Feiyu Shen
Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
Jul 24, 2025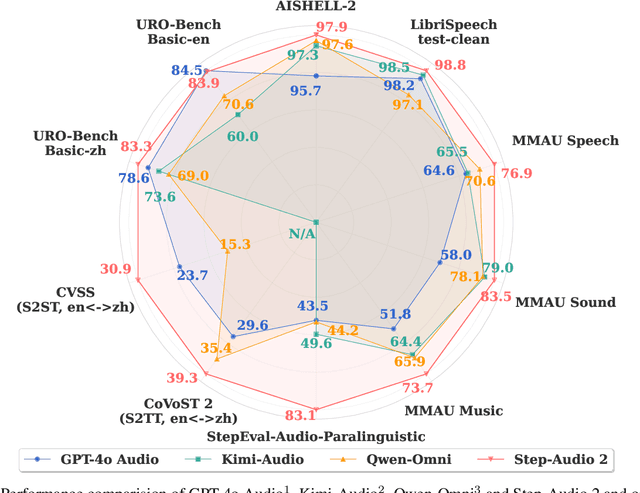

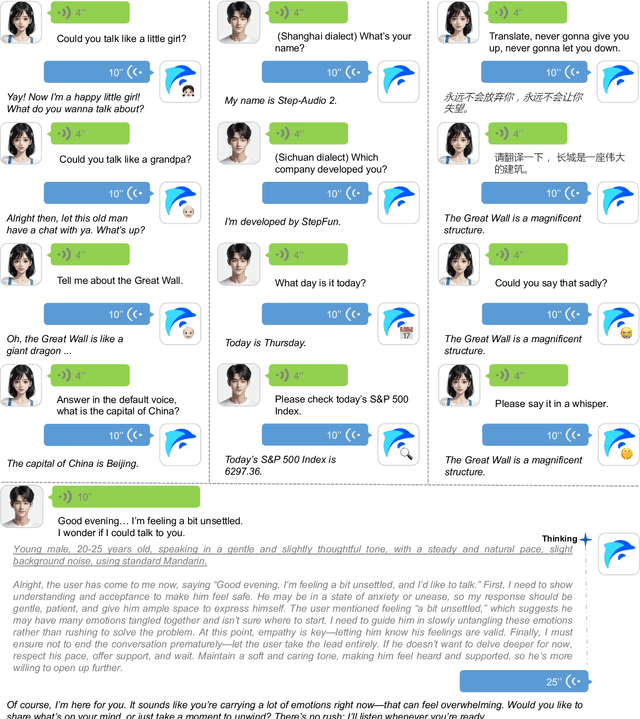

Abstract:This paper presents Step-Audio 2, an end-to-end multi-modal large language model designed for industry-strength audio understanding and speech conversation. By integrating a latent audio encoder and reasoning-centric reinforcement learning (RL), Step-Audio 2 achieves promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio understanding. To facilitate genuine end-to-end speech conversation, Step-Audio 2 incorporates the generation of discrete audio tokens into language modeling, significantly enhancing its responsiveness to paralinguistic information such as speaking styles and emotions. To effectively leverage the rich textual and acoustic knowledge in real-world data, Step-Audio 2 integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is able to call external tools such as web search to mitigate hallucination and audio search to switch timbres. Trained on millions of hours of speech and audio data, Step-Audio 2 delivers intelligence and expressiveness across diverse conversational scenarios. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various audio understanding and conversational benchmarks compared to other open-source and commercial solutions. Please visit https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio2 for more information.
Step-Audio: Unified Understanding and Generation in Intelligent Speech Interaction
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Real-time speech interaction, serving as a fundamental interface for human-machine collaboration, holds immense potential. However, current open-source models face limitations such as high costs in voice data collection, weakness in dynamic control, and limited intelligence. To address these challenges, this paper introduces Step-Audio, the first production-ready open-source solution. Key contributions include: 1) a 130B-parameter unified speech-text multi-modal model that achieves unified understanding and generation, with the Step-Audio-Chat version open-sourced; 2) a generative speech data engine that establishes an affordable voice cloning framework and produces the open-sourced lightweight Step-Audio-TTS-3B model through distillation; 3) an instruction-driven fine control system enabling dynamic adjustments across dialects, emotions, singing, and RAP; 4) an enhanced cognitive architecture augmented with tool calling and role-playing abilities to manage complex tasks effectively. Based on our new StepEval-Audio-360 evaluation benchmark, Step-Audio achieves state-of-the-art performance in human evaluations, especially in terms of instruction following. On open-source benchmarks like LLaMA Question, shows 9.3% average performance improvement, demonstrating our commitment to advancing the development of open-source multi-modal language technologies. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio.
On the Effectiveness of Acoustic BPE in Decoder-Only TTS
Jul 04, 2024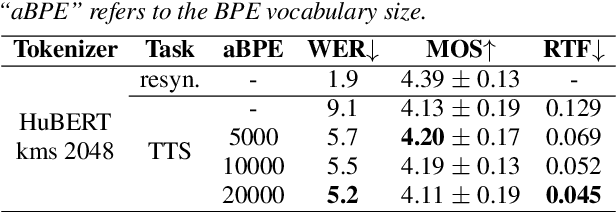
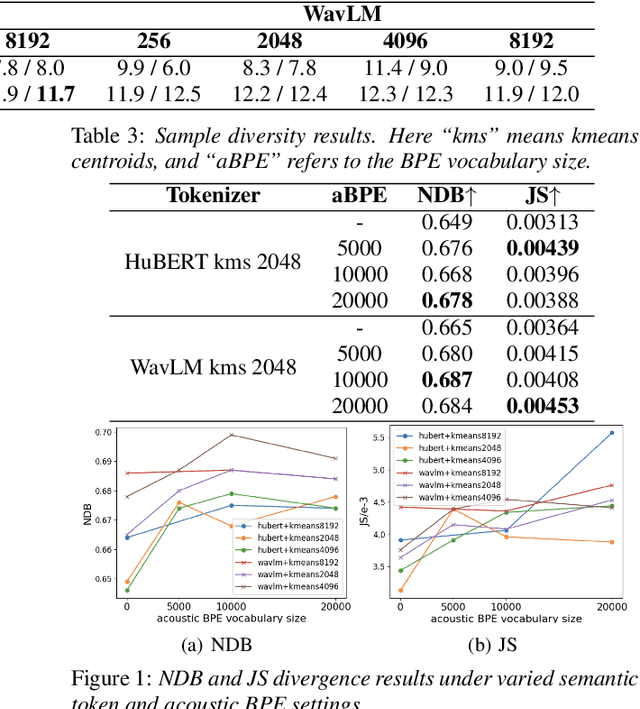
Abstract:Discretizing speech into tokens and generating them by a decoder-only model have been a promising direction for text-to-speech (TTS) and spoken language modeling (SLM). To shorten the sequence length of speech tokens, acoustic byte-pair encoding (BPE) has emerged in SLM that treats speech tokens from self-supervised semantic representations as characters to further compress the token sequence. But the gain in TTS has not been fully investigated, and the proper choice of acoustic BPE remains unclear. In this work, we conduct a comprehensive study on various settings of acoustic BPE to explore its effectiveness in decoder-only TTS models with semantic speech tokens. Experiments on LibriTTS verify that acoustic BPE uniformly increases the intelligibility and diversity of synthesized speech, while showing different features across BPE settings. Hence, acoustic BPE is a favorable tool for decoder-only TTS.
Acoustic BPE for Speech Generation with Discrete Tokens
Oct 23, 2023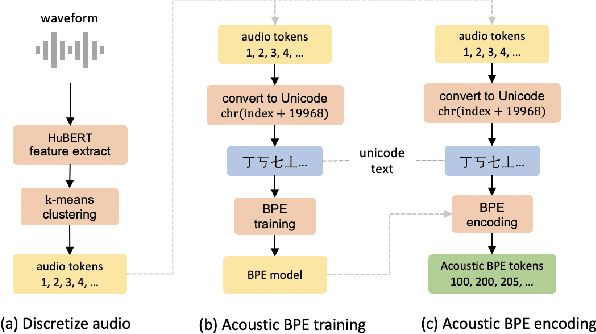
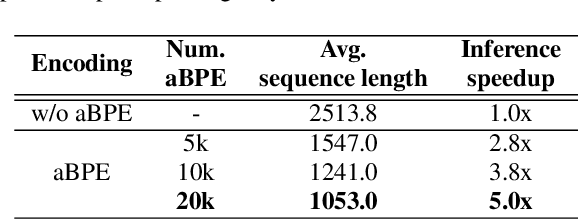
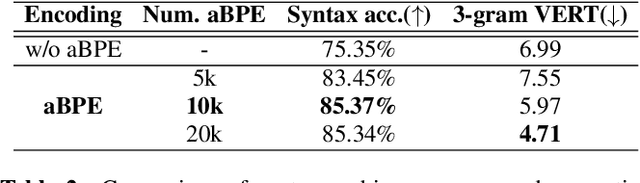
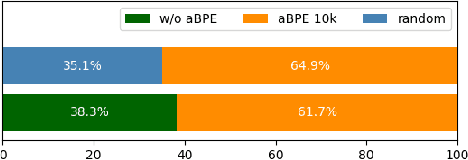
Abstract:Discrete audio tokens derived from self-supervised learning models have gained widespread usage in speech generation. However, current practice of directly utilizing audio tokens poses challenges for sequence modeling due to the length of the token sequence. Additionally, this approach places the burden on the model to establish correlations between tokens, further complicating the modeling process. To address this issue, we propose acoustic BPE which encodes frequent audio token patterns by utilizing byte-pair encoding. Acoustic BPE effectively reduces the sequence length and leverages the prior morphological information present in token sequence, which alleviates the modeling challenges of token correlation. Through comprehensive investigations on a speech language model trained with acoustic BPE, we confirm the notable advantages it offers, including faster inference and improved syntax capturing capabilities. In addition, we propose a novel rescore method to select the optimal synthetic speech among multiple candidates generated by rich-diversity TTS system. Experiments prove that rescore selection aligns closely with human preference, which highlights acoustic BPE's potential to other speech generation tasks.
Towards Universal Speech Discrete Tokens: A Case Study for ASR and TTS
Sep 14, 2023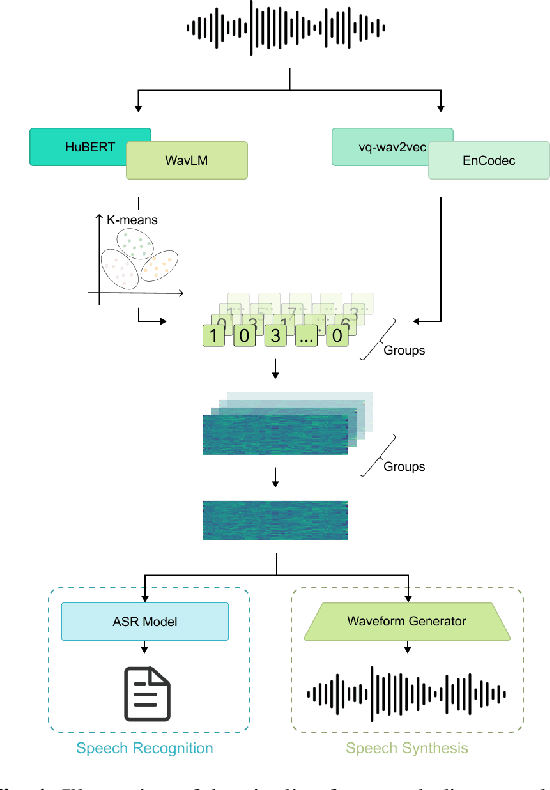
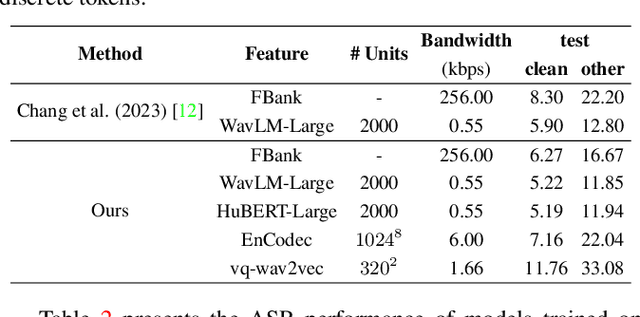
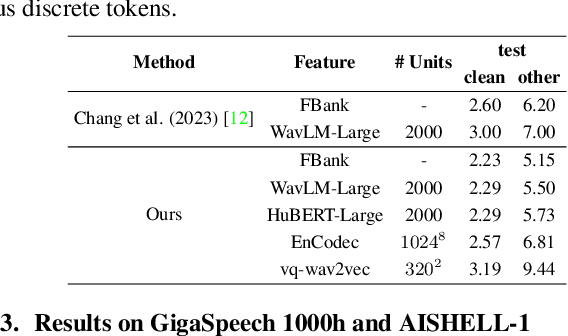
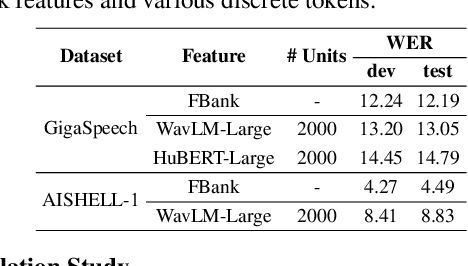
Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) proficiency in speech-related tasks has driven research into utilizing discrete tokens for speech tasks like recognition and translation, which offer lower storage requirements and great potential to employ natural language processing techniques. However, these studies, mainly single-task focused, faced challenges like overfitting and performance degradation in speech recognition tasks, often at the cost of sacrificing performance in multi-task scenarios. This study presents a comprehensive comparison and optimization of discrete tokens generated by various leading SSL models in speech recognition and synthesis tasks. We aim to explore the universality of speech discrete tokens across multiple speech tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that discrete tokens achieve comparable results against systems trained on FBank features in speech recognition tasks and outperform mel-spectrogram features in speech synthesis in subjective and objective metrics. These findings suggest that universal discrete tokens have enormous potential in various speech-related tasks. Our work is open-source and publicly available to facilitate research in this direction.
UniCATS: A Unified Context-Aware Text-to-Speech Framework with Contextual VQ-Diffusion and Vocoding
Jun 18, 2023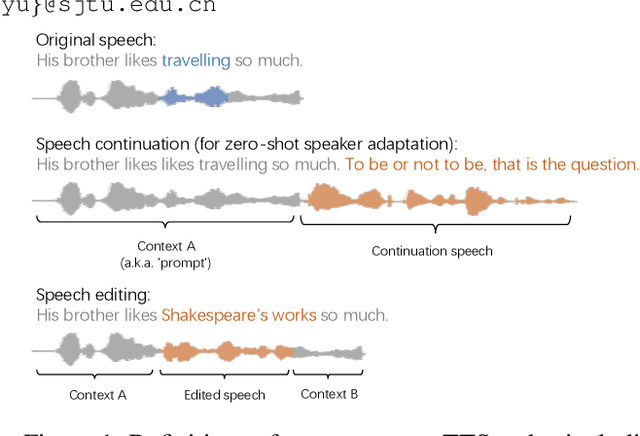

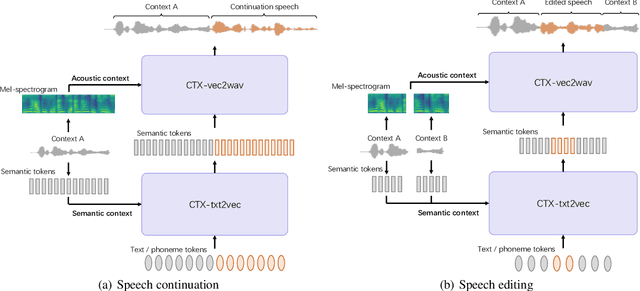
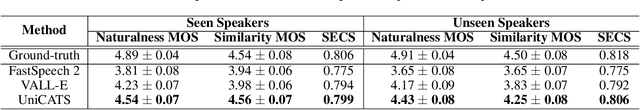
Abstract:The utilization of discrete speech tokens, divided into semantic tokens and acoustic tokens, has been proven superior to traditional acoustic feature mel-spectrograms in terms of naturalness and robustness for text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis. Recent popular models, such as VALL-E and SPEAR-TTS, allow zero-shot speaker adaptation through auto-regressive (AR) continuation of acoustic tokens extracted from a short speech prompt. However, these AR models are restricted to generate speech only in a left-to-right direction, making them unsuitable for speech editing where both preceding and following contexts are provided. Furthermore, these models rely on acoustic tokens, which have audio quality limitations imposed by the performance of audio codec models. In this study, we propose a unified context-aware TTS framework called UniCATS, which is capable of both speech continuation and editing. UniCATS comprises two components, an acoustic model CTX-txt2vec and a vocoder CTX-vec2wav. CTX-txt2vec employs contextual VQ-diffusion to predict semantic tokens from the input text, enabling it to incorporate the semantic context and maintain seamless concatenation with the surrounding context. Following that, CTX-vec2wav utilizes contextual vocoding to convert these semantic tokens into waveforms, taking into consideration the acoustic context. Our experimental results demonstrate that CTX-vec2wav outperforms HifiGAN and AudioLM in terms of speech resynthesis from semantic tokens. Moreover, we show that UniCATS achieves state-of-the-art performance in both speech continuation and editing.
Multi-Speaker Multi-Lingual VQTTS System for LIMMITS 2023 Challenge
Apr 25, 2023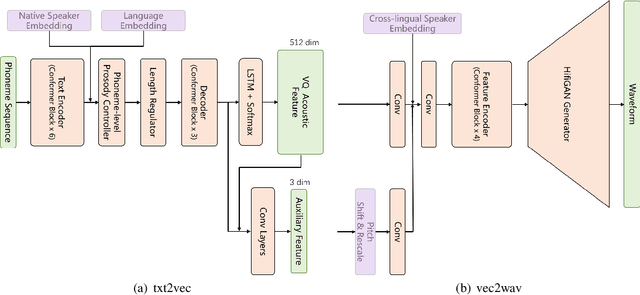

Abstract:In this paper, we describe the systems developed by the SJTU X-LANCE team for LIMMITS 2023 Challenge, and we mainly focus on the winning system on naturalness for track 1. The aim of this challenge is to build a multi-speaker multi-lingual text-to-speech (TTS) system for Marathi, Hindi and Telugu. Each of the languages has a male and a female speaker in the given dataset. In track 1, only 5 hours data from each speaker can be selected to train the TTS model. Our system is based on the recently proposed VQTTS that utilizes VQ acoustic feature rather than mel-spectrogram. We introduce additional speaker embeddings and language embeddings to VQTTS for controlling the speaker and language information. In the cross-lingual evaluations where we need to synthesize speech in a cross-lingual speaker's voice, we provide a native speaker's embedding to the acoustic model and the target speaker's embedding to the vocoder. In the subjective MOS listening test on naturalness, our system achieves 4.77 which ranks first.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge