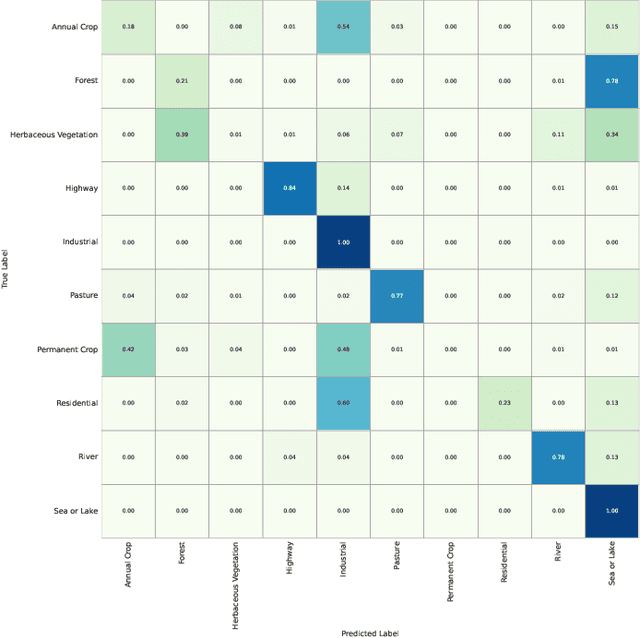
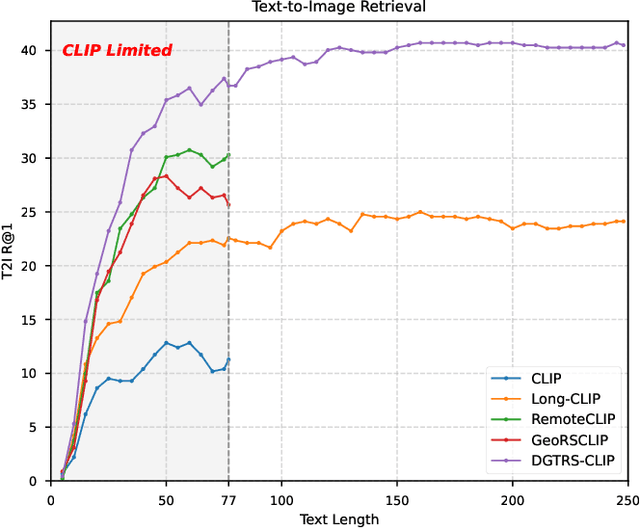
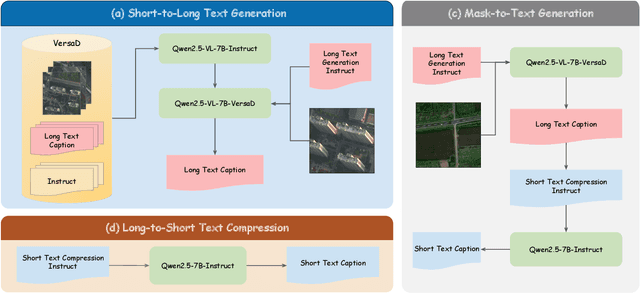
Abstract:This study addresses the technical bottlenecks in handling long text and the "hallucination" issue caused by insufficient short text information in remote sensing vision-language foundation models (VLFM). We propose a novel vision-language foundation model, LRSCLIP, and a multimodal dataset, LRS2M. The main contributions are as follows: (1) By integrating multi-source remote sensing data and adopting a large language model labeling strategy, we construct the LRS2M dataset, which contains 2 million image-text pairs, providing both short and long texts for the first time, thus solving the problem of semantic granularity limitations in existing datasets; (2) The design of the LRSCLIP architecture based on Long-CLIP's KPS module, which extends CLIP's text processing capacity and achieves fine-grained cross-modal feature alignment through a dual-text loss weighting mechanism. Experimental results show that LRSCLIP improves retrieval accuracy by 10\%-20\% over the Long-CLIP baseline in the zero-shot long-text cross-modal retrieval task. For the zero-shot short-text cross-modal retrieval task, LRSCLIP achieves improvements over the current best model, GeoRSCLIP, with increases of 0.17\%, 0.67\%, and 0.92\% in Text to Image R@1, Image to Text R@1, and mR on RSITMD, respectively, and 0.04\%, 2.93\%, and 1.28\% on RSICD. In the zero-shot image classification task (average accuracy=75.75\%) and semantic localization task (Rmi=0.7653), LRSCLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance. These results validate the dual advantages of fine-grained semantic understanding and global feature matching in LRSCLIP. This work provides a new benchmark model and data support for remote sensing multimodal learning. The related code has been open source and is available at https://github.com/MitsuiChen14/LRSCLIP.
Step-Video-TI2V Technical Report: A State-of-the-Art Text-Driven Image-to-Video Generation Model
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:We present Step-Video-TI2V, a state-of-the-art text-driven image-to-video generation model with 30B parameters, capable of generating videos up to 102 frames based on both text and image inputs. We build Step-Video-TI2V-Eval as a new benchmark for the text-driven image-to-video task and compare Step-Video-TI2V with open-source and commercial TI2V engines using this dataset. Experimental results demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of Step-Video-TI2V in the image-to-video generation task. Both Step-Video-TI2V and Step-Video-TI2V-Eval are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Video-TI2V.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge