Hongwei Yu
A2RNet: Adversarial Attack Resilient Network for Robust Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
Dec 18, 2024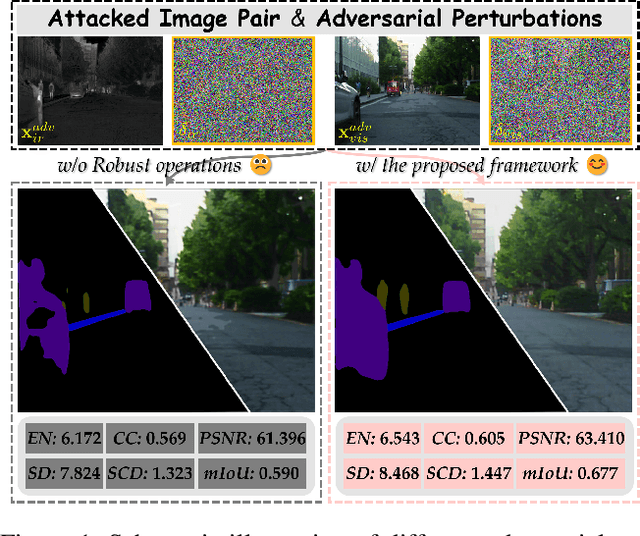
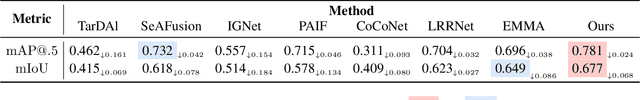
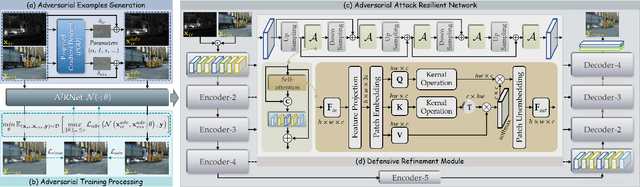
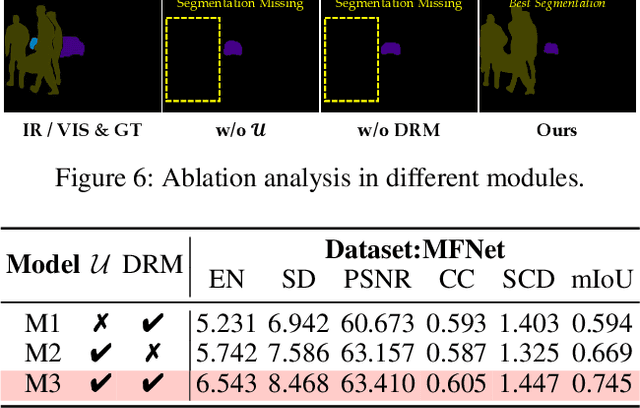
Abstract:Infrared and visible image fusion (IVIF) is a crucial technique for enhancing visual performance by integrating unique information from different modalities into one fused image. Exiting methods pay more attention to conducting fusion with undisturbed data, while overlooking the impact of deliberate interference on the effectiveness of fusion results. To investigate the robustness of fusion models, in this paper, we propose a novel adversarial attack resilient network, called $\textrm{A}^{\textrm{2}}$RNet. Specifically, we develop an adversarial paradigm with an anti-attack loss function to implement adversarial attacks and training. It is constructed based on the intrinsic nature of IVIF and provide a robust foundation for future research advancements. We adopt a Unet as the pipeline with a transformer-based defensive refinement module (DRM) under this paradigm, which guarantees fused image quality in a robust coarse-to-fine manner. Compared to previous works, our method mitigates the adverse effects of adversarial perturbations, consistently maintaining high-fidelity fusion results. Furthermore, the performance of downstream tasks can also be well maintained under adversarial attacks. Code is available at https://github.com/lok-18/A2RNet.
$\textrm{A}^{\textrm{2}}$RNet: Adversarial Attack Resilient Network for Robust Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Infrared and visible image fusion (IVIF) is a crucial technique for enhancing visual performance by integrating unique information from different modalities into one fused image. Exiting methods pay more attention to conducting fusion with undisturbed data, while overlooking the impact of deliberate interference on the effectiveness of fusion results. To investigate the robustness of fusion models, in this paper, we propose a novel adversarial attack resilient network, called $\textrm{A}^{\textrm{2}}$RNet. Specifically, we develop an adversarial paradigm with an anti-attack loss function to implement adversarial attacks and training. It is constructed based on the intrinsic nature of IVIF and provide a robust foundation for future research advancements. We adopt a Unet as the pipeline with a transformer-based defensive refinement module (DRM) under this paradigm, which guarantees fused image quality in a robust coarse-to-fine manner. Compared to previous works, our method mitigates the adverse effects of adversarial perturbations, consistently maintaining high-fidelity fusion results. Furthermore, the performance of downstream tasks can also be well maintained under adversarial attacks. Code is available at https://github.com/lok-18/A2RNet.
Fed-MUnet: Multi-modal Federated Unet for Brain Tumor Segmentation
Sep 02, 2024
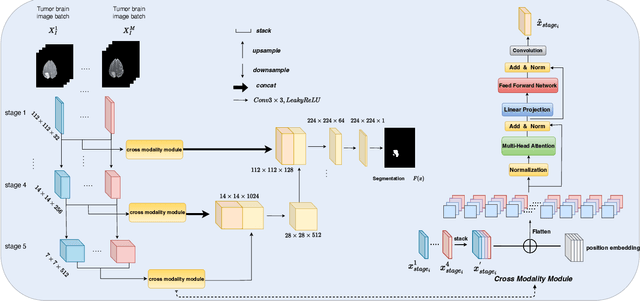


Abstract:Deep learning-based techniques have been widely utilized for brain tumor segmentation using both single and multi-modal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) images. Most current studies focus on centralized training due to the intrinsic challenge of data sharing across clinics. To mitigate privacy concerns, researchers have introduced Federated Learning (FL) methods to brain tumor segmentation tasks. However, currently such methods are focusing on single modal MRI, with limited study on multi-modal MRI. The challenges include complex structure, large-scale parameters, and overfitting issues of the FL based methods using multi-modal MRI. To address the above challenges, we propose a novel multi-modal FL framework for brain tumor segmentation (Fed-MUnet) that is suitable for FL training. We evaluate our approach with the BraTS2022 datasets, which are publicly available. The experimental results demonstrate that our framework achieves FL nature of distributed learning and privacy preserving. For the enhancing tumor, tumor core and whole tumor, the mean of five major metrics were 87.5%, 90.6% and 92.2%, respectively, which were higher than SOTA methods while preserving privacy. In terms of parameters count, quantity of floating-point operations (FLOPs) and inference, Fed-MUnet is Pareto optimal compared with the state-of-the-art segmentation backbone while achieves higher performance and tackles privacy issue. Our codes are open-sourced at https://github.com/Arnold-Jun/Fed-MUnet.
BotanicGarden: A high-quality and large-scale robot navigation dataset in challenging natural environments
Jun 25, 2023



Abstract:The rapid developments of mobile robotics and autonomous navigation over the years are largely empowered by public datasets for testing and upgrading, such as SLAM and localization tasks. Impressive demos and benchmark results have arisen, indicating the establishment of a mature technical framework. However, from the view point of real-world deployments, there are still critical defects of robustness in challenging environments, especially in large-scale, GNSS-denied, textural-monotonous, and unstructured scenarios. To meet the pressing validation demands in such scope, we build a novel challenging robot navigation dataset in a large botanic garden of more than 48000m2. Comprehensive sensors are employed, including high-res/rate stereo Gray&RGB cameras, rotational and forward 3D LiDARs, and low-cost and industrial-grade IMUs, all of which are well calibrated and accurately hardware-synchronized. An all-terrain wheeled robot is configured to mount the sensor suite and provide odometry data. A total of 32 long and short sequences of 2.3 million images are collected, covering scenes of thick woods, riversides, narrow paths, bridges, and grasslands that rarely appeared in previous resources. Excitedly, both highly-accurate ego-motions and 3D map ground truth are provided, along with fine-annotated vision semantics. Our goal is to contribute a high-quality dataset to advance robot navigation and sensor fusion research to a higher level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge